If you've ever admired the vibrant colors of anodized titanium jewelry or wondered how industrial components achieve such a durable finish, you're in the right place. The anodized titanium process is a fascinating blend of science and art, transforming plain titanium into a spectrum of colors with enhanced properties. This process not only allows for a stunning aesthetic transformation but also enhances the material's functional capabilities, making it highly sought after across various industries. Let's dive into the details of this intriguing process, exploring what makes anodized titanium so unique and beneficial.
Titanium anodizing is a surface treatment that changes the properties of titanium. This process enhances its appearance and durability by applying an oxide layer. Unlike painting or plating, anodizing alters the surface itself, resulting in a finish that's integral to the titanium. This integration means that the anodized layer won't peel or flake off, maintaining its integrity even under stress or wear.
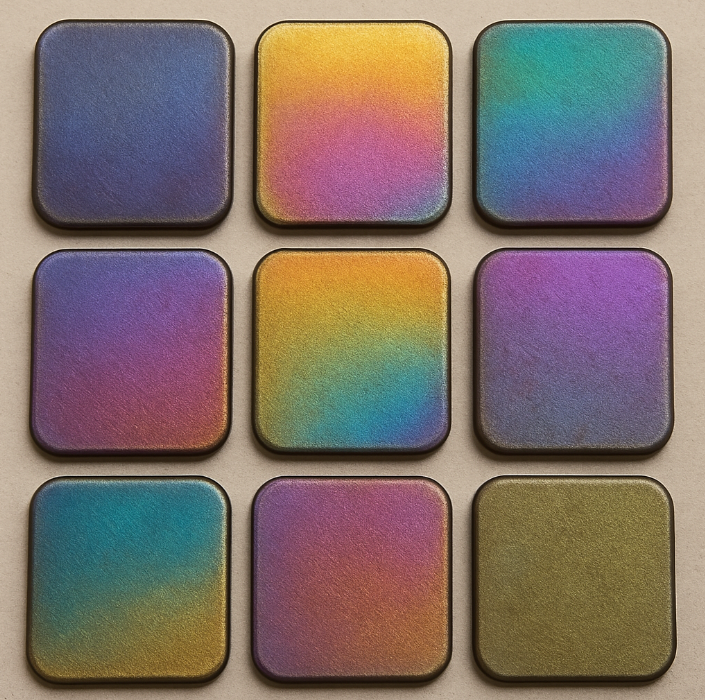

The anodizing process involves immersing titanium into an electrolytic solution and passing an electric current through it. This creates an oxide layer on the surface. The thickness of this layer determines the color of the anodized titanium. Essentially, the light refracts off the oxide layer, producing different colors without any dyes. This physical change in the surface is permanent, offering a long-lasting finish that can withstand various environmental challenges.
The process begins with a thorough cleaning of the titanium to remove impurities, ensuring a uniform oxide layer. Once the titanium is submerged in the electrolyte, the current causes oxygen ions to combine with the titanium surface, building up the oxide layer. By manipulating the voltage, technicians can finely tune the color outcomes, allowing for a wide range of vibrant hues.
The colors in anodized titanium are not due to pigments but are a result of light interference. As the oxide layer thickens, it creates different hues. The specific voltage applied during anodizing controls the thickness of the oxide layer, and thus, the resulting color. Lower voltages typically yield golds and yellows, while higher voltages produce blues and purples. This color variation is due to the phenomenon of optical interference, where different wavelengths of light are reflected and refracted by the oxide layer.
This interference effect is similar to what occurs in soap bubbles or oil slicks, where thin films create iridescent colors. The anodizing process can produce a spectrum of colors that are not only visually striking but also unique to titanium. This allows for customization in various applications, from jewelry to industrial components, where specific colors might be desired for branding or aesthetic purposes.
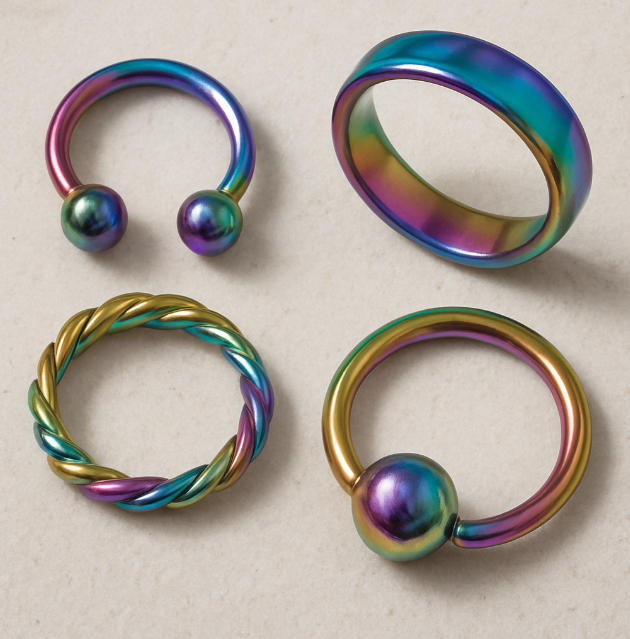
Anodizing titanium is popular not just for its aesthetic appeal but also for the practical benefits it offers. Here are some reasons why anodized titanium is highly valued across various industries:
Titanium is already known for its excellent resistance to corrosion. Anodizing further enhances this property by adding an additional protective layer. This makes anodized titanium ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as marine or chemical settings. The oxide layer acts as a barrier against corrosive elements, extending the lifespan of the material significantly in challenging conditions.
This enhanced corrosion resistance means that anodized titanium can be used in environments where other metals might fail. It is particularly useful in chemical processing plants, offshore structures, and any application where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern. The durability and reliability of anodized titanium in these settings make it a preferred choice for engineers and designers.
The anodizing process increases the surface hardness of titanium, making it more resistant to wear and tear. This is particularly beneficial for components exposed to friction or abrasive conditions, extending their lifespan significantly. The added hardness ensures that the anodized surface can withstand mechanical stresses, making it suitable for high-wear applications.
This increased hardness also contributes to the material's scratch resistance, maintaining the aesthetic appeal of anodized titanium products over time. This property is especially important in consumer products like jewelry or watches, where the visual quality is paramount. The enhanced durability of anodized titanium ensures that it remains looking new longer than untreated titanium.
The anodized surface provides an excellent base for additional coatings or adhesives, ensuring better bonding. This is useful in applications where further surface treatments are required. The rougher surface created by the anodizing process allows coatings to adhere more effectively, leading to more durable finishes.
This improved adhesion capability means that anodized titanium can be used as a substrate in complex layered systems, where multiple coatings are necessary for specific applications. This property is particularly beneficial in aerospace and automotive industries, where performance coatings are often applied to enhance functionality.
Anodized titanium is biocompatible, meaning it can safely interact with human tissue. This makes it a preferred choice for medical implants and devices, where both durability and compatibility are crucial. The oxide layer not only protects the titanium but also ensures that it does not react adversely with the body.
This biocompatibility is critical in medical applications, as it reduces the risk of rejection or allergic reactions. Anodized titanium is used in a wide range of medical devices, from joint replacements to dental implants, where its combination of strength, lightweight, and safety makes it an ideal material.
The unique properties of anodized titanium make it suitable for a wide range of applications. Let's explore some of the common uses:
The vibrant colors and corrosion resistance make anodized titanium a favorite in the fashion industry. From rings to necklaces, the metal's ability to maintain its shine without tarnishing makes it perfect for jewelry. Its hypoallergenic nature also adds to its appeal, making it suitable for those with sensitive skin.
Anodized titanium is also popular in eyewear and accessory manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and durability. Designers can experiment with various colors and finishes, creating unique, eye-catching pieces that stand out in the market. The ability to produce consistent, repeatable colors ensures that brands can maintain their aesthetic identity across different product lines.
In industries where weight, strength, and durability are critical, anodized titanium is a valuable material. It's used in various components, including fasteners and structural parts, due to its lightweight nature and enhanced properties. The added layer of oxide not only enhances durability but also reduces maintenance needs, making it cost-effective over time.
The aerospace industry values anodized titanium for its strength-to-weight ratio, which contributes to fuel efficiency and performance in aircraft. In the automotive industry, it's used in high-performance and luxury vehicles where both aesthetics and functionality are important. The material's ability to withstand extreme conditions makes it a reliable choice in these demanding fields.
Anodized titanium is extensively used in medical devices and implants. Its biocompatibility ensures that it does not cause adverse reactions in the body, making it ideal for surgical instruments and implants. The anodized layer also provides an additional layer of protection against corrosion, ensuring long-term performance inside the body.
The precision with which anodized titanium can be manufactured allows for the creation of intricate medical devices that meet stringent regulatory standards. This precision, combined with the material's safety profile, makes it indispensable in the healthcare industry, where reliability and patient safety are paramount.
Artists and sculptors appreciate anodized titanium for its ability to hold vibrant colors and withstand outdoor elements. It's often used in sculptures and art installations that require a long-lasting, durable finish. The material's unique interplay of color and light adds an element of dynamic beauty to artistic creations.
The versatility of anodized titanium allows artists to push the boundaries of traditional materials, experimenting with form and color in new and exciting ways. Its durability ensures that outdoor installations can withstand the test of time, maintaining their aesthetic impact regardless of environmental conditions.
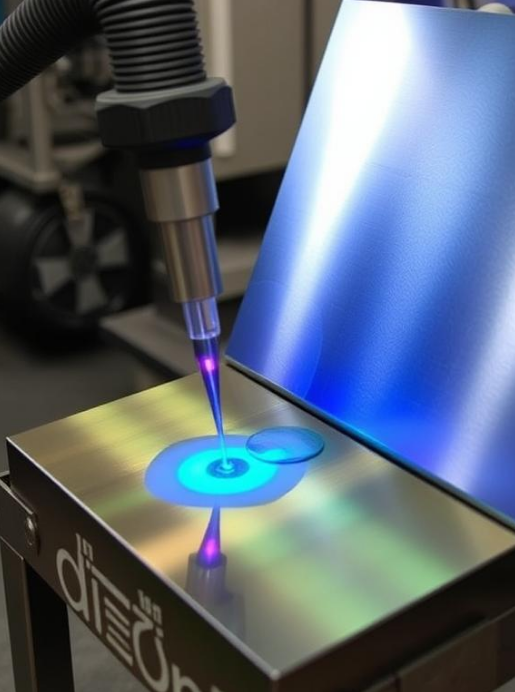

The titanium surface must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any grease, dirt, or contaminants. This ensures that the anodizing process is effective and the final finish is flawless. Proper cleaning is vital as any residual material can cause defects in the oxide layer, affecting both appearance and performance.
This initial step often involves a combination of chemical and mechanical cleaning methods. Specialized detergents and ultrasonic cleaners are used to ensure that the titanium is completely free of impurities, providing a pristine surface for the subsequent steps.
The titanium is then etched to create a rough surface, which enhances the adhesion of the oxide layer. This step is crucial for achieving a uniform anodized finish. The etching process typically involves using an acid solution that microscopically roughens the surface, increasing surface area and promoting better oxide layer formation.
Etching also helps to remove any remaining surface oxides that might interfere with the anodizing process. By creating an ideal surface for anodization, etching ensures that the final product meets the desired specifications for both appearance and performance.
The cleaned and etched titanium is submerged in an electrolyte bath. An electric current is passed through, forming the oxide layer. By adjusting the voltage, technicians control the thickness of the layer and thus the color. This stage requires precision and expertise, as slight variations in voltage can lead to significant differences in color.
The choice of electrolyte and the conditions of the bath (such as temperature and pH) are carefully controlled to achieve consistent results. The anodizing process can be tailored to produce specific colors, offering a wide palette for various applications. This customization is one of the key advantages of anodized titanium.
After anodizing, the titanium is rinsed to remove any residual chemicals. It may also be sealed to enhance corrosion resistance and lock in the colors. Sealing often involves immersing the anodized titanium in hot water or steam, which hydrates the oxide layer and closes the pores, providing additional protection.
This final step is essential for ensuring the longevity of the anodized finish. Proper sealing not only enhances corrosion resistance but also helps maintain the vibrant colors achieved during anodization, preserving the material's aesthetic appeal over time.
To preserve the beauty and functionality of anodized titanium, proper maintenance is essential. Here are some tips:
Use mild soap and water to clean anodized titanium, avoiding harsh chemicals that might damage the surface. A soft cloth can help remove dirt without scratching the finish. Regular cleaning prevents the buildup of grime, which can dull the appearance of the anodized surface over time.
Avoid using abrasive cleaning pads or brushes that might wear down the oxide layer. Gentle, consistent maintenance will ensure that anodized titanium retains its vibrant appearance and functional properties for years.
Steer clear of abrasive materials or cleaners that can wear down the oxide layer. Gentle cleaning preserves the anodized surface and maintains its vibrant colors. This precaution extends the life of anodized titanium products, ensuring they continue to look and perform as intended.
For particularly stubborn stains, specialized cleaners designed for anodized surfaces can be used. These products are formulated to clean effectively without damaging the oxide layer, providing an additional tool for maintaining your anodized titanium items.
Store anodized titanium items separately to prevent scratches. If possible, keep them in a soft pouch or lined box. Proper storage minimizes the risk of accidental damage and helps maintain the pristine condition of the anodized finish.
For larger items, such as artwork or industrial components, ensure that they are stored in environments that are free from corrosive substances or extreme conditions. Taking these precautions will ensure that anodized titanium continues to deliver both aesthetic and functional benefits.
Titanium anodizing is a remarkable process that combines scientific precision with artistic expression. By understanding the anodized titanium process, you can appreciate the craftsmanship behind each piece and its wide-ranging applications. Whether used in fashion, industry, or healthcare, anodized titanium continues to impress with its vibrant colors and durable finish.
As you explore the world of anodized titanium, remember the balance of art and science that brings this unique material to life. It's not just about aesthetics—it's about enhancing the intrinsic properties of titanium for better performance in a myriad of applications. Anodized titanium exemplifies how innovation in material science can lead to products that are both beautiful and functional, meeting the diverse needs of various industries.