Anodized titanium is a marvel of modern material science. It combines beauty with strength, offering a spectrum of vibrant colors through the titanium anodizing process. But what exactly gives anodized titanium its unique hues?
The answer lies in the science of light and electrochemistry. Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances titanium's surface. This process creates a protective oxide layer, which is key to its color formation and can be referenced through a comprehensive titanium anodizing color chart.
Unlike painted surfaces, anodized titanium metal color variations are not from dyes. Instead, they result from light interference within the oxide layer. The thickness of this layer determines the color seen, making the titanium voltage color chart an essential reference tool.
Different voltages during anodizing produce various colors. This is where the titanium anodizing chart becomes essential. It guides engineers and designers in achieving precise color outcomes, whether they're working with traditional anodizing or exploring titanium heat color chart applications.
Anodized titanium is not just about aesthetics. It offers enhanced corrosion resistance and durability. This makes it ideal for industries like aerospace, medical, and jewelry, where both the titanium colour chart and performance characteristics matter.
Understanding the science behind anodized titanium colors can transform design and engineering. It allows for innovative applications and sustainable choices. Let's delve deeper into this fascinating topic and explore the complete anodizing colors chart.
Anodized titanium represents a fascinating blend of technology and nature. Its defining feature is the thin oxide layer formed during anodization. This layer not only transforms the metal's appearance but also enhances its physical properties, creating the distinctive titanium anodising colours we see.
At its core, anodizing is an electrochemical process. This process involves immersing titanium in an electrolyte bath and applying an electrical current. The electricity stimulates the formation of an oxide layer on the metal's surface, which can be precisely controlled using an anodizing chart.
This oxide layer offers significant benefits. It increases corrosion resistance, making the metal more durable. Additionally, it allows for unique color effects due to light diffraction, creating the beautiful spectrum shown in any comprehensive anodizing colors chart.
Let's break down the key features of anodized titanium:
Corrosion Resistance: A protective oxide layer shields the titanium.
Enhanced Durability: The process makes the metal harder and more resilient.
Spectacular Colors: Colors arise from light interacting with the oxide layer, as detailed in titanium color chart references.
The anodized titanium's versatility enables its use across various fields. These include aerospace, where strength and weight matter, and jewelry, where aesthetics are key. The interplay of science and design in anodized titanium creates endless possibilities for innovation and creativity in material applications.
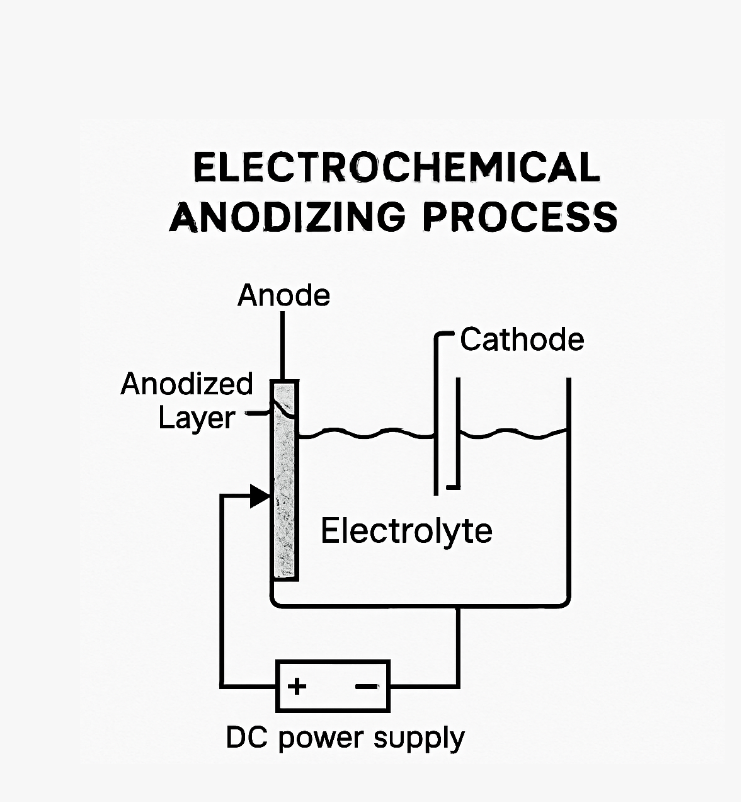
The anodizing process is a marvel of chemistry and engineering. It begins by carefully cleaning the titanium surface to remove any impurities. This preparation ensures a smooth and even oxide layer formation during the process, which is crucial for achieving consistent results shown in the titanium voltage color chart.
Once clean, the titanium is submerged in an electrolyte solution. Usually, this solution is a diluted acid, such as sulfuric or phosphoric acid. The choice of electrolyte can influence the anodizing outcome, affecting factors like color and surface finish as documented in various titanium anodizing color chart references.
An electrical current is then passed through the solution. This current is crucial as it facilitates the formation of the oxide layer. The titanium acts as the anode, while the cathode is typically made of an inert material. The voltage applied directly correlates to the final color, making the anodizing chart an indispensable tool.
As the current flows, oxygen ions interact with the titanium surface to form titanium dioxide. The thickness of this oxide layer grows proportionately with the voltage applied. It's this layer thickness that dictates the resultant colors, creating the beautiful spectrum seen in any titanium colour chart.
The steps involved in titanium anodizing are:
Surface Preparation: Clean and polish the titanium.
Submersion in Electrolyte: Immerse in an acidic solution.
Electrification: Pass a current to start oxidation.
Color Formation: Control voltage to achieve desired thickness using the titanium anodizing chart.
After anodizing, the titanium is rinsed and dried to seal the oxide layer. This final step ensures the colors remain vibrant and the surface is protected. Each stage is critical, impacting both the beauty and durability of anodized titanium. The science of anodizing balances precision and creativity, allowing for tailored applications across many industries.
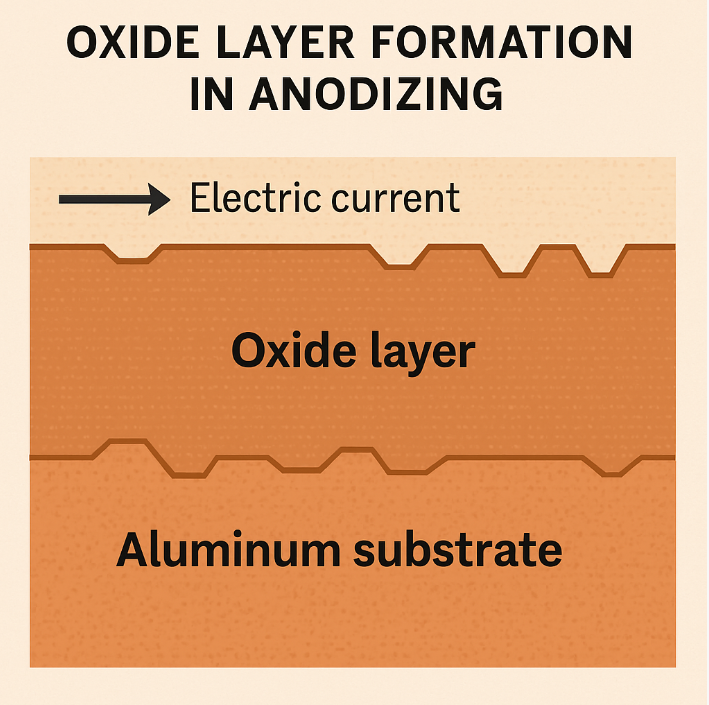
Anodized titanium's vibrant colors are the result of a fascinating interaction between light and oxide layers. Unlike dyes or pigments, these titanium anodising colours stem from the physical properties of the oxide layer itself.
When light strikes the anodized titanium surface, it penetrates the thin oxide layer. This layer splits incoming light into multiple beams, creating interference. The interference intensifies certain wavelengths, producing the visible colors documented in comprehensive anodizing colors chart references.
The color observed depends on the oxide layer's thickness. As this thickness increases, different colors emerge. Thin layers might produce blues or purples, while thicker layers can generate yellows or greens. This relationship is precisely mapped in the titanium voltage color chart.
Voltage plays a critical role in determining the oxide layer's thickness. By precisely adjusting the voltage during anodizing, manufacturers can achieve specific colors. This precision allows for diverse color palettes without altering titanium's inherent properties, making the titanium color chart an essential design tool.
The variables influencing anodized titanium metal color include:
Oxide Layer Thickness: Determines the interference pattern.
Voltage Levels: Controls layer growth to fine-tune colors as shown in the titanium anodizing color chart.
Angle of Light: Affects color perception and intensity.
Understanding this interplay between light and physics allows engineers and designers to exploit titanium's aesthetic potential. Anodized titanium surfaces can showcase striking and long-lasting visual effects. This color stability is ideal for applications requiring both beauty and durability. In essence, anodized titanium captures the essence of art and science in a single, stunning material.
Titanium anodizing color charts are indispensable tools for engineers and designers alike. They provide a visual guide to the relationship between voltage and the colors produced during anodizing. This precise control enables consistent results across different projects and serves as the foundation for any comprehensive anodizing chart.
Each color chart typically includes various categories of color, represented alongside corresponding voltages. This information is critical for achieving desired aesthetic outcomes and ensuring functionality in applications. The titanium voltage color chart becomes particularly valuable when precision is paramount.
A typical color progression in anodizing might include:
Low Voltage (10–20V): Golds and yellows
Medium Voltage (20–50V): Purples, blues, and greens
High Voltage (50–100V): Pink hues to vibrant greens
These voltage levels can be fine-tuned within each range to adjust the hue further. This granularity allows for precise customization, which is essential in applications where brand consistency is vital. The titanium colour chart provides this level of detail for professional applications.
Moreover, these charts often feature additional details such as:
Thickness of Oxide Layers: Correlating with different colors in the anodizing colors chart
Comparison with Other Metals: Highlighting titanium's unique properties
For construction managers and designers, these charts provide a reliable reference to ensure compliance with design specifications. By using them, it's possible to guide the selection process effectively, achieving both structural and aesthetic requirements. Thus, the mastery of these charts is an asset in any industry relying on the unique characteristics of anodized titanium.
The appearance of titanium can change significantly when subjected to different processes. Two common methods are anodizing and heat treatment. While they both produce color changes, the underlying mechanisms differ greatly, and understanding both the titanium anodizing color chart and titanium heat color chart is essential for proper material selection.
Anodized colors arise from an electrochemical process. This creates an oxide layer that causes light interference. Conversely, heat colors result from oxidation, which occurs at high temperatures without the use of electrical current. The titanium heat color chart shows a different spectrum of colors compared to traditional anodizing methods.
When comparing these two methods, consider the following:
Color Consistency: Anodizing offers precise control through the titanium voltage color chart, while heat colors can be inconsistent.
Durability: Anodized layers are typically more robust against wear and fade.
Process: Anodizing requires electrical setup; heat coloring involves high-temperature exposure as detailed in titanium heat color chart references.

For product designers and engineers, understanding these differences is crucial. It affects material selection for both aesthetics and performance. In situations where durability and color precision are critical, anodized titanium with its predictable anodizing colors chart is often preferred. However, for unique, less reproducible aesthetics, heat-induced colors can offer an intriguing alternative. With the right application, both processes can contribute to visually striking and functional designs.
Anodized titanium offers a blend of benefits across various disciplines. Engineers appreciate its enhanced surface durability, which effectively resists wear and corrosion. This durability is crucial in high-stress environments where material longevity is paramount, and the titanium metal color stability adds to its appeal.
In the realm of design, anodized titanium captivates with its vibrant, stable colors. These colors are achieved without dyes, ensuring they won't fade, even under extreme conditions. This stability allows designers to create products that maintain their visual appeal over time, referencing the comprehensive titanium colour chart for consistency.
For construction managers, the material's strength-to-weight ratio is invaluable. Anodized titanium is lightweight yet structurally sound, reducing load while maintaining integrity. It's ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential, and the titanium anodising colours provide aesthetic flexibility.
Key benefits include:
Corrosion Resistance: Prevents degradation from environmental exposure.
Biocompatibility: Safe for medical applications, including implants.
UV Resistance: Colors remain unaffected by sunlight, as documented in anodizing chart specifications.

Moreover, the anodizing process is eco-friendly, lacking harmful chemicals. This sustainability aspect is increasingly important in both design and construction. As industries move towards greener practices, anodized titanium stands out as a forward-thinking choice. Whether for its aesthetic allure or technical prowess, its versatility makes it a favored material in numerous applications.
Anodized titanium's unique properties make it a preferred choice in various industries. Its vibrant colors and durability appeal to sectors ranging from aerospace to consumer electronics. The material's adaptability enhances both function and form across these applications, with the titanium anodizing color chart serving as a crucial reference for color selection.
In the aerospace industry, anodized titanium is highly valued for its lightweight nature and resistance to extreme conditions. Components made from anodized titanium withstand high temperatures and pressure changes without compromising performance. This makes it a reliable material for aircraft parts, where both the anodizing colors chart and performance specifications must be met.
In the medical field, its biocompatibility is unmatched. The anodized surface not only resists corrosion but also integrates well with human tissues. This makes it ideal for implants and surgical instruments, where both strength and safety are critical, and the titanium metal color can be customized for specific applications.

Additionally, the jewelry industry benefits from the mesmerizing colors anodized titanium offers. Designers create eye-catching pieces that retain their luster and don't cause allergic reactions, utilizing the full spectrum of the titanium colour chart.
Moreover, in the realm of consumer electronics, anodized titanium is used to produce durable and aesthetically pleasing components. From smartphone casings to wearable devices, the material enhances both appearance and lifespan, with manufacturers often referencing the titanium voltage color chart for consistency.
Key Applications:
Aerospace components
Medical devices and implants
Jewelry
Consumer electronics
These diverse applications highlight anodized titanium's versatility. Its combination of aesthetic appeal and functional excellence continues to drive innovation. Industries leverage this material to push the boundaries of design and performance.

Selecting the correct anodizing parameters is crucial for achieving desired colors and performance in titanium components. Engineers and designers must understand how voltage, time, and electrolyte composition affect the final outcome. This knowledge ensures both aesthetic and functional goals are met, with the titanium anodizing color chart serving as the primary reference.
A controlled anodizing process allows for consistent and repeatable results. Designers often refer to titanium anodizing voltage charts to predict the colors corresponding to specific voltages. This aids in integrating the right hue into a product design without trial and error, making the anodizing chart an invaluable tool.
It's also vital to consider the end-use environment of anodized titanium products. For example, outdoor applications require UV stability and environmental resistance. This can influence the choice of oxide layer thickness and anodizing conditions, as detailed in comprehensive anodizing colors chart documentation.
Key considerations in the anodizing process:
Voltage: Determines color according to the titanium voltage color chart.
Time: Influences oxide layer thickness.
Electrolyte Composition: Affects color uniformity and final titanium anodising colours.
Achieving ideal anodized titanium color chart results thus involves balancing these factors, ensuring designs that are both visually striking and durable. This precision in design helps maintain the integrity of products across diverse industries, whether referencing traditional anodizing methods or exploring titanium heat color chart alternatives.
Anodized titanium is recognized for its sustainability in various industries. The anodizing process enhances the material's durability without introducing harmful chemicals, making it environmentally friendly. This characteristic is particularly important for eco-conscious industries that also value the aesthetic flexibility of the titanium colour chart.
The process of anodizing titanium is not only efficient but also involves minimal waste. Unlike other coating methods, it uses a simple electrochemical reaction that generates a protective oxide layer without significant by-products. This efficiency ensures that anodized titanium maintains its eco-friendly status while providing the full spectrum of titanium anodising colours.
Key sustainability benefits of anodized titanium include:
Non-toxic: Safe for diverse applications.
Recyclable: Easy to reuse.
Low waste: Minimal environmental impact during the anodizing process.
These attributes make anodized titanium an excellent choice for projects demanding both performance and environmental responsibility. The material's long lifespan and recyclability further enhance its credentials as a sustainable resource, while the comprehensive anodizing colors chart ensures design flexibility without environmental compromise.
Many people wonder about the durability of anodized titanium metal color variations. These hues are exceptionally stable, resisting fading over time. This stability is due to the nature of the oxide layer formed during anodizing, as documented in various titanium anodizing color chart references.
Another common question revolves around the variety of colors available. Anodizing allows a wide range of vibrant colors without affecting the metal's base properties. This makes it a favored choice for aesthetic applications, with the complete anodizing colors chart showing the full spectrum of possibilities.
Here are some additional FAQs:
Can anodizing be undone? Yes, with specific processes.
Is anodizing cost-effective? Generally, yes, especially when considering longevity and the precision offered by the titanium voltage color chart.
Does anodizing alter titanium's strength? No, it enhances surface properties without changing inherent strength.
How does the titanium heat color chart compare to anodizing? Heat treatment offers different colors but less control than anodizing.
Anodized titanium stands out as a versatile material for various industries. Its unique colors, achieved through precise anodizing techniques and guided by comprehensive titanium anodizing color charts, provide a blend of aesthetic appeal and functional advantages.
This technology not only enhances the visual impact of titanium but also reinforces its durability. As a result, it continues to be a popular choice in fields like engineering, product design, and construction, where both the anodizing chart precision and material performance are crucial.
Whether you're working with traditional titanium anodising colours, exploring titanium heat color chart alternatives, or referencing the comprehensive titanium colour chart for design consistency, anodized titanium offers unparalleled versatility. The titanium voltage color chart provides the precision needed for professional applications, while the complete anodizing colors chart ensures you have access to the full spectrum of possibilities.
Embracing anodized titanium means embracing innovation and sustainability. For professionals seeking to elevate their designs and enhance performance, anodized titanium offers the perfect combination of durability, beauty, and versatility. The comprehensive understanding of titanium metal color variations and their applications continues to drive innovation across industries.