Introduction: Unveiling Titanium Bars for Modern Engineering
Titanium bars are a cornerstone of modern engineering. They offer an unparalleled blend of properties. These attributes make them indispensable in the most demanding industrial applications.
Understanding the diverse titanium bar forms, shapes, and dimensions is critical. This knowledge empowers engineers and material scientists to make informed decisions. Proper selection ensures optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for any project.
This comprehensive guide explores the landscape of titanium properties. It details available configurations and their specific engineering applications. Furthermore, it outlines key considerations for procurement and effective use of this advanced material
Understanding Titanium Bar Forms and Shapes
Titanium bars come in several standard physical configurations. Each distinct titanium bar shape serves unique structural or manufacturing purposes. Choosing the correct form is paramount for project success and efficient fabrication.
This section details the primary shapes in which titanium bar forms are supplied. It explains how each configuration addresses different design and fabrication needs, from simple shafts to complex structural elements.
Round Titanium Bars: Versatility in Cylindrical Forms
Round titanium bars are the most common and versatile form. Manufacturers produce them through processes like hot rolling and cold drawing. These cylindrical bars are highly adaptable for various applications.
They are often used where extensive machining titanium is required. Ideal uses include shafts, precision fasteners, and structural pins. Their inherent rotational symmetry simplifies turning, grinding, and other machining operations.
Square and Rectangular Titanium Bars: Structural Strength and Fabrication
Square titanium bars and rectangular titanium bars offer robust structural support. Often referred to as titanium flat stock, these shapes are crucial for frameworks, support structures, and mounting plates.
Their flat, parallel surfaces facilitate easy assembly and secure mounting of components. They are widely utilized in fabrication where strong, rigid, and stable sections are essential for demanding loads.
Hexagonal Titanium Bars: Precision Fasteners and Machined Parts
Hexagonal titanium bars are specifically engineered for precision applications. They are excellent for manufacturing high-performance titanium fasteners, nuts, and bolts. The distinct hexagonal shape provides secure wrenching surfaces, preventing slippage.
This hex stock ensures reliable, high-performance assemblies in critical environments. It is a preferred choice for applications demanding exact torque specifications and superior joint integrity.
Custom Titanium Bar Profiles: Tailored Solutions for Unique Needs
Many advanced projects demand specialized titanium shapes. Custom titanium profiles are engineered to address these complex, unique design requirements. Manufacturers can produce bespoke titanium bars through advanced extrusion or specialized rolling techniques.
This level of customization optimizes material usage, reduces machining waste, and ensures the perfect fit for highly specialized applications. Chinatitaniumfactory.com provides comprehensive services for such specialized and unique requests, turning complex designs into reality.
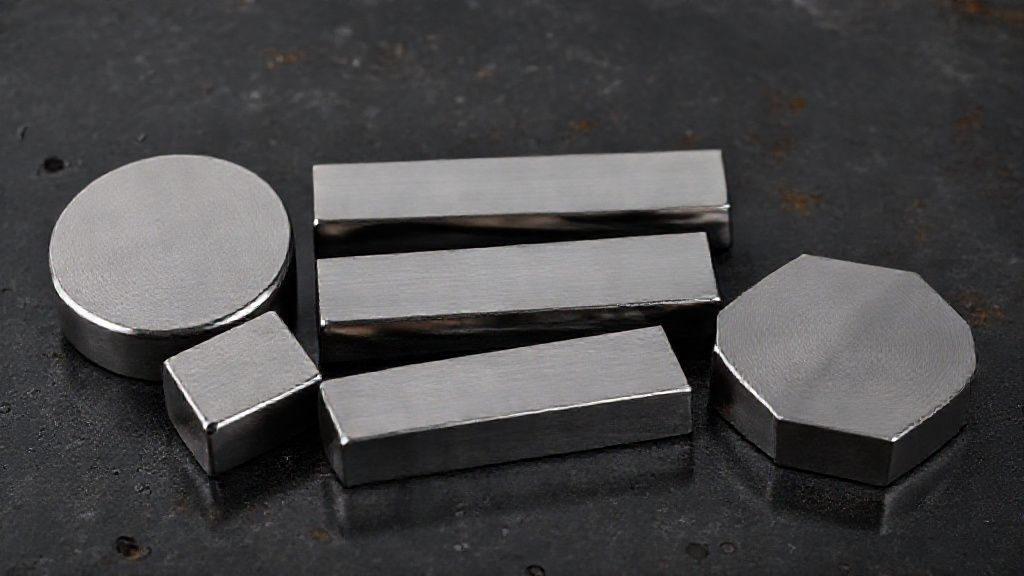

Standard and Custom Dimensions of Titanium Bars
Accurate titanium bar dimensions are absolutely vital for precise design and efficient procurement. This section covers typical sizes, standard lengths, and critical dimensional tolerances. It also guides users on specifying custom requirements for specialized projects.
Common Diameters, Widths, and Thicknesses
Standard measurements significantly simplify material sourcing and project planning. Titanium bar diameter, width, and thickness vary by form and are generally available as off-the-shelf stock sizes.
For instance, round bars commonly range from 0.125 inches to over 10 inches in diameter. Rectangular bars offer a broad spectrum of width and thickness combinations. Always consult specific supplier specifications for exact availability and lead times.
| Bar Form | Common Diameter/Width Range (inches) | Common Lengths (feet) |
|---|---|---|
| Round | 0.125 - 10.0+ | 8 - 14 |
| Square | 0.250 - 4.0 | 8 - 12 |
| Rectangular (Flat) | Width: 0.5 - 6.0; Thickness: 0.125 - 2.0 | 8 - 12 |
| Hexagonal | 0.250 - 2.0 (across flats) | 8 - 12 |
Understanding Dimensional Tolerances and Surface Finishes
Dimensional tolerances define the permissible variation in a bar's size. Precision is paramount in critical applications like aerospace or medical devices. For example, a tolerance of +/- 0.005 inches is common for highly machined parts.
Surface finish titanium also significantly impacts component performance and aesthetics. Options include descaled, ground, or polished. Each finish affects factors like component fit, fatigue life, and ultimately, the overall project cost.
ASTM Standards for Titanium Bar Dimensions and Quality
Industry standards ensure consistency, reliability, and interoperability. ASTM standards titanium are globally recognized benchmarks. ASTM B348 is the primary specification governing titanium and titanium alloy bars and billets.
These standards rigorously define chemical composition, mechanical properties, and permissible dimensional variations. For aerospace applications, AMS standards (Aerospace Material Specifications) provide even stricter guidelines. Compliance guarantees stringent quality control and absolute material integrity. More details can be found on the ASTM International website.
"ASTM B348 covers annealed titanium and titanium alloy bars and billets. It specifies requirements for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and permissible variations in dimensions, ensuring consistent quality across the industry."
Interactive Dimension Calculator & Visualizer
An advanced interactive tool can revolutionize material selection. Imagine a dynamic titanium dimension calculator where users input desired parameters like length, width, or diameter. The tool would instantly display available standard sizes, compatible grades, and even estimated weights.
Further, a sophisticated 3D titanium viewer could visualize custom bar configurator options in real-time. This innovative feature would significantly enhance the user experience, streamline the design process, and simplify specification for even the most complex components, reducing errors and saving valuable time.
Titanium Bar Grades and Their Unique Properties
The ultimate performance of titanium bars hinges critically on their specific grade. Each grade possesses a unique metallurgical composition. This composition directly dictates its mechanical properties, workability, and suitability for various operational environments.
Informed material selection is paramount for project success. This section delves into the most common and specialized titanium bar grades. We highlight their distinct characteristics to help engineers tackle diverse engineering challenges with confidence.

Commercially Pure Titanium Grades (CP Ti)
CP titanium refers to commercially pure grades, including Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3, and Grade 4. These grades are distinguished by increasing strength and decreasing ductility, with Grade 1 being the softest and Grade 4 the strongest.
Grade 2 titanium properties are widely utilized due to its excellent balance of strength and formability. All CP grades offer exceptional corrosion resistance and good weldability. This makes them ideal for chemical processing, marine, and architectural applications where corrosion is a primary concern.
Titanium Alloys: The Strength of Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V)
Grade 5 titanium, famously known as Ti-6Al-4V, is the most prevalent titanium alloy. It boasts a superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it incredibly efficient. This alpha-beta alloy is heat-treatable, offering excellent fatigue resistance and high-temperature performance.
Its robust titanium alloy properties make it the material of choice for demanding sectors. These include aerospace grade components like jet engine blades and airframe structures, as well as high-performance medical implants. Learn more about Grade 5 titanium products available from Chinatitaniumfactory.com and its specific applications.
Other Specialized Titanium Grades for Advanced Applications
Beyond CP grades and Grade 5, several other specialized titanium grades serve highly niche applications. Grade 7 titanium, alloyed with palladium, offers unparalleled crevice corrosion resistance, especially in reducing acid environments. Grade 12 titanium also provides superior crevice corrosion resistance, particularly effective in hot brine solutions and aggressive chemical processes.
Grade 23 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V ELI), an extra-low interstitial version of Grade 5, is specifically preferred for biomedical titanium implants due to its enhanced ductility and fracture toughness. These high performance alloys are engineered to meet very specific, critical requirements.
Comparative Analysis of Titanium Bar Properties
This titanium grade comparison table is an invaluable tool for engineers. It helps in selecting the precise material for any given project. The table below outlines key mechanical properties table and physical attributes for common grades. This data aids in making informed decisions, serving as a practical material selection guide.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (min psi) | Yield Strength (min psi) | Elongation (% min) | Density (g/cm³) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 35,000 | 20,000 | 24 | 4.51 | Most ductile, excellent formability, highest corrosion resistance |
| Grade 2 | 50,000 | 30,000 | 20 | Workhorse CP grade, good balance of strength & ductility | |
| Grade 5 | 130,000 | 120,000 | 10 | High strength-to-weight, aerospace and medical favorite | |
| Grade 7 | 50,000 | 30,000 | 20 | Superior crevice corrosion resistance with palladium | |
| Grade 23 | 120,000 | 110,000 | 10 | Biocompatible, enhanced fracture toughness for implants |
Diverse Applications of Titanium Bars Across Industries
Titanium bar applications are incredibly broad, spanning numerous high-tech industries globally. This remarkable versatility stems directly from titanium's unique and advantageous properties.
These properties include an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, unparalleled corrosion resistance, and inherent biocompatibility. This section showcases titanium's critical roles with compelling, real-world examples across key sectors.
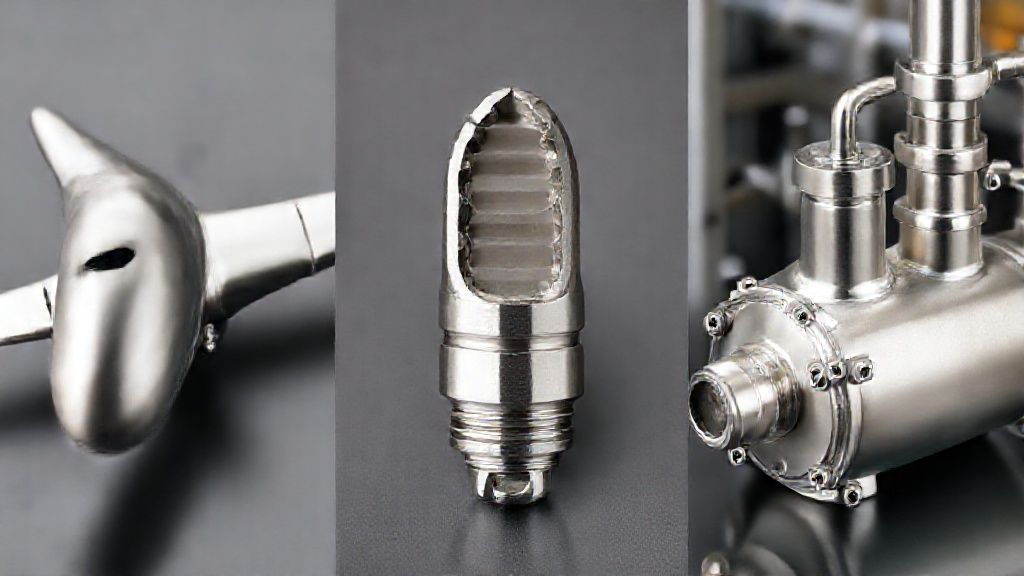

Aerospace and Defense: Lightweight Strength for Critical Components
Aerospace titanium bars are absolutely indispensable. They are extensively used in aircraft components such as landing gear, engine parts (e.g., fan blades, compressor disks), and structural airframe elements. Titanium also features prominently in advanced spacecraft structures and missile systems.
Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio directly contributes to reduced fuel consumption and increased payload capacity. High fatigue resistance and temperature stability are paramount for flight safety and mission success. These qualities are vital for both commercial aviation and demanding defense applications.
Medical and Biomedical: Biocompatibility and Durability for Implants
Titanium is the material of choice for critical medical implants titanium. Its unparalleled biocompatibility means the human body readily accepts it, causing no adverse reactions or immune responses. This makes it incredibly safe for long-term use within the body.
Applications include surgical implants like hip and knee replacements, spinal fusion devices, prosthetics, and dental implants. Titanium's superior corrosion resistance and non-toxicity are crucial for long-term patient health and implant durability. Biomedical titanium ensures both safety and lasting performance.
Industrial and Chemical Processing: Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Environments
Industrial titanium excels in the most aggressive environments. It offers exceptional resistance to harsh chemicals, high temperatures, and corrosive media, including chlorides and strong acids. This makes it the material of choice for chemical processing equipment.
Key uses include heat exchangers, pressure vessels, reactors, and piping systems in chemical plants. Titanium ensures operational longevity, reduces maintenance, and enhances safety in critical infrastructure. It is a reliable choice for environments where other metals quickly fail.
Marine and Offshore: Withstanding Harsh Saline Conditions
Marine titanium is perfectly suited for saltwater applications. It offers unparalleled saltwater corrosion resistance, preventing degradation from harsh oceanic conditions, including biofouling and erosion, far outperforming stainless steel.
Applications include shipbuilding components, critical parts for offshore platforms, and robust subsea equipment like ROV housings and heat exchangers. Desalination plants also heavily rely on titanium's resistance to chloride attack. It ensures long-term performance and reliability in challenging marine environments.
Case Studies and Customer Testimonials: Real-World Successes
Titanium case studies vividly highlight successful projects and innovative solutions. They demonstrate precisely how specific bar forms and grades deliver optimal performance and significant benefits. These application examples provide invaluable practical insights for prospective users.
For instance, a leading aerospace manufacturer achieved a 15% weight reduction on their new regional jet's landing gear by switching to Grade 5 titanium bars, leading to significant fuel savings and extended operational range. Another chemical plant improved its heat exchanger lifespan by 300% with Grade 2 titanium, drastically cutting maintenance costs. Chinatitaniumfactory.com's blog often features such detailed success stories and compelling customer testimonials, showcasing our commitment to excellence.
Manufacturing Processes and Customization Options for Titanium Bars
The journey from raw material to a finished titanium bar is intricate and demanding. It involves several highly specialized production processes. Understanding these meticulous steps is crucial for ensuring superior material quality and performance.
Furthermore, extensive custom titanium fabrication capabilities exist to meet highly specific project needs and exacting design specifications. This section explores how titanium bars are expertly made and precisely customized to client requirements.
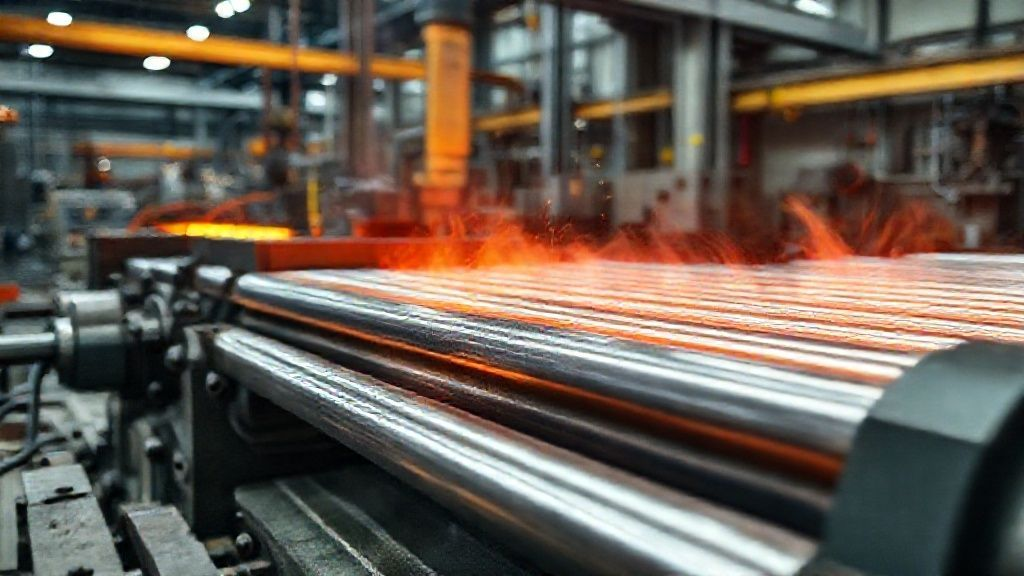

From Ingot to Bar: Key Manufacturing Steps
Titanium production typically begins with melting high-purity titanium sponge, often in a vacuum arc remelt (VAR) furnace, to form a solid ingot. This ingot then undergoes primary working processes to refine its internal structure.
Key steps include powerful titanium forging and precise hot rolling. These processes break down the coarse grain structure and shape the material closer to its final form. Subsequent cold drawing and controlled annealing achieve the exact final dimensions and desired mechanical properties. These meticulous steps ensure superior metallurgical integrity and consistent quality. Chinatitaniumfactory.com details its advanced manufacturing capabilities, ensuring premium quality titanium products.
Precision Machining and Fabrication of Titanium Bars: Best Practices
Machining titanium bars demands specific techniques and careful attention. Titanium's low thermal conductivity and high strength can lead to rapid tool wear and work hardening. Proper tool selection, rigid setups, and optimized cutting parameters are absolutely essential.
Using sharp, high-quality carbide tools, maintaining constant feed rates, and employing ample cooling/lubrication prevents overheating and ensures optimal results when cutting titanium or shaping titanium. Always consult industry guides for detailed titanium fabrication guide best practices to maximize efficiency and finish quality. An excellent resource is the Machine Design article on machining titanium.
Specifying Custom Orders: Lengths, Finishes, and Unique Profiles
For custom titanium orders, purchasers must clearly communicate all specifications to ensure precise order fulfillment. Always specify exact custom lengths, precise dimensional tolerances, and any specific straightness requirements.
Detail desired surface finish options, which might include peeled, centerless ground, or polished, each impacting the final application. For bespoke profiles, provide detailed technical drawings and 3D models. Contact Chinatitaniumfactory.com for expert assistance with custom titanium specifications, ensuring your unique requirements are met with precision.
Sustainability and Responsible Sourcing of Titanium Bars
The entire production and lifecycle of titanium bars involve significant environmental considerations. Titanium sustainability efforts are increasingly focused on minimizing ecological impact. This includes rigorous responsible sourcing of raw materials and highly efficient recycling processes.
Promoting ethical production practices is crucial for the industry. It actively supports the transition towards a circular economy for advanced industrial materials. This section addresses the vital environmental aspects of titanium production and consumption.
Environmental Impact of Titanium Production and Mitigation Efforts
Titanium manufacturing, particularly the Kroll process for sponge production, can be energy-intensive. It involves considerable energy consumption and the generation of certain by-products. However, significant efforts are underway to reduce the overall titanium environmental footprint.
Innovations in sustainable manufacturing aim to improve process efficiency and reduce energy demand. This includes developing cleaner extraction methods and utilizing renewable energy sources. Responsible producers prioritize stringent waste management and active carbon footprint reduction strategies.
Recycling and Lifecycle Management of Titanium
Titanium boasts excellent recyclability, making titanium recycling a cornerstone of its long-term sustainability. Recycling titanium scrap significantly reduces the demand for virgin resources and lowers the substantial energy needed for new primary production.
This aligns perfectly with circular economy principles, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible. Effective material lifecycle management promotes resource efficiency and minimizes environmental impact throughout the material's lifespan. Read more about titanium's crucial role in a circular economy from the International Titanium Association.
Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Bars
This section provides quick, authoritative answers to common queries about titanium bars. It covers key properties, diverse applications, manufacturing insights, and procurement considerations. This information offers clear and concise guidance for engineers and purchasers alike.
What are the main advantages of using titanium bars?
The primary titanium advantages are its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance benefits, especially against chlorides and seawater. Titanium is also highly biocompatible, non-toxic, and maintains excellent performance at high temperatures. These combined properties make it ideal for critical, high-stress applications across various industries.
How do I choose the right titanium grade for my project?
To choose titanium grade, carefully consider your specific project requirements. Evaluate the necessary mechanical properties (strength, ductility), environmental conditions (corrosion, temperature), and your budget. For example, Grade 2 is excellent for general corrosion resistance and formability, while Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is preferred for high-strength, lightweight needs in aerospace. Refer to the detailed grade comparison table earlier in this guide for a quick reference.
Are custom titanium bar shapes more expensive?
Yes, the custom titanium cost is generally higher than for standard stock shapes. This is due to several factors: specialized tooling costs for unique dies, longer setup times, and often larger MOQ titanium (Minimum Order Quantity) requirements. The increased manufacturing complexity and specialized engineering also contribute to the higher expense. However, custom profiles can lead to significant savings in subsequent machining and assembly.
What are the typical lead times for titanium bar orders?
Titanium lead times can vary significantly. Standard stock sizes, readily available in common grades and dimensions, might ship within days or a few weeks. However, custom order lead time can extend several weeks or even months. This depends heavily on the complexity of the profile, the specific grade required, and current production schedules. Always confirm precise order delivery estimates directly with your supplier at the time of inquiry.
Ready to Engineer with the Best Titanium?
Discover premium titanium bars tailored to your exact specifications. Partner with Chinatitaniumfactory.com for unparalleled quality, precision, and service in industrial materials. Let's build the future, together.
Get a Custom Quote Today !