Understanding Different Titanium Grades, Properties, and Applications
Titanium metal grades are standardized classifications that define the chemical composition and mechanical properties of titanium materials. The grading system, primarily governed by ASTM standards, provides a universal framework for specifying titanium materials across global industries. Each grade is assigned a unique designation that corresponds to specific purity levels, alloying elements, and performance characteristics.
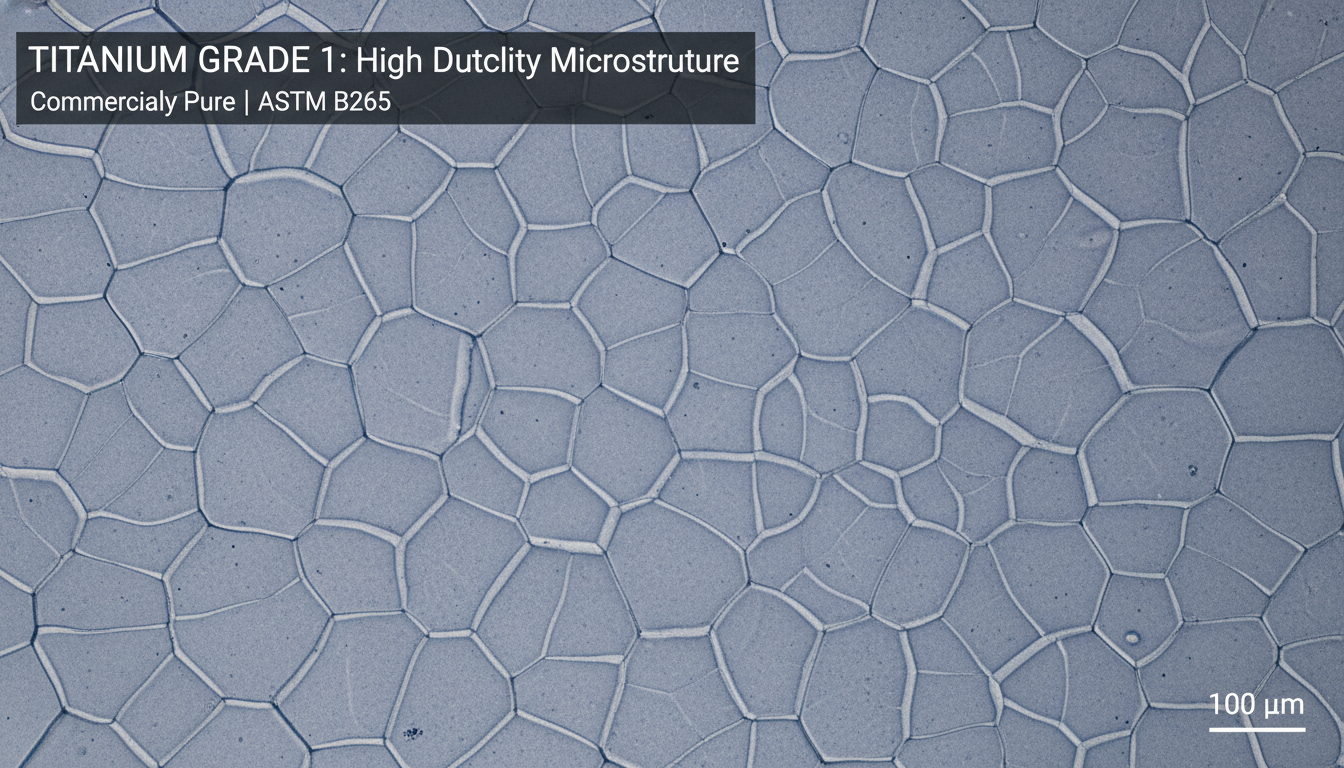
Commercially pure titanium encompasses Grades 1 through 4, characterized by high titanium content (98.9% to 99.5% pure) with minimal alloying elements.
Titanium alloys extend performance through strategic addition of elements like aluminum and vanadium. They are classified into alpha, alpha-beta, and beta alloys.
| Grade | Composition | Tensile Strength (Min) | Yield Strength (Min) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 99.5% Pure Ti | 240 MPa | 138 MPa | Highest ductility, excellent formability |
| Grade 2 | 99% Pure Ti | 345 MPa | 275 MPa | Best balance of strength and formability |
| Grade 4 | 99% Pure Ti | 550 MPa | 483 MPa | Highest strength CP grade |
| Grade 5 | Ti-6Al-4V | 895 MPa | 828 MPa | Highest strength, fatigue resistance |
| Grade 7 | Ti + Pd | 345 MPa | 275 MPa | Enhanced corrosion resistance |
| Grade 9 | Ti-3Al-2.5V | 620 MPa | 483 MPa | Good strength, excellent cold formability |
| Grade 23 | Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 828 MPa | 759 MPa | Superior biocompatibility for implants |
Aerospace Industry: Grade 5 dominates structural applications, while Grade 9 is used for hydraulic tubing and honeycomb structures.
Medical and Biomedical: Grade 23 (ELI) is the gold standard for orthopedic and dental implants due to its superior biocompatibility.
Chemical Processing: Grade 2 is used for general oxidizing acids, while Grade 7 and 12 are specified for aggressive reducing environments.
Marine and Offshore: Grade 2 is the primary material for seawater cooling systems and desalination plants due to its immunity to seawater corrosion.
The selection process should account for Mechanical Property Requirements, Corrosion Resistance Considerations, Manufacturing and Fabrication Requirements, and a thorough Cost-Benefit Analysis. Ensuring compliance with ASTM Standards (B348, B265, B338, B381) is essential for quality assurance and material traceability.
Need expert guidance on selecting the right titanium grade for your project?
Consult Our Technical Team