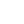Introduction: The Role of Titanium Anodizing in Aerospace
Aerospace demands materials that can take a beating and keep on ticking. Titanium, with its unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio and inherent corrosion resistance, is a front-runner. From the skeletal structure of commercial jets to the intricate components of spacecraft, titanium alloys are everywhere. Yet, even this workhorse metal benefits from an extra layer of defense. Enter titanium anodizing.
This surface treatment isn't just about making parts look good. It's about fundamentally altering the surface to create a more robust, reliable component. For aerospace material science, where failure isn't an option, enhancing titanium's already impressive properties is a game-changer. It extends component life, reduces maintenance, and ultimately contributes to safer, more efficient flight.
Understanding the Titanium Anodizing Process
Titanium anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process. It grows a controlled, protective oxide layer on the surface of titanium parts. Unlike plating, which adds material, anodizing converts the existing surface metal into an oxide. This makes the layer integral to the substrate.
The process involves immersing titanium components in an electrolyte bath and passing an electrical current through them. This forces an electrochemical reaction. The resulting oxide layer is typically compact, tenacious, and incredibly uniform. Different anodizing methods and chemical baths can yield varying oxide thicknesses and properties, tailored for specific aerospace industry standards.
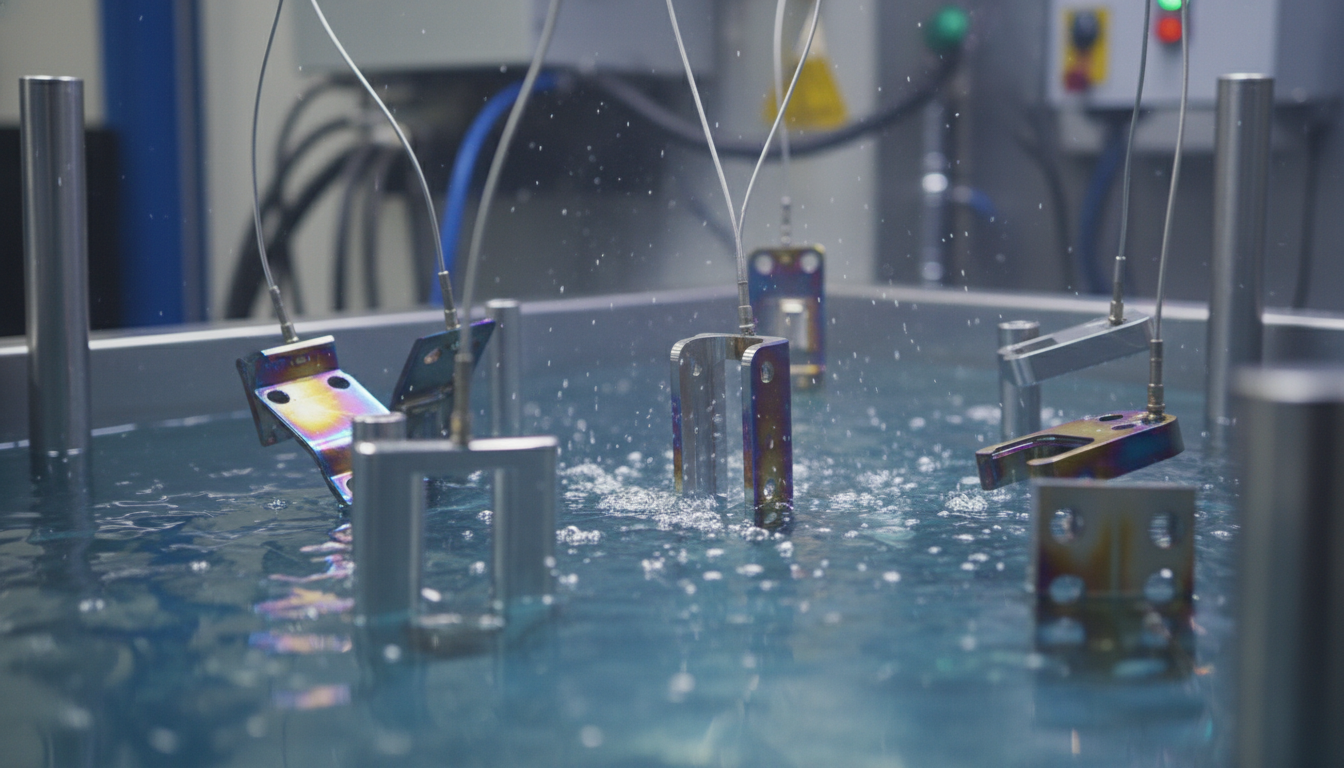
There are several types of titanium anodizing, often categorized by the resulting oxide characteristics. For instance, Type II (thin film) and Type III (thick film) processes are common, each offering distinct advantages in terms of wear and corrosion protection. Precision in aerospace anodizing equipment and strict control over bath chemistry are non-negotiable.
Anodizing: An electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts. It's commonly applied to aluminum, titanium, and magnesium to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and provide decorative finishes.
Key Benefits of Anodized Titanium for Aerospace Components
Anodized titanium isn't just a nicety; it's a necessity for high-performance aerospace applications. The treatment provides a host of advantages that make components more durable and reliable.
These benefits translate directly into extended service life and reduced operational costs. This makes anodized titanium an indispensable part of aerospace component enhancement strategies.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance for Extreme Environments
Titanium already boasts excellent natural corrosion resistance. However, the anodizing process takes this a step further. It creates a robust, highly passive oxide layer that acts as an impermeable barrier. This layer shields the underlying metal from aggressive aerospace operating conditions.
Think about jet engines exposed to saltwater spray, high temperatures, and corrosive fuels. Or spacecraft components facing atomic oxygen in low Earth orbit. Anodized titanium stands firm. It ensures long-term integrity where other materials might falter. This is especially crucial for parts in direct contact with harsh environments, giving them a fighting chance against nature's fury and operational stresses. For comprehensive protection, consider the full range of titanium fabrication services that include advanced surface treatments.
According to a study published in the Journal of Surface and Coatings Technology, anodic films on titanium can significantly reduce degradation rates in aggressive environments, particularly in chloride-rich solutions relevant to naval aviation.
Improved Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Moving parts in aircraft and spacecraft endure constant friction and abrasion. Unprotected titanium, while strong, can still suffer wear. The hard, ceramic-like anodic layer drastically reduces this vulnerability. It provides a tougher exterior, much like putting armor on a knight.
This means critical aerospace parts — think landing gear components, actuators, or fastener systems — last longer. Less wear translates to less material loss, fewer replacements, and ultimately, lower operational costs. Component longevity isn't just a bonus; it's a safety imperative in aerospace.
Increased Fatigue Life and Structural Integrity
Aircraft and spacecraft components are subjected to countless stress cycles throughout their operational lives. Fatigue failure is a major concern. Anodizing can actually improve the fatigue performance of titanium components. How? The uniform, compressive stress state induced by the anodic layer can counteract tensile stresses that initiate cracks.
This improvement in fatigue life is a big deal. It means structural integrity is maintained over longer periods, enhancing overall component reliability and safety. It ensures that titanium parts can weather repeated stress without cracking under pressure. The team at China Titanium Factory understands the critical importance of these properties for aerospace applications.

Biocompatibility in Specialized Aerospace Applications
While often associated with medical implants, biocompatibility finds niche applications in aerospace. Think human-rated spacecraft systems or specialized medical devices for astronauts. Anodized titanium enhances the material's already excellent biocompatibility. It creates an even more inert surface.
This is crucial for components that might come into contact with human tissue or biological systems during space exploration missions. The stable oxide layer minimizes unwanted reactions, ensuring safety and reliability for human occupants.
Aesthetic and Decorative Properties for Aerospace Design
Beyond pure function, aesthetics play a role. Anodizing titanium can produce a vibrant array of colors without dyes, simply by controlling the oxide layer thickness. This optical interference effect provides unique color customization options.
Such decorative anodizing is valuable for component identification, branding, or simply enhancing the visual appeal of internal or external aerospace components. It's not just pretty; it can be functional, aiding in quick visual inspection and differentiation of parts.
Electrical Insulation Properties of Anodized Titanium
Metals conduct electricity. Titanium, like other metals, is conductive. However, the anodic oxide layer is a dielectric. This means it acts as an electrical insulator. This property is highly beneficial for certain electronic and sensor applications within aerospace systems.
For instance, it can prevent short circuits, isolate components, or protect sensitive electronics from stray currents. This dielectric property adds another dimension of utility to anodized titanium, making it suitable for complex integrated systems.
Diverse Applications of Anodized Titanium in Aerospace
The benefits of anodized titanium translate into a broad spectrum of real-world applications across various aerospace sectors. Its versatility makes it a go-to material for engineers pushing the envelope.
From the smallest fastener to critical structural elements, anodized titanium consistently delivers.
| Application Area | Specific Components | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Structural Components | Wing spars, fuselage frames, landing gear supports | Increased fatigue life, corrosion resistance |
| Engine Parts | Compressor blades, casings, exhaust nozzles | High-temperature corrosion, wear resistance |
| Fasteners and Fittings | Bolts, rivets, brackets | Improved lubricity, galling resistance, corrosion protection |
| Satellite and Spacecraft Components | Antenna mounts, sensor housings, structural panels | Atomic oxygen resistance, thermal stability, electrical insulation |
| Hydraulic Systems | Valve bodies, pistons, tubing | Wear resistance, smooth operation, corrosion protection from fluids |
Each application leverages specific enhancements provided by the anodized layer. For example, satellite parts benefit from resistance to the harsh vacuum of space, while engine components demand resilience against extreme heat and corrosive exhaust gases. This widespread adoption underscores the treatment's value. More information on aerospace titanium alloy products is available.
Anodizing Compared to Other Surface Treatments for Aerospace
Titanium isn't the only material needing surface treatment, nor is anodizing the only game in town. Other common aerospace surface finishes include plating, painting, and various chemical conversion coatings. Each has its place, but anodizing often holds a unique advantage for titanium.
Unlike plating, which deposits a layer of a different metal (like chrome or nickel) onto the surface, anodizing converts the titanium itself. This means no issues with adhesion or dissimilar metal corrosion. It's a cohesive, integrated layer. Painting offers protection and aesthetics but can chip or scratch, compromising the barrier. Anodizing's hard, ceramic-like film is far more resilient. Chemical conversion coatings are effective but often provide thinner, less durable protection than anodizing. For many aerospace applications, anodizing strikes a powerful balance between protection, durability, and weight efficiency.
Passivation: A process of treating or coating a metal to reduce the chemical reactivity of its surface. In the context of metals like titanium, it refers to the formation of a protective oxide layer that inhibits corrosion.
Challenges and Quality Control in Titanium Anodizing
Getting anodizing right isn't always a walk in the park. It's a precise science, particularly for aerospace applications where tolerances are tight and performance is critical. Challenges include achieving uniform coating thickness across complex geometries and maintaining consistent process parameters.
Quality control is paramount. This involves rigorous inspection for coating thickness uniformity, adhesion, and freedom from defects. Environmental impact from chemical baths also needs careful management, with strict adherence to regulations. Reputable facilities often follow industry standards like AMS 2488 for titanium anodizing to ensure process consistency and component reliability.
The SAE International Aerospace Material Specifications (AMS) provide detailed standards for these processes, ensuring components meet the stringent requirements of the industry. This level of meticulousness ensures that every anodized titanium part performs as expected, without cutting corners.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Implementing Titanium Anodizing
At first glance, adding another process step might seem like an extra cost. However, a long-term view reveals a different story. The initial investment in titanium anodizing often pays dividends, and then some, over the lifecycle of an aerospace component.
Reduced maintenance cycles, extended component life, and fewer unexpected failures all contribute to significant savings down the line. Avoiding costly repairs or replacements, especially for critical parts, makes the value proposition of anodizing clear. It's an investment in longevity and reliability, ultimately lowering the total cost of ownership. Think of it as spending a little to save a lot, keeping aerospace operations running smoothly and safely.
Future Trends and Innovations in Aerospace Titanium Anodizing
The world of material science never stands still. For aerospace titanium anodizing, researchers are constantly exploring new frontiers. We're seeing advancements in plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO), which can produce even harder, more wear-resistant coatings.
Nanotechnology is also playing a role, with efforts to incorporate nanoparticles into anodic layers for enhanced properties. These advanced anodizing techniques promise even greater performance, pushing the boundaries of what titanium can do. The goal is always the same: lighter, stronger, more durable components that can withstand the ever-increasing demands of aerospace exploration and travel. These innovations will continue to shape aerospace material trends for decades to come.

Partnering for Excellence: Accessing Specialized Titanium Anodizing Services
For aerospace manufacturers, selecting the right partner for surface treatments is as crucial as selecting the right material. Off-the-shelf solutions rarely cut it. You need a provider with deep expertise in aerospace-grade processing.
This means a facility capable of precision, adherence to stringent industry standards, and a track record of reliability. Specialized Titanium Anodizing Services are not just about dipping parts in a tank. They involve meticulous preparation, controlled environments, advanced equipment, and stringent quality assurance protocols. Such expertise ensures that every component receives the optimal treatment, contributing directly to project success and unparalleled component reliability.
When the stakes are high, as they always are in aerospace, partnering with an expert anodizing provider like China Titanium Factory is not just a choice; it's a strategic advantage. They bring the technical know-how and state-of-the-art facilities to deliver the precise surface enhancements your critical components demand.
Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Anodizing in Aerospace
Why is titanium anodized for aerospace applications?
Titanium is anodized to significantly enhance its inherent properties. This includes boosting corrosion resistance in harsh environments, improving wear and abrasion resistance, extending fatigue life, and providing specific benefits like electrical insulation or decorative finishes. These enhancements are critical for the safety, reliability, and longevity of aerospace components.
How does anodizing improve the fatigue life of titanium?
Anodizing can improve fatigue life by creating a uniform, compressive stress layer on the titanium's surface. This compressive layer helps to resist the formation and propagation of microscopic cracks that typically lead to fatigue failure. It essentially makes the surface more resilient to repeated stress cycles.
Are there different types of titanium anodizing for aerospace?
Yes, there are several types. Common ones include Type II (thin film) and Type III (thick film) anodizing, as well as specialized processes like plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO). Each offers distinct properties in terms of oxide layer thickness, hardness, and porosity, tailored to specific performance requirements and industry standards.
Does titanium anodizing affect component dimensions?
Yes, the anodizing process adds a very thin layer of oxide to the surface, which can result in a slight increase in component dimensions. However, this increase is typically very small, often in the range of micrometers, and is accounted for in the design and manufacturing processes for aerospace-grade parts.
What are the environmental considerations for titanium anodizing?
Titanium anodizing, like any chemical process, involves environmental considerations, primarily related to the disposal of chemical baths and wastewater. Responsible providers adhere to strict environmental regulations, employing advanced filtration and waste treatment systems to minimize ecological impact. The process itself is generally considered more environmentally friendly than some traditional plating methods.
Need Aerospace-Grade Titanium Anodizing?
Ensure your critical aerospace components receive the highest level of surface enhancement. Partner with experts who deliver precision, reliability, and unparalleled quality.
Get a Quote Today