The Unrivaled Role of Titanium Bars in Modern Industry
Titanium bars represent a cornerstone material in contemporary engineering. They are vital across numerous high-performance industrial sectors. Their unique blend of properties makes them indispensable for demanding applications.
This article explores the critical applications and benefits of titanium bars. It highlights their significance in precision and reliability-focused industries.
Understanding Titanium Bars: Core Properties and Advantages
Titanium bars are celebrated for an exceptional suite of material properties. These attributes position them as a superior choice. They outperform many traditional metals in critical environments.
Key advantages include a high strength-to-weight ratio. They also offer excellent corrosion resistance and remarkable biocompatibility. These factors are crucial for their widespread industrial adoption.

Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Unmatched Performance
Titanium alloys boast a strength similar to steel. However, they are approximately 45% lighter. This characteristic is vital for applications where weight reduction is critical. This includes aerospace and high-performance automotive sectors.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
A passive oxide layer forms on titanium's surface. This layer provides outstanding resistance to various corrosive media. It performs well in saltwater, chlorine, and many acids. This property is indispensable for marine and chemical processing.
Corrosion Resistance: The ability of a material to withstand deterioration caused by chemical reactions with its environment.
Biocompatibility for Medical Advancements
Titanium is non-toxic and compatible with human tissues. This makes it an ideal material for medical implants. It does not provoke adverse reactions within the body. This property is known as biocompatibility.
Biocompatibility: The ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific application.
High Temperature Performance
Certain titanium alloys maintain their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. This makes them suitable for jet engines and exhaust systems. They resist creep and oxidation effectively.
Overview of Common Titanium Grades
Different titanium grades offer specific property sets. These are tailored for diverse industrial needs. Understanding these grades is key to optimal material selection.
| Grade | Composition | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Commercially Pure (CP) | Highest ductility, excellent corrosion resistance, lowest strength. | Chemical processing, desalination, architectural. |
| Grade 2 | Commercially Pure (CP) | Good strength, excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability. | Aerospace, marine, medical, power generation. |
| Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | Ti-6%Al-4%V Alloy | High strength, good corrosion resistance, excellent fatigue properties. | Aerospace structures, medical implants, high-performance automotive. |
| Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) | Ti-6%Al-4%V Extra Low Interstitial Alloy | Improved ductility and fracture toughness over Grade 5, biocompatible. | Surgical implants, dental, orthopedic devices. |
Titanium in Flight: Aerospace Industry Applications
The aerospace industry heavily relies on titanium bars. Their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio is a key driver. This material contributes significantly to safety, performance, and fuel efficiency.
Titanium is found in critical aircraft components. These range from structural elements to complex engine parts. Its reliability under extreme conditions is paramount.
Aircraft Components & Structural Integrity
Titanium bars are machined into vital aircraft structures. These include airframes, wings, and fuselage sections. Their lightweight nature reduces overall aircraft mass. This directly translates to lower fuel consumption and increased payload capacity.
High stress resistance ensures durability. This is critical for the long operational life of an aircraft.
Engine Parts & High-Temperature Performance
Jet engines operate under immense temperatures and pressures. Titanium alloys, particularly Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), are ideal for these conditions. They are used in turbine blades, engine casings, and exhaust components.
Their ability to maintain strength at high temperatures prevents creep. This ensures engine integrity and safety. For specialized titanium fabrication, precision is essential.
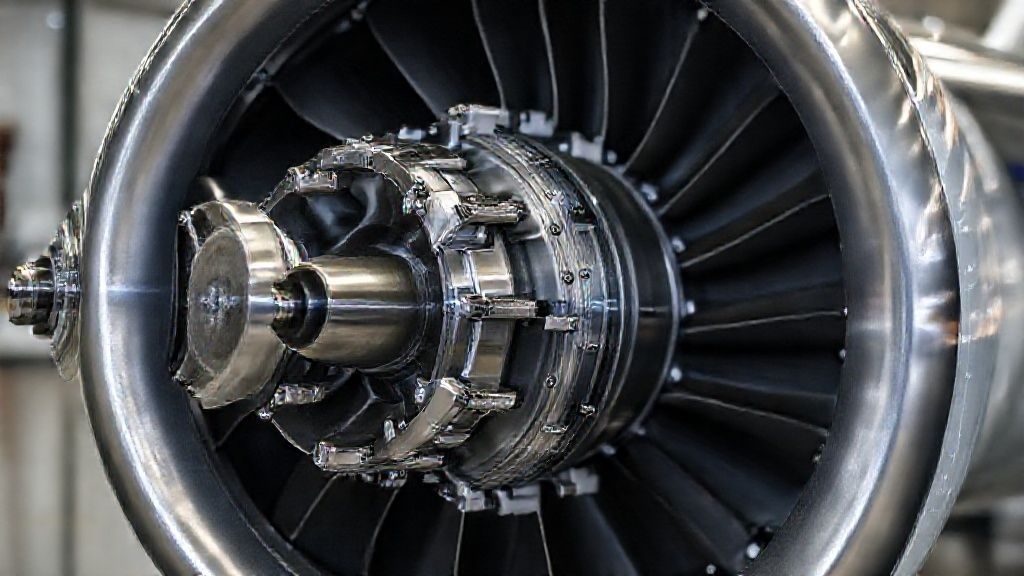

Fasteners & Landing Gear: Ensuring Reliability
Titanium is used in critical aerospace fasteners. These parts require high strength and fatigue resistance. Landing gear components also utilize titanium extensively. This ensures the structural reliability of the aircraft during takeoff and landing.
The material's corrosion resistance prevents degradation. This is crucial for components exposed to varying atmospheric conditions. SAE International standards often specify titanium for these high-stress applications.
Healing & Innovation: Medical and Biomedical Applications
Titanium's role in medicine is unparalleled. Its exceptional biocompatibility and mechanical strength are key. These properties make it ideal for medical devices and implants.
The material integrates well with the human body. This minimizes rejection and promotes long-term success. It is a cornerstone of modern healthcare innovation.
Surgical Implants & Prosthetics: A Body-Friendly Material
Titanium bars are the material of choice for orthopedic implants. This includes joint replacements, such as hips and knees. They are also used for spinal implants and bone plates.
The material promotes osseointegration. This is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing implant. This ensures long-term stability.
Dental Implants & Orthopedic Devices
In dentistry, titanium forms the foundation of dental implants. These implants fuse with the jawbone. They provide a stable base for crowns and bridges. Patient safety and implant longevity are significantly enhanced.
Beyond implants, titanium is used in bone screws and fixation devices. Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) is often preferred for its improved ductility. This is vital for complex medical components.
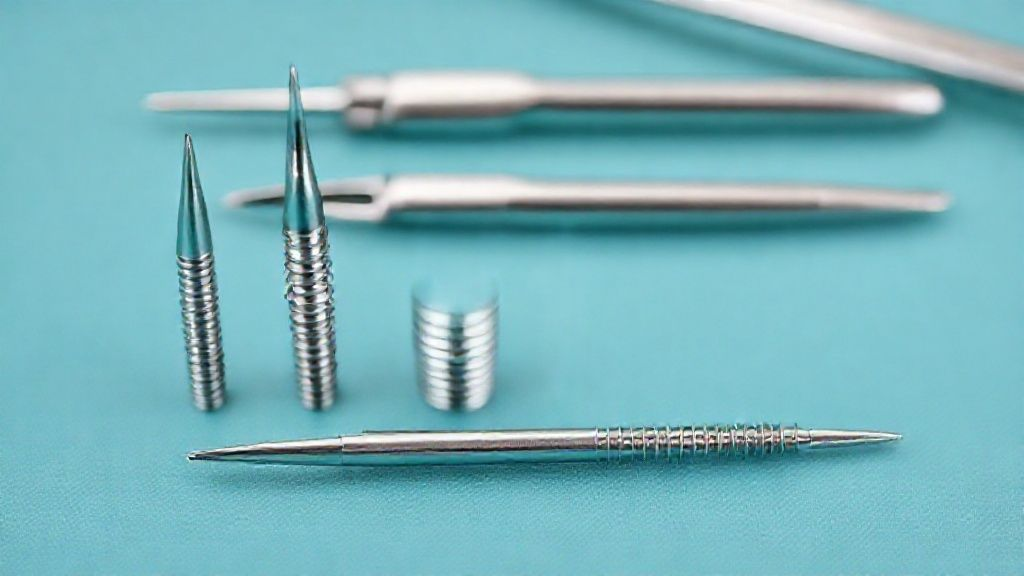
Medical Instruments: Precision and Sterility
Surgical instruments require exceptional durability and corrosion resistance. Titanium bars are machined into scalpels, forceps, and retractors. They withstand repeated sterilization processes without degradation.
Their lightweight nature also reduces surgeon fatigue. This contributes to greater precision during delicate procedures. The material's non-magnetic properties are also beneficial for MRI compatibility.
Resilience in Harsh Environments: Chemical Processing & Marine Applications
Titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance makes it indispensable. It thrives in challenging industrial settings. These include aggressive chemical plants and corrosive marine environments.
Its durability ensures long operational life. This minimizes maintenance and replacement costs. It is a reliable material for critical infrastructure.
Corrosion Resistance in Chemical Plants
Chemical processing often involves highly aggressive substances. Titanium withstands exposure to acids, chlorides, and other harsh chemicals. It is used in reactors, heat exchangers, and industrial piping systems.
This prevents material degradation and contamination. It ensures the safety and efficiency of chemical processes. ASTM standards define the quality for these critical applications.
Marine Engineering & Offshore Structures
Saltwater is highly corrosive to many metals. Titanium's resistance to saltwater corrosion is superior. This makes it ideal for marine engineering applications.
It is used in shipbuilding, offshore oil and gas platforms, and subsea equipment. Components like risers, pumps, and valves benefit from titanium's longevity. This extends the lifespan of marine structures significantly.
Desalination Plants: A Solution for Water Scarcity
Desalination technologies convert seawater into fresh water. These processes involve highly corrosive brine environments. Titanium's durability in these conditions is unmatched.
It is critical for heat exchangers and piping in reverse osmosis plants. Titanium ensures efficient and reliable water treatment. This contributes to global efforts to combat water scarcity.
Speed & Strength: Automotive and Motorsports Applications
In high-end automotive and motorsports, performance is paramount. Titanium bars contribute to enhanced vehicle performance. They enable lightweighting and increased durability.
This material helps engineers push the boundaries of speed and efficiency. It is favored in competitive racing environments.
High-Performance Engine Components
Titanium is increasingly used in high-performance engines. Connecting rods, valves, and crankshafts are examples. Its low density reduces reciprocating mass. This allows for higher engine RPMs and improved power output.
The material's strength ensures reliability under extreme loads. It withstands the rigorous demands of racing.
Exhaust Systems and Suspension Parts
Titanium exhaust systems offer significant weight savings. They also provide excellent heat resistance. This improves overall vehicle dynamics and aesthetics.
Suspension components, such as springs, also benefit. Titanium reduces unsprung weight. This enhances handling and responsiveness. These applications demonstrate titanium's versatility.
The Manufacturing Journey: Producing High-Quality Titanium Bars
Producing high-quality titanium bars involves several precise steps. The journey begins with raw material extraction. It progresses through various processing stages.
Each step ensures the final product meets stringent industrial requirements. Quality control is paramount throughout the entire process.

Melting and Ingot Formation
Titanium sponge is melted in a vacuum arc remelting (VAR) furnace. This creates high-purity ingots. Multiple melts ensure homogeneity and remove impurities. This foundational step is crucial for material integrity.
Forging and Rolling
Ingots are then forged into billets. This process refines the grain structure. Billets are hot rolled into bars of various diameters. This mechanical working imparts desired mechanical properties.
Precision titanium machining services are often required for final dimensions.
Heat Treatment and Finishing
Heat treatment optimizes the material's properties. This can include annealing or solution treatment. Finishing processes involve straightening, cutting, and surface conditioning. This ensures the bars meet strict dimensional tolerances and surface finish requirements.
Reputable suppliers like China Titanium Factory adhere to international quality standards.
Emerging Trends and Future Innovations in Titanium Technology
Titanium technology continues to evolve rapidly. New developments promise even wider applications. Advancements in alloys and manufacturing techniques are at the forefront.
These innovations address current industrial challenges. They also open doors to entirely new possibilities.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Titanium powder is increasingly used in 3D printing. This allows for complex geometries and custom designs. It reduces material waste significantly. This method is revolutionizing prototyping and low-volume production.
It is particularly beneficial for aerospace and medical components. These applications often require intricate, lightweight structures.
Advanced Titanium Alloys
Research into new titanium alloys is ongoing. These alloys aim for enhanced properties. This includes higher strength, improved creep resistance, and better workability. This expands titanium's utility in extreme environments.
Developments target applications in hypersonic flight and deep-sea exploration. This pushes material science boundaries.
Surface Modification Techniques
Surface treatments can further enhance titanium's properties. Examples include anodizing, nitriding, and coating. These techniques improve wear resistance, hardness, and even aesthetics. They tailor the material for very specific functional requirements.
Beyond the Price Tag: Nuanced Cost Considerations for Titanium Bars
The initial cost of titanium can be higher than other metals. However, a nuanced view reveals its true economic value. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a critical factor. It often positions titanium as a more cost-effective solution long-term.
This section explores the economic advantages that titanium offers.
Long-Term Value and Durability
Titanium's exceptional durability ensures a longer lifespan for components. Its resistance to corrosion and fatigue means fewer replacements. This reduces downtime and operational costs over time. The material's longevity provides significant return on investment.
Reduced Maintenance and Repair
The inherent resistance of titanium minimizes maintenance needs. Components made from titanium require less frequent inspection and repair. This is especially true in harsh or inaccessible environments. The savings in labor and materials are substantial.
Performance Benefits and Efficiency Gains
Titanium's lightweight nature leads to efficiency gains. In aerospace, it means less fuel consumption. In medical, it means better patient outcomes. These performance benefits often justify the initial material investment. They contribute to overall system optimization.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Titanium Production
The environmental aspects of titanium are increasingly important. Efforts are focused on sustainable production. Its recyclability plays a crucial role in reducing its ecological footprint.
Titanium supports eco-friendly engineering solutions. This aligns with global sustainability goals.
Recyclability and Resource Efficiency
Titanium is 100% recyclable. Scrap titanium can be reprocessed into new material. This reduces the need for virgin ore extraction. It minimizes waste and conserves natural resources. The circular economy model benefits greatly from titanium's recyclability.
Efforts Towards Green Manufacturing
The titanium industry is working to reduce its environmental impact. This includes optimizing energy consumption during production. It also involves minimizing chemical waste. Innovations in processing aim for a greener manufacturing footprint.
For more insights into responsible sourcing, visit China Titanium Factory's About Us page.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Titanium Bars
What makes titanium bars ideal for industrial use?
Titanium bars offer a unique combination of properties. These include high strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. They also perform well at high temperatures. This makes them suitable for demanding industrial applications across various sectors.
Are titanium bars expensive compared to other metals?
The initial purchase price of titanium bars can be higher. However, their long-term value often surpasses alternatives. This is due to superior durability, reduced maintenance, and performance benefits. These factors contribute to a lower total cost of ownership.
How is titanium processed into bars?
Titanium processing involves several key steps. It begins with melting titanium sponge into ingots. These ingots are then forged and hot rolled. This forms bars of specific dimensions. Subsequent heat treatments and finishing ensure desired properties and surface quality.
Can titanium be recycled?
Yes, titanium is 100% recyclable. Scrap titanium can be reprocessed and reused. This makes it a sustainable material choice. Recycling helps conserve raw materials and reduces environmental impact.
What are the different grades of titanium bars and their uses?
Common grades include Commercially Pure (CP) Grades 1-4. These offer varying strengths and ductility. Alloyed titanium, such as Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), provides much higher strength. Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) is enhanced for medical implants. Each grade is tailored for specific applications, from chemical processing to aerospace and medical devices.
Unlock Precision and Reliability with Titanium Bars
Ready to elevate your engineering projects with superior titanium? China Titanium Factory offers a comprehensive range of high-quality titanium bars and custom fabrication services. Our expertise ensures you receive materials perfectly suited for your most demanding applications.
Contact Our Experts Today