BWMS electrodes are fundamental for achieving and maintaining international maritime compliance, particularly through electro-chlorination.
Optimal electrode selection considers material (e.g., MMO, DSA), compatibility, salinity, and regulatory standards.
Advanced electrode design directly enhances treatment efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
Proactive maintenance and understanding degradation mechanisms are crucial for extending electrode lifespan and ensuring operational reliability.
Investing in high-quality electrodes delivers long-term economic benefits, including reduced TCO and sustained compliance.
Sustainable practices in electrode manufacturing and disposal are increasingly vital for environmental stewardship.
Understanding Electrodes in Ballast Water Management Systems
Maximizing BWMS Performance Through Advanced Electrode Design
Essential Maintenance and Replacement Protocols for BWMS Electrodes
Economic Considerations: A Cost-Benefit Analysis of BWMS Electrode Investment
Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable Practices for BWMS Electrodes
The maritime industry faces stringent regulatory demands for environmental protection, particularly concerning ballast water discharge. Ballast Water Management Systems (BWMS) are critical technologies designed to prevent the transfer of harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens.
At the core of many effective BWMS lies the electrode, a component pivotal for the electro-chlorination process. Optimal electrode performance is not merely an operational concern; it is a fundamental requirement for achieving and maintaining international maritime compliance.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of BWMS electrodes, offering insights for shipowners, engineers, and procurement managers. It aims to facilitate informed decision-making regarding selection, optimization, maintenance, and environmental considerations.
Ballast Water Management Systems (BWMS) are onboard installations designed to treat ballast water before discharge. Their primary objective is to neutralize or remove invasive species, aligning with global environmental regulations.
Among the various treatment methods, electro-chlorination stands out for its efficacy and widespread adoption. This process utilizes electrodes to generate active substances, primarily hypochlorite, which disinfect the ballast water.
Definition: Electro-chlorination is an electrochemical process where an electric current passes through seawater, causing the electrolysis of chloride ions (Cl-) to produce hypochlorite (ClO-), a potent disinfectant used in ballast water treatment.
The electrodes are the active surfaces where these electrochemical reactions occur. Their design, material composition, and operational integrity directly dictate the system's ability to meet the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) D-2 standards for ballast water discharge.
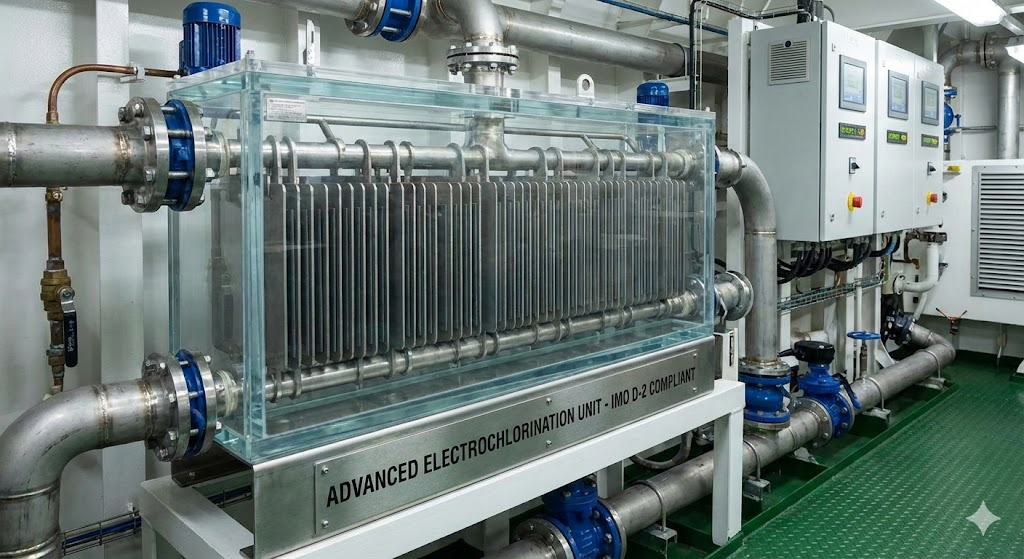

Compliance with IMO D-2 standards is non-negotiable for vessels operating internationally. These standards specify the maximum allowable concentration of viable organisms in discharged ballast water.
Ineffective electrodes can lead to insufficient disinfectant generation, resulting in non-compliant discharge and potential penalties. Therefore, selecting robust and efficient electrodes is a foundational decision for sustained operational legality.
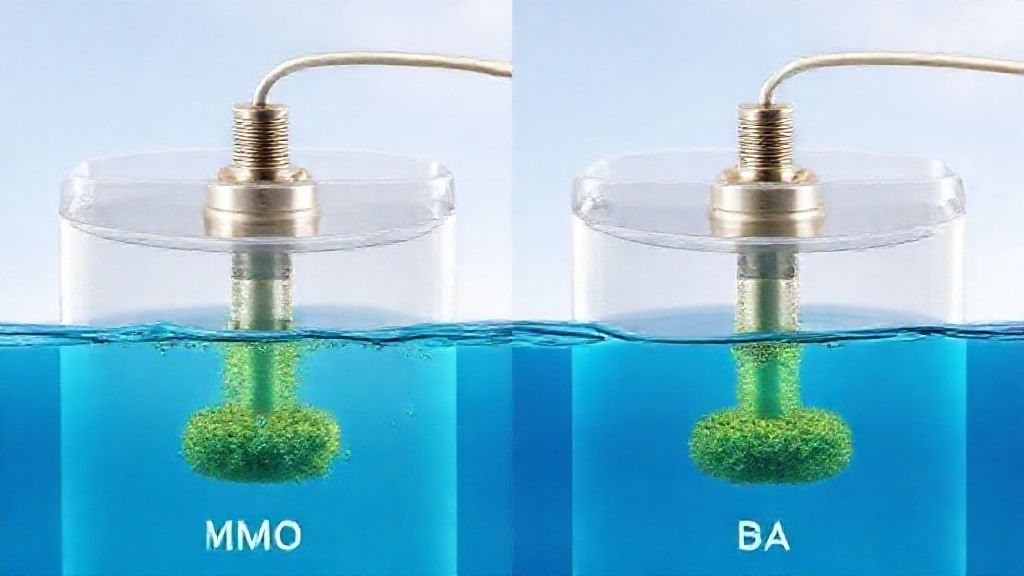
The performance and longevity of BWMS electrodes are heavily influenced by the materials used in their construction. Two prominent technologies dominate the market: Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) and Dimensionally Stable Anodes (DSA).
These electrode types offer distinct advantages and are chosen based on specific operational requirements and environmental conditions.
MMO electrodes feature a conductive substrate, typically titanium, coated with a layer of mixed metal oxides, often iridium and ruthenium. This coating provides excellent electrocatalytic properties for chlorine evolution.
MMO electrodes are known for their high efficiency, corrosion resistance, and relatively long service life in various saline conditions. They are a preferred choice for many electro-chlorination BWMS due to their stable performance.
DSA electrodes, a broader category that includes MMOs, are characterized by their dimensional stability and robust catalytic activity. They resist dissolution and mechanical degradation, maintaining their shape and performance over extended periods.
The specific composition of the metal oxide coating can be tailored to optimize performance for particular electrochemical reactions, making them highly versatile for demanding industrial applications like BWMS.

The selection between different electrode materials involves evaluating their specific operational characteristics. Factors such as efficiency, lifespan, and resistance to environmental stressors are paramount.
The following table provides a comparative overview of common electrode characteristics in BWMS:
| Feature | MMO Electrodes | DSA Electrodes (General) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Material | Titanium substrate with Mixed Metal Oxide coating (e.g., IrO2, RuO2) | Titanium substrate with various metal oxide coatings |
| Electrocatalytic Activity | High for chlorine evolution | High, customizable for specific reactions |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in saline environments | Excellent, dimensionally stable |
| Lifespan | Long, typically several years with proper maintenance | Long, dependent on coating and operating conditions |
| Energy Efficiency | High, lower overpotential | High, can be optimized |
The process of selecting electrodes for a BWMS requires careful consideration of several technical and operational factors. A well-informed decision ensures both system efficiency and regulatory compliance.
System Compatibility: Electrodes must integrate seamlessly with the existing BWMS infrastructure, including power supply, cell design, and control logic.
Water Salinity Range: The operational environment varies significantly, from freshwater to highly saline conditions. Electrodes must perform effectively across the expected salinity spectrum without compromising efficiency or durability.
Power Requirements: Efficient electrodes minimize energy consumption, reducing operational costs. Their design should align with the system's power capabilities and efficiency targets.
Regulatory Adherence: Chosen electrodes must facilitate the BWMS in consistently meeting IMO D-2 standards and any specific regional regulations.
Material Durability and Lifespan: Resistance to corrosion, erosion, and fouling is crucial for extending service life and reducing replacement frequencies.
For complex BWMS configurations or unique operational profiles, a customized electrode solution may offer superior performance. Specialists at China Titanium Factory can provide tailored advice and products designed for specific challenges, ensuring optimal integration and longevity. Consult with experts to analyze specific operational data and identify the most suitable electrode technology.
The sophistication of electrode design directly correlates with the overall efficiency and effectiveness of a BWMS. Innovative engineering advancements focus on enhancing performance, reducing energy consumption, and improving treatment outcomes.
Optimized Surface Area: Electrodes with a high active surface area facilitate greater contact with the ballast water, leading to more efficient electrochemical reactions and higher disinfectant production.
Hydrodynamic Design: The physical shape and configuration of electrodes can influence water flow dynamics within the electrolysis cell. Designs that minimize stagnant zones and promote uniform flow enhance contact efficiency and prevent localized fouling.
Advanced Coating Technology: Multi-layer or gradient coatings can improve electrocatalytic activity, reduce overpotential, and extend the lifespan of the electrode by providing enhanced resistance to wear and corrosion.
Self-Cleaning Mechanisms: Some advanced designs incorporate features that reduce fouling, such as reverse polarity capabilities or specialized surface textures, minimizing maintenance requirements.
A major container vessel operator experienced challenges with fluctuating treatment efficacy in varied water conditions. Their existing BWMS, equipped with standard electrodes, struggled to consistently meet D-2 standards when transiting between brackish and highly saline waters.
Upon upgrading to advanced titanium-based MMO electrodes featuring optimized coating formulations and a unique hydrodynamic profile, the vessel observed a significant improvement. Disinfectant generation became more stable across all salinity ranges, leading to a 15% reduction in overall energy consumption for the same treatment capacity.
This improvement was attributed to the electrodes' superior electrocatalytic properties and enhanced mass transfer within the electrolysis cell. The upgrade resulted in consistent compliance, reduced operational costs, and extended intervals between electrode cleaning cycles.

Electrode degradation is an inevitable process influenced by operational conditions and environmental factors. Understanding and actively mitigating these causes are crucial for extending the lifespan of BWMS electrodes and ensuring continuous system reliability.
Fouling: Accumulation of marine organisms, scale, or precipitates on the electrode surface reduces active area and hinders electrochemical reactions.
Corrosion: While highly resistant, even advanced materials can experience localized corrosion, especially in aggressive environments or under improper operating parameters.
Erosion/Wear: Mechanical abrasion from high water flow rates or abrasive particles can degrade the electrode coating over time.
Electrochemical Degradation: Prolonged operation at high current densities or in highly corrosive media can lead to the gradual dissolution or deactivation of the catalytic coating.
Proactive measures are essential. Regular monitoring of current density, voltage, and water quality parameters can help identify early signs of stress. Implementing proper filtration upstream of the electrolysis unit minimizes particulate fouling.
Periodic cleaning, either through chemical washes or mechanical methods, removes accumulated deposits without damaging the electrode surface. Adherence to manufacturer-recommended operating windows for temperature and salinity also plays a vital role. For insights into specialized materials, refer to resources like Titanium.com on Titanium in Electrolysis.
A bulk carrier operating primarily in coastal waters with high sediment loads frequently experienced premature fouling and degradation of its BWMS electrodes. The vessel was replacing electrodes every 18 months, significantly impacting operational costs and downtime.
An investigation revealed inadequate pre-filtration and inconsistent backwashing protocols. The solution involved upgrading the filtration system with finer mesh filters and implementing an automated, optimized backwash schedule for the electrodes, including periodic low-concentration acid cleaning.
This integrated approach, combined with the use of robust titanium electrodes from a reputable supplier, extended the electrode lifespan to over 36 months. This represented a 100% improvement, drastically reducing maintenance expenditures and ensuring uninterrupted compliance.
Consistent and rigorous maintenance is paramount for the sustained efficiency and regulatory compliance of any BWMS. Electrodes, as the active components, require specific protocols for inspection, cleaning, and timely replacement.
Regular visual inspections should be conducted during planned maintenance intervals. Technicians should look for signs of fouling, discoloration, pitting, or any physical damage to the electrode surface.
Monitoring key operational parameters, such as cell voltage, current, and disinfectant residual, provides early indicators of electrode performance degradation. Deviations from baseline values often signal a need for intervention.
Chemical Cleaning: Mild acid solutions (e.g., dilute hydrochloric acid or citric acid) are commonly used to dissolve scale and inorganic deposits. The concentration and contact time must be carefully controlled to avoid damage to the electrode coating.
Mechanical Cleaning: Soft brushes or high-pressure water jets can remove loose fouling. Abrasive methods should be avoided as they can damage the delicate catalytic coating.
Reverse Polarity: Some BWMS designs incorporate a reverse polarity function, which periodically switches the anode and cathode roles. This can help dislodge deposits and prevent scale buildup.
Establish a comprehensive preventative maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and operational experience. This schedule should include routine inspections, parameter checks, and scheduled cleaning intervals. Proactive maintenance significantly reduces the risk of sudden system failure and costly emergency repairs. For specific product maintenance guidelines, consult China Titanium Factory's service offerings.
Despite best maintenance efforts, electrodes have a finite lifespan. Replacement should occur before performance drops below acceptable levels or before visible signs of severe degradation. This prevents non-compliance and potential damage to other BWMS components.
Maintaining an inventory of spare electrodes, especially for vessels operating in remote areas, ensures quick turnaround during replacement. Partnering with a reliable supplier like China Titanium Factory guarantees access to high-quality, compatible replacement units.
Investing in BWMS electrodes extends beyond the initial purchase price. A comprehensive understanding of the total cost of ownership (TCO) is crucial for making economically sound decisions that balance upfront expenditure with long-term operational efficiency and compliance.
Initial Procurement Cost: The direct purchase price of the electrodes. High-quality electrodes may have a higher initial cost but often offer superior long-term value.
Energy Consumption: Electrodes with lower overpotential require less electrical energy to produce the same amount of disinfectant, leading to significant savings over their operational life.
Maintenance Expenditures: Costs associated with cleaning chemicals, labor for inspections and cleaning, and any specialized equipment. Durable electrodes may require less frequent, less intensive maintenance.
Replacement Costs: The cost of new electrodes and associated labor for their installation. Longer-lasting electrodes reduce the frequency of these expenditures.
Downtime Costs: The economic impact of a vessel being out of service due to electrode failure or extensive maintenance. Reliable electrodes minimize this risk.
Non-Compliance Penalties: The financial repercussions of failing to meet IMO D-2 standards, which can include fines, operational restrictions, and reputational damage.
While cheaper electrodes might offer immediate savings, their potentially shorter lifespan, higher energy consumption, and increased maintenance requirements can lead to a significantly higher TCO. Conversely, a higher initial investment in premium electrodes can yield substantial long-term benefits.
These benefits include reduced energy bills, fewer replacements, minimized downtime, and critically, consistent compliance with environmental regulations. Shipowners should prioritize electrodes that offer a balanced combination of efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness over their entire operational cycle. Contact China Titanium Factory for a detailed quote and analysis of electrode solutions.
Beyond their role in preventing invasive species, the manufacturing, operation, and disposal of BWMS electrodes also carry an environmental footprint. Embracing sustainable practices is increasingly important for the maritime industry's broader commitment to environmental stewardship.
The extraction of raw materials, particularly rare earth elements and noble metals used in catalytic coatings, has environmental implications. Manufacturing processes can also be energy-intensive and may involve the use of various chemicals.
During operation, the primary concern is the potential for discharge of disinfection by-products (DBPs). Modern BWMS are designed to minimize DBP formation, often through neutralization steps, but the choice of electrode material and operational parameters can influence this aspect.
At the end of their service life, electrodes contain valuable and sometimes hazardous materials. Proper disposal is crucial to prevent environmental contamination. This often involves specialized recycling processes to recover noble metals and safely manage other components.
Manufacturers and suppliers who offer take-back programs or clearly defined recycling pathways contribute significantly to sustainable maritime operations. For more information on responsible recycling, consult organizations like the IMO on Ship Recycling.
Research and development efforts are increasingly focused on identifying more abundant, less environmentally impactful materials for electrode coatings without compromising performance. The goal is to reduce reliance on critical raw materials and minimize the overall ecological footprint of BWMS technology.
The field of BWMS electrode technology is dynamic, driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced efficiency, extended longevity, and improved environmental performance. Emerging innovations promise to further refine ballast water treatment capabilities.
Nanomaterial Coatings: The application of nanotechnology can create highly porous and reactive electrode surfaces, significantly increasing active area and catalytic efficiency while potentially reducing the amount of precious metal required.
Novel Catalyst Development: Researchers are exploring new, more earth-abundant catalyst materials that can achieve similar or superior performance to traditional noble metal oxides, reducing cost and environmental impact.
Smart Electrodes: Integrating sensors and self-diagnostic capabilities into electrodes could enable real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing system reliability and reducing manual intervention.

Ongoing R&D prioritizes reducing energy consumption, improving fouling resistance, and extending the operational lifespan of electrodes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for optimizing electrode performance and predicting maintenance needs is also gaining traction.
These advancements aim to make BWMS even more robust, autonomous, and cost-effective, ensuring long-term sustainability for global shipping. Further research in electrochemistry can be found via academic resources like the Royal Society of Chemistry's journals.
The journey towards robust maritime compliance is inextricably linked to the performance and reliability of BWMS electrodes. Informed decision-making in their selection, maintenance, and eventual replacement is critical.
Prioritizing quality, efficiency, and longevity ensures not only adherence to international regulations but also contributes to the operational and economic sustainability of a vessel.
Shipowners and operators are encouraged to engage with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who demonstrate expertise in advanced electrode technologies. This partnership ensures access to products that are rigorously tested and specifically designed for the demanding marine environment.
For tailored advice on BWMS electrode solutions, including advanced materials and custom designs, consulting with specialists is recommended. Experts at China Titanium Factory are available to provide comprehensive support and product information.
The primary function of electrodes in a BWMS is to facilitate the electro-chlorination process. They generate active disinfectants, primarily hypochlorite, from seawater to neutralize harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens in ballast water, ensuring compliance with international discharge standards.
MMO (Mixed Metal Oxide) and DSA (Dimensionally Stable Anodes) are types of electrodes commonly used in BWMS. MMO electrodes typically feature a titanium substrate coated with mixed metal oxides like iridium and ruthenium, offering high efficiency and corrosion resistance. DSA is a broader category of stable, catalytic electrodes that includes MMOs, designed for durability and consistent performance in electrochemical processes.
Water salinity significantly affects electrode performance. Electro-chlorination relies on the presence of chloride ions in the water. In low-salinity or freshwater conditions, the efficiency of disinfectant generation can decrease, potentially requiring higher power input or specialized electrode designs to maintain treatment efficacy. High-quality electrodes are designed to perform across a wide range of salinities.
Common causes of electrode degradation include fouling (accumulation of marine growth, scale, or precipitates), corrosion, erosion from abrasive particles, and electrochemical degradation from prolonged operation at high current densities. These factors can reduce efficiency and shorten the electrode's lifespan.
Regular maintenance is crucial for BWMS electrodes to ensure continuous optimal performance, extend their operational lifespan, and maintain regulatory compliance. Proper cleaning prevents fouling and scale buildup, while routine inspections help identify and address degradation early, preventing costly failures and ensuring efficient ballast water treatment.