Titanium is a remarkable metal known for its strength and light weight. It is often used in industries like aerospace and jewelry. One popular way to enhance titanium's properties is through anodization.
Anodization is an electrochemical process that changes the surface of the metal. This process creates a durable oxide layer that can be colored. The vibrant colors of anodized titanium are achieved without dyes, making it unique.
But does anodization wear off titanium over time? This is a common question among those who use or work with titanium. Understanding the durability of anodized titanium is crucial for its various applications.
In this article, we will explore the anodization process and its effects on titanium. We will also discuss other surface treatments and their benefits. Whether you're a jeweler or an engineer, this guide will provide valuable insights.
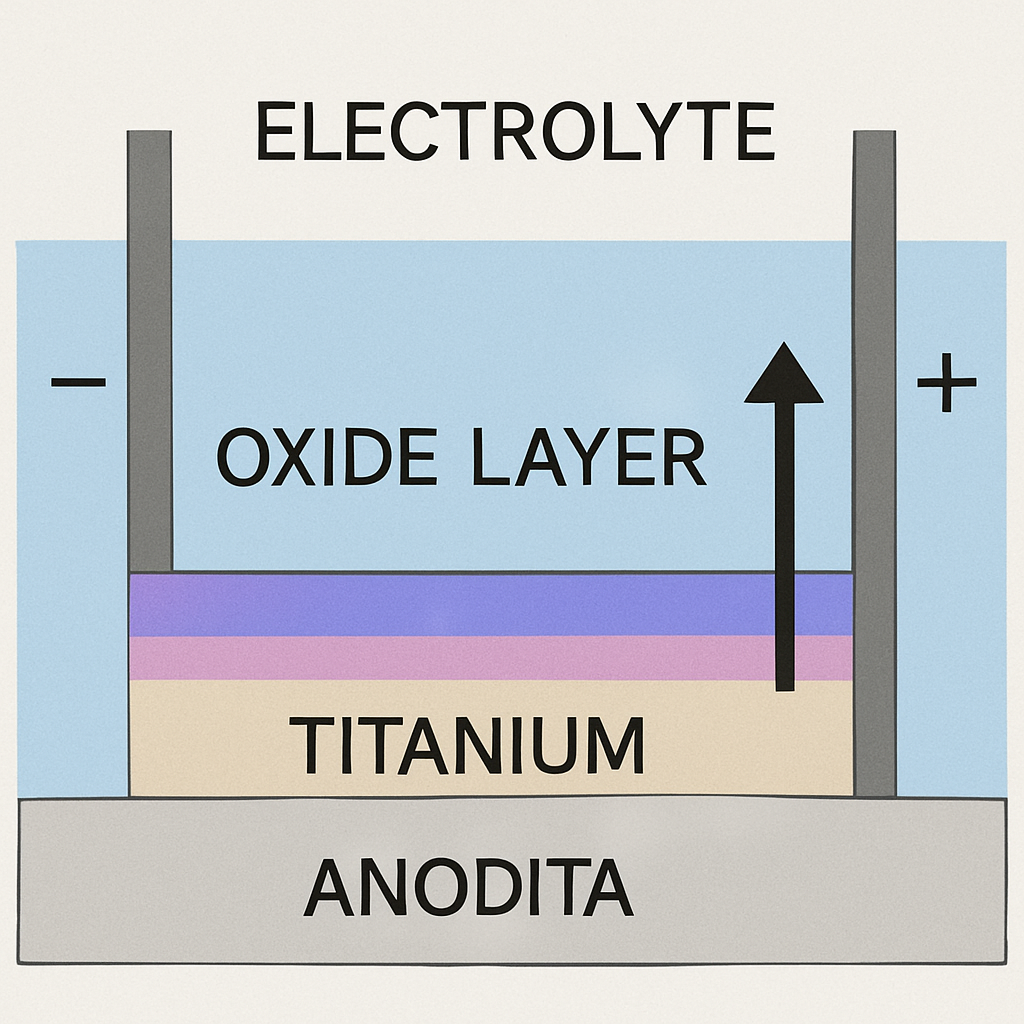
Titanium anodization is a fascinating process that enhances the metal's surface. This process involves an electrochemical technique used to form an oxide layer on titanium. Unlike coatings, this layer becomes an integral part of the metal itself.
Anodization provides more than just aesthetic benefits. The process enhances corrosion resistance, making the metal more durable. This is particularly important for applications in harsh environments like the ocean or space.
One of the most striking features of anodized titanium is the vibrant colors it can display. These colors result from light interference within the oxide layer, not from artificial dyes. The process allows for a wide range of colors by simply adjusting the voltage.
Here's what anodization offers:
Vibrant Colors: Achieved naturally, without dyes.
Improved Corrosion Resistance: Ideal for tough environments.
Integral Surface Layer: Not just a coating.
Anodized titanium is both functional and visually appealing, making it a popular choice across different industries.
The anodization process begins by cleaning the titanium surface thoroughly. This step removes dirt and grease, ensuring uniform oxide layer formation. A clean surface is crucial for a successful anodization.
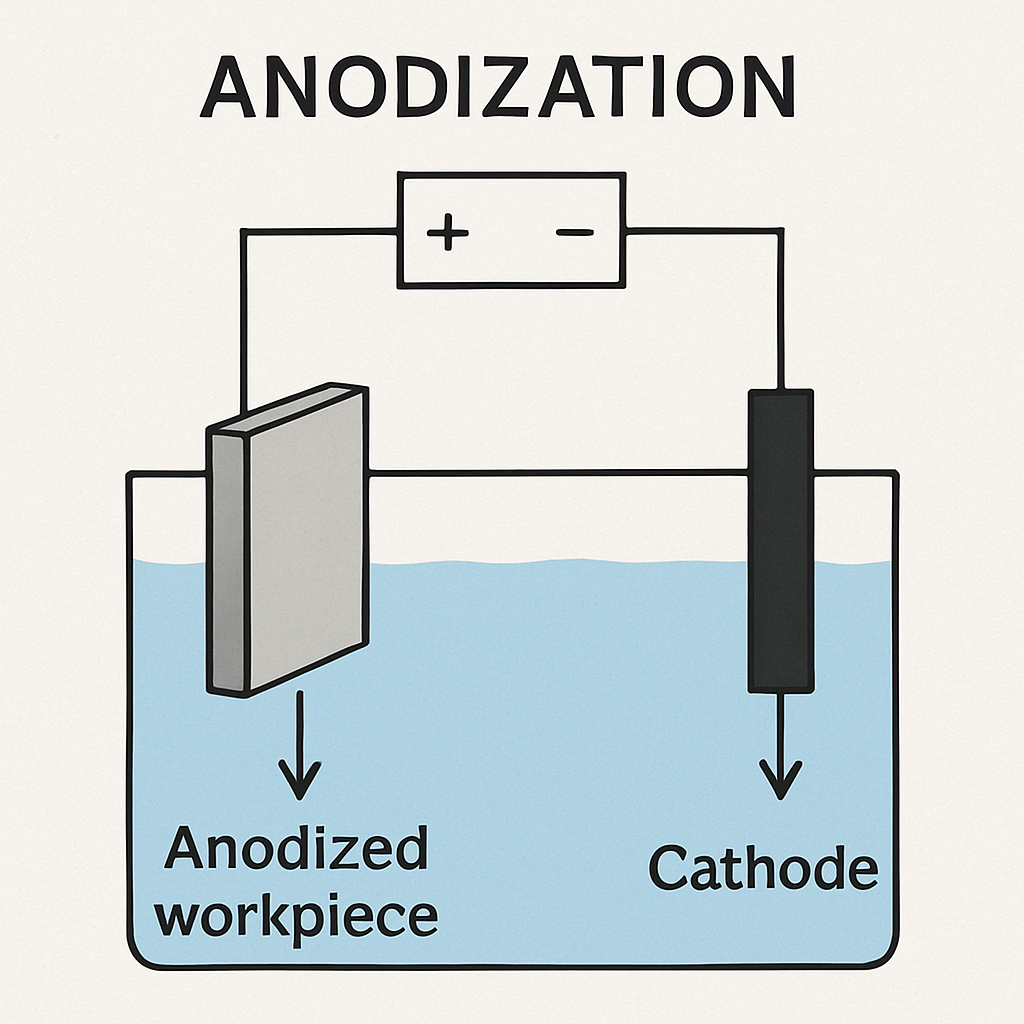
Once cleaned, the titanium serves as an anode in an electrolyte bath. This setup allows an electric current to pass through the solution, initiating the anodization process. The current triggers the formation of the oxide layer on the titanium's surface.
The thickness of the oxide layer is controlled by adjusting the voltage. Higher voltages result in thicker layers and different interference colors. The process is precise and requires careful monitoring of conditions.
Key steps in the anodization process include:
Cleaning: Ensures surface preparation.
Electrolyte Bath: The environment for the anodization.
Voltage Control: Dictates layer thickness and color.
This electrochemical method is efficient and allows for custom applications based on the specific needs of various industries.
Titanium offers numerous surface treatment options beyond anodization. These treatments enhance durability, appearance, and functionality. Understanding each is crucial for selecting the right one for your project.
Common surface treatments for titanium include:
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Applies a thin film for wear resistance.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Coats surfaces using chemical reactions.
Thermal Spraying: Deposits materials for added protection.
Each treatment offers unique benefits suited for specific applications. PVD and CVD, for example, are preferred for precision coatings in aerospace applications. Thermal spraying is ideal for large, robust parts requiring enhanced longevity.
Choosing the correct surface treatment depends on the intended use and environmental factors. Consider factors like cost, desired appearance, and performance requirements.
Selecting a surface treatment involves understanding your project's unique demands. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of titanium components across industries.
Anodized titanium is highly praised for its durability and vibrant colors. However, questions often arise about its longevity. Understanding its wear characteristics is vital.
The anodized layer forms a part of the metal, enhancing surface properties. Yet, like all materials, it is susceptible to wear. High-friction conditions can significantly accelerate its deterioration.
Factors influencing wear include:
Environmental Exposure: Harsh chemicals can weaken the anodized layer.
Physical Abrasion: Frequent contact with rough surfaces speeds up wear.
Thickness of Oxide Layer: Thicker layers offer better protection.
Maintaining anodized titanium involves avoiding abrasive environments. Proper care can greatly extend its useful life, keeping the surface both functional and appealing.
In most conditions, anodized titanium remains a durable choice. Its ability to resist rust and withstand impact makes it popular for many uses, like jewelry and airplane parts.
While anodized titanium can wear off under specific conditions, it generally remains robust and enduring. Awareness of factors affecting its durability can help maximize its lifespan.
Several factors influence the wear and longevity of anodized titanium. Understanding these elements helps optimize its durability. They vary from environmental conditions to mechanical stress.
One of the primary factors is environmental exposure. Anodized titanium is generally resistant to UV radiation, but extreme chemical exposure can lead to deterioration. Avoiding harsh chemicals is crucial for maintaining its integrity over time.
Mechanical stress and abrasion can also impact its lifespan. Contact with rough surfaces causes gradual wearing, especially if the oxide layer is thin. Therefore, applications with high friction should utilize thicker anodized layers.
Other aspects impacting anodization longevity include:
Temperature Fluctuations: Extreme temperatures can affect the oxide layer.
Cleaning Methods: Abrasive cleaning products can scratch the surface.
Usage Frequency: Higher usage increases the chance of wear.

Routine care and mindful use play crucial roles. Implementing preventative measures can help keep anodized titanium surfaces looking vibrant and functionally intact for years. Recognizing these factors will ensure informed decisions and enhanced durability.
Titanium surface treatments vary in process and results. Anodization is distinct due to its vibrant colors and eco-friendliness. While it does not alter the core properties of titanium, it enhances aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
In contrast, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) involves depositing a thin film on the surface. PVD offers exceptional durability but lacks the color variability of anodization. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) also forms a coating but with different chemical reactions, providing strong wear resistance.
Thermal spraying applies a layer to the surface, enhancing wear properties significantly. However, it lacks the environmental benefits of anodization. When comparing options, consider these features:
Anodization: Colorful, eco-friendly, moderate durability
PVD: Durable coating, limited colors
CVD: Strong chemical resistance
Thermal spraying: High wear resistance
Each treatment has unique strengths. Choosing depends on specific application needs, balancing aesthetics, and functional durability.
Anodized titanium is prized for its vibrant colors and durability. It finds broad applications across various industries due to its unique qualities. Its resistance to corrosion and aesthetic appeal make it a favorite choice.
In the jewelry sector, anodized titanium is popular for rings and necklaces. Its hypoallergenic nature adds to its appeal. This makes it suitable for all skin types, including sensitive ones.
Apart from jewelry, anodized titanium is also used in:
Medical devices for implants and surgical tools
Aerospace components due to its lightweight and strength
Consumer electronics for aesthetic and protective purposes
These diverse applications demonstrate how anodized titanium caters to both functional and decorative needs. Its unique properties make it essential in numerous fields.
Proper care enhances the lifespan of anodized titanium. Regular maintenance ensures the surface retains its vibrant colors and characteristics. It's essential to follow recommended guidelines.
Use mild soap and water for routine cleaning. Harsh chemicals can dull the colors. Avoid abrasive cleaning tools which might damage the oxide layer.
To preserve the finish, consider the following tips:
Store away from direct sunlight to prevent fading
Clean with a non-abrasive cloth to avoid scratches
Keep away from harsh chemicals, including chlorine
With these simple practices, anodized titanium stays beautiful and functional. Consistent care ensures it withstands the test of time.
Anodization can indeed be repaired or reapplied if needed. Over time, wear can affect the oxide layer, especially in high-friction environments. Re-anodizing restores both appearance and protective qualities.
Re-applying anodization involves cleaning and preparing the surface anew. It's crucial to ensure all residues and previous wear marks are removed. This process might be professional work, as it requires precision.
Consider these repair options:
Consulting a professional for best results
Following specific steps for DIY re-anodization
Utilizing appropriate equipment and materials
Repairing anodization ensures longevity and maintains the desired aesthetic and functional properties of titanium.
Many people have questions about anodized titanium due to its unique properties. Here, we'll address some common queries.
Can anodized titanium rust? No, titanium's natural oxide layer prevents rust. Anodization further enhances this protection.
How long does anodization last? The duration depends on factors like usage and environment. With care, it can last many years.
Is anodized titanium safe for the skin? Yes, it's hypoallergenic, making it ideal for jewelry and body modifications.
Common questions include:
Does anodization fade over time?
How should anodized titanium be cleaned?
Can anodized titanium be polished?
Understanding these aspects helps users make informed decisions regarding anodized titanium.
Choosing anodized titanium depends on your specific needs and conditions. If durability, vibrant colors, and resistance to corrosion are essential, it's an excellent choice.
However, consider the environment where the titanium will be used. High-friction or abrasive settings may reduce its lifespan. Overall, anodized titanium offers many benefits, making it suitable for various applications, from jewelry to industrial uses.