Titanium plates are indispensable materials in various advanced industries. Their unique combination of characteristics makes them highly valued. This guide explores the comprehensive properties of titanium plates. It provides critical insights for engineers and material scientists.
What Are Titanium Plates? A Fundamental Overview
Titanium plates are flat sheets of titanium metal. They are produced through various rolling processes. These plates are foundational materials in modern engineering. They come in two main forms: commercially pure (CP) titanium and titanium alloys.
CP titanium offers excellent corrosion resistance and ductility. Titanium alloys, however, achieve higher strength. Alloying elements like aluminum and vanadium enhance specific properties. These materials have evolved significantly. Today, they are critical for high-performance applications globally.

Unpacking the Physical Properties of Titanium Plates
Physical properties dictate how a material interacts with its environment. For titanium, these attributes are key. They influence material selection and design considerations. Understanding them ensures optimal performance across diverse applications.
These properties include density, thermal behavior, and electrical characteristics. They are fundamental to titanium's widespread utility. We will explore each in detail.
Density and Weight Characteristics: The Lightweight Advantage
Titanium is renowned for its low density. This translates to a significant lightweight advantage. Its specific gravity is approximately 4.5 g/cm³. This is roughly 60% that of steel. Yet, titanium maintains comparable or superior strength.
This high strength-to-weight ratio is critical. It reduces overall mass in aerospace and automotive designs. This leads to improved fuel efficiency and performance. For example, titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) offer exceptional strength at low weight. This makes them invaluable.
"Density is a measure of mass per unit volume. For titanium, its relatively low density, combined with high strength, makes it a preferred material for applications where weight reduction is paramount."
Thermal Properties: Conductivity and Melting Point
Titanium exhibits relatively low thermal conductivity. This property makes it a suitable barrier to heat transfer. It is useful in applications requiring thermal insulation. Its melting point is impressively high, around 1,668 °C (3,034 °F).
This high melting point contributes to its excellent performance. It withstands elevated temperatures without significant degradation. This stability is vital for jet engines and heat exchangers. However, thermal expansion must be considered in design. Titanium's thermal expansion is moderate compared to other metals.
For more detailed thermal property data, resources like AZoM.com provide comprehensive material specifications.
Electrical Properties and Modulus of Elasticity
Titanium is not a highly conductive electrical material. Its electrical conductivity is lower than copper or aluminum. This can be an advantage in some specialized applications. It prevents unwanted electrical interference.
The modulus of elasticity, or Young's modulus, measures stiffness. Titanium has a modulus of approximately 100-120 GPa. This value is lower than steel. This indicates greater flexibility or elasticity. This property is crucial for components that must flex without permanent deformation. It also affects vibration characteristics.
Hardness and Mechanical Strength
Titanium plates possess good hardness. This contributes to their wear resistance. They can withstand abrasive environments effectively. The hardness varies depending on the specific grade and heat treatment.
Mechanical strength is where titanium truly shines. Its tensile strength ranges from 240 MPa for CP Grade 1 to over 1100 MPa for high-strength alloys like Ti-6Al-4V. This strength, coupled with its low density, ensures exceptional performance under demanding loads. Understanding these mechanical properties is essential for structural integrity.

Chemical Properties and Environmental Resistance of Titanium Plates
Titanium's chemical properties are highly advantageous. They include outstanding resistance to corrosion. Its unique biological compatibility is also a key feature. These make titanium suitable for the harshest and most sensitive environments.
The material forms a passive oxide layer. This layer is responsible for its remarkable durability. It protects against various aggressive agents. This section explores these critical chemical attributes.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: A Deep Dive
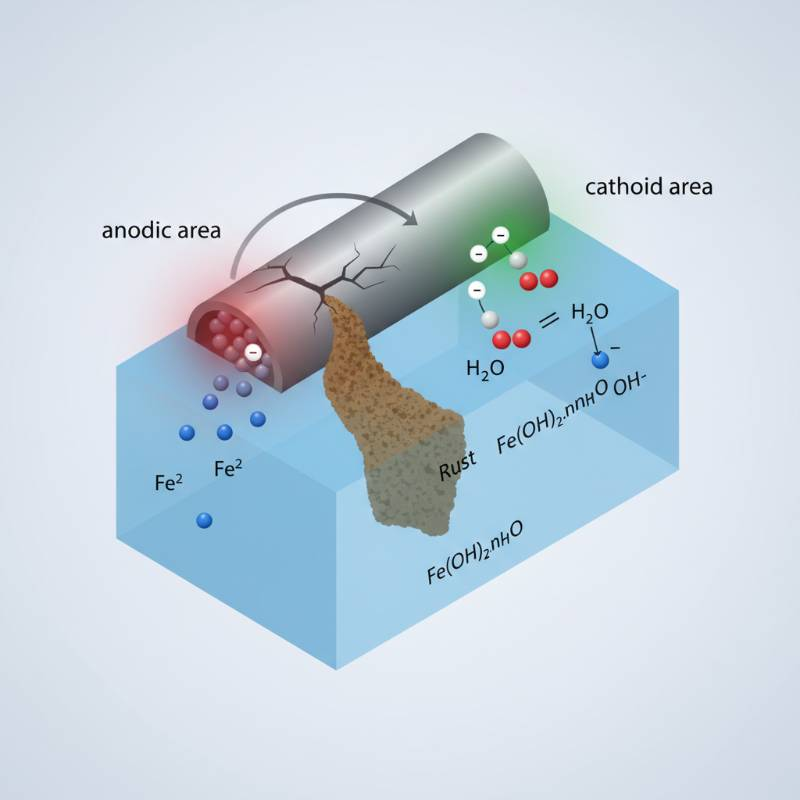
Titanium's resistance to corrosion is legendary. It forms a stable, tenacious, passive oxide layer (TiO₂) on its surface. This layer spontaneously regenerates if damaged. It provides protection against a wide range of corrosive media.
This includes seawater, chlorine solutions, and many acids. It performs exceptionally well in oxidizing environments. This property makes it superior to many stainless steels and nickel alloys. Specific examples include its use in desalinization plants and chemical processing equipment. The integrity of this oxide layer is key to its performance.
"Corrosion resistance refers to a material's ability to withstand degradation due to chemical reactions with its environment. Titanium achieves this through a protective, self-healing oxide film."
For more information on corrosion standards and testing, consult resources from organizations like NACE International (now AMPP).
Reactivity and Allotropic Transformations
While highly corrosion-resistant, titanium is chemically reactive. It reacts readily with oxygen to form its protective oxide. At elevated temperatures, it can react with nitrogen and hydrogen. This requires careful processing techniques.
Titanium also exhibits allotropic transformations. It exists in an alpha (hexagonal close-packed) phase at lower temperatures. Above 882 °C (1620 °F), it transforms to a beta (body-centered cubic) phase. Alloying elements stabilize these phases. This allows for tailored mechanical properties through heat treatment. Understanding these phases is crucial for metallurgy and processing.
Biocompatibility: A Medical Marvel
Titanium is exceptionally biocompatible. This means it can exist safely within the human body. It causes minimal adverse reactions. This property makes it the material of choice for medical and dental implants.
The passive oxide layer is non-toxic and non-allergenic. It prevents the body from rejecting the implant. This promotes osseointegration, where bone grows directly onto the implant surface. This ensures long-term stability and success in healthcare applications.
The Unmatched Value Proposition of Titanium Plates
Titanium plates offer a compelling combination of properties. This positions them as a premium engineering material. Their value extends beyond simple material cost. They deliver significant performance and economic benefits.
The synergy of these properties makes titanium the material of choice. It excels in the most demanding industries. This section summarizes these key advantages.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Performance Without Bulk
The unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio of titanium is a primary benefit. It allows for lighter designs without compromising structural integrity. In aerospace, this translates to improved fuel efficiency. It also increases payload capacity. This is vital for both commercial and military aircraft.
For example, a titanium component can be significantly lighter than a steel equivalent. Yet, it performs the same function. This efficiency is critical in high-performance applications. It drives innovation in many sectors.
Superior Corrosion and Temperature Performance
Titanium's dual advantage in corrosion and temperature resistance is powerful. It thrives in extreme environments. These include aggressive chemical processing or high-temperature jet engine components. Other materials often fail under such combined stresses. Titanium maintains its integrity and performance.
This synergistic value ensures long operational lifespans. It reduces maintenance costs and improves safety. These factors contribute significantly to its overall economic value proposition.
Key Applications of Titanium Plates Across Industries
Titanium plates solve critical engineering challenges. They are utilized extensively across numerous industries. Their unique properties enable groundbreaking solutions. This section highlights specific examples of titanium's real-world uses.
From the skies to the seas, titanium's versatility is evident. China Titanium Factory offers a range of high-quality titanium products for these demanding sectors.
Aerospace and Defense: The Ultimate Performance Material
Titanium is indispensable in aerospace and defense. Its strength, light weight, and temperature resistance are paramount. It is used in aircraft structures, landing gear, and jet engine components. Fighter jets and spacecraft rely on titanium for critical parts.
The material contributes to fuel efficiency, increased speed, and enhanced safety. It withstands the extreme conditions of flight. This includes high stresses and varying temperatures. Its reliability is unmatched in this sector.
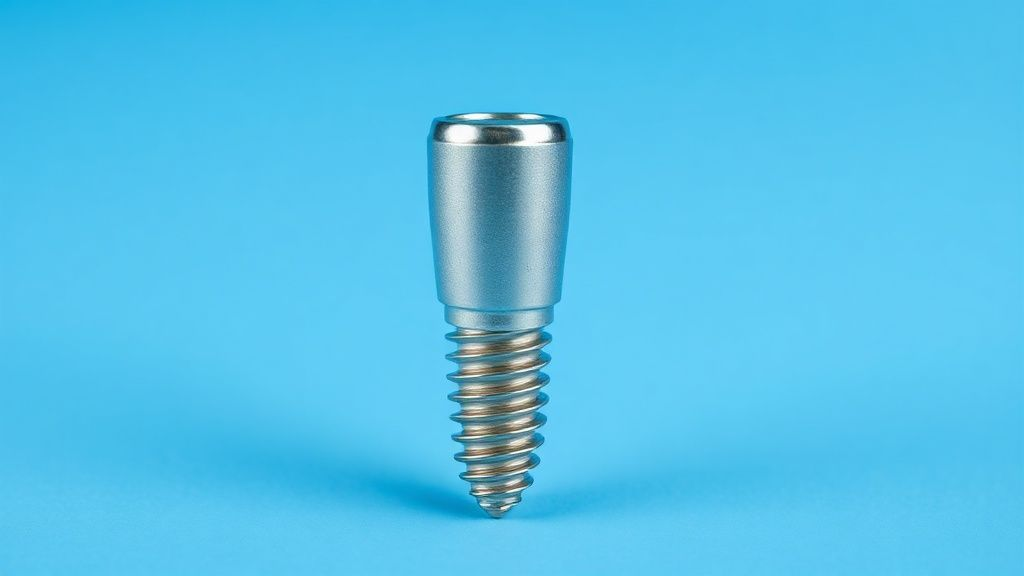
Medical and Biomedical: Enabling Human Health
In medical and biomedical fields, titanium is a lifesaver. Its biocompatibility makes it ideal for implants. These include joint replacements, bone plates, and dental implants. Surgical instruments also frequently utilize titanium.
It resists corrosion from bodily fluids. This ensures long-term performance and patient safety. Titanium's role in improving human health is profound and continuously expanding.

Marine and Offshore: Conquering Corrosive Waters
Titanium excels in marine and offshore applications. Its exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion is key. It prevents degradation in harsh oceanic environments. This makes it suitable for shipbuilding, submersibles, and offshore platforms.
Components like heat exchangers, piping, and sonar domes benefit. It also resists biofouling, the accumulation of marine organisms. This ensures longevity and reduced maintenance in underwater systems.
Chemical Processing and Industrial: Durability in Harsh Environments
The chemical processing industry relies heavily on titanium. Its durability and resistance to aggressive chemicals are critical. It is used in heat exchangers, reaction vessels, and piping systems. These applications involve highly corrosive substances.
Titanium ensures long-term operational integrity. It minimizes downtime and enhances safety. Its robust performance in extreme industrial settings makes it irreplaceable. For custom industrial solutions, explore titanium fabrication services.
Manufacturing and Processing of Titanium Plates: From Ore to Application
The journey of titanium from raw ore to finished plate is complex. It involves specialized manufacturing processes. Understanding these techniques is vital. It ensures the material's unique properties are preserved and optimized.
Working with titanium requires specific considerations. This is due to its mechanical properties and reactivity. Experienced manufacturers adhere to stringent standards.
Alloying Elements and Grade Selection
Alloying elements are crucial for tailoring titanium's properties. Aluminum, vanadium, and molybdenum are common additives. Aluminum enhances strength and creep resistance. Vanadium improves ductility and strength. Molybdenum increases strength and corrosion resistance.
These elements create different titanium grades. Each grade is suited for specific applications. For example, CP Grades (1-4) offer increasing strength with good ductility. Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is a widely used alloy. It balances high strength, low weight, and excellent corrosion resistance. Selecting the correct grade is paramount for performance.
| Grade | Composition | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Commercially Pure (CP) | Most ductile, excellent corrosion resistance, high formability. | Chemical processing, desalination, medical devices. |
| Grade 2 | Commercially Pure (CP) | Good strength, excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability. | Aerospace, marine, power generation, heat exchangers. |
| Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium | High strength, lightweight, excellent fatigue resistance. | Aerospace structures, medical implants, high-performance automotive. |
Fabrication Methods and Forming
Fabricating titanium plates involves several methods. These include rolling, forging, and pressing. Hot working is often preferred. It improves ductility and reduces forming loads. Cold working is also possible for some grades. It achieves tighter tolerances.
Due to titanium's unique properties, specific techniques are required. Its low modulus of elasticity means it experiences more springback during forming. Its reactivity necessitates controlled atmospheres. This prevents contamination during high-temperature operations.
Welding and Machining Titanium: Best Practices
Welding titanium presents unique challenges. Contamination from atmospheric gases is a primary concern. Inert gas shielding (argon or helium) is essential. This protects the weld pool and surrounding hot metal. Techniques like TIG welding are commonly used. Proper joint preparation is also critical.
Machining titanium requires careful attention. Its low thermal conductivity can lead to heat buildup. This causes tool wear and work hardening. Low cutting speeds, high feed rates, and ample coolant are recommended. Sharp tools with positive rake angles are crucial. Adhering to these best practices ensures quality and efficiency.

Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Plate Properties
This section addresses common inquiries regarding titanium plates. It covers their properties, applications, and characteristics. These answers provide clear, authoritative information. They are valuable for engineers, researchers, and procurement specialists.
What is the primary advantage of titanium plates over steel?
The primary advantage is titanium's superior strength-to-weight ratio. It offers comparable or greater strength than many steels. Yet, it is approximately 45% lighter. Additionally, titanium provides exceptional corrosion resistance. This is especially true in chloride environments. Most steel alloys cannot match this performance.
Is titanium truly non-corrosive?
Titanium exhibits outstanding corrosion resistance. This is due to its stable, passive oxide layer. However, it is not entirely "non-corrosive" under all extreme conditions. Highly reducing acids or molten metals can attack it. Understanding specific environmental conditions is crucial. This ensures appropriate grade selection and application.
How does temperature affect titanium plate properties?
Titanium generally performs well at elevated temperatures. It retains significant strength and creep resistance. This makes it suitable for high-temperature applications. It also maintains good ductility and strength at cryogenic temperatures. However, prolonged exposure to very high temperatures can lead to oxidation. This can affect its mechanical properties.
What are the common grades of titanium plates and their uses?
Common commercially pure (CP) grades include Grade 1, 2, 3, and 4. Grade 1 is the most ductile, used in chemical processing. Grade 2 is a workhorse, common in aerospace and marine. The most prevalent alloy is Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V). It offers high strength for aerospace and medical implants. Other alloys exist for specialized high-temperature or high-strength needs.
Can titanium plates be recycled?
Yes, titanium is fully recyclable. Scrap titanium is highly valued. It is reprocessed and reintroduced into the supply chain. This makes titanium a sustainable material. Recycling reduces the need for virgin ore extraction. It also lowers energy consumption. This contributes to a circular economy.
The Enduring Legacy and Future of Titanium Plates
Titanium plates represent a pinnacle of material science. Their unique properties are indispensable. They drive innovation across numerous engineering sectors. The combination of strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance is unmatched.
As technology advances, so too will titanium's applications. From aerospace to medical implants, its value continues to grow. Titanium's legacy is one of high performance and reliability. Its future promises even greater contributions to advanced engineering.
Elevate Your Projects with Premium Titanium Plates
Ready to leverage the superior properties of titanium for your next challenge?
Partner with a trusted expert in high-quality titanium manufacturing.