Titanium is a truly special metal, famous for being super strong, light, and tough against rust. It's become really popular in many industries because of these great qualities. From airplanes to medical tools, pure titanium metal is incredibly useful. This article will explore the awesome titanium benefits and uses of pure titanium, showing why it's a top choice for so many different fields. We'll also peek into what's next for titanium and how new research is making it even better.

Titanium, often called Ti, is a metal known for its amazing titanium strength for its weight. It's as strong as steel but almost half the weight (45% lighter), making it perfect for anything where weight really matters. This lightness not only adds to its titanium strength but also makes it easier to work with in complex manufacturing. Plus, pure titanium metal is safe for the human body, meaning it won't cause harm or be rejected. This makes it ideal for medical uses, like implants, improving people's health and life quality. These unique titanium properties are key to its wide use.
One of the best titanium properties is its incredible titanium strength. It can handle extreme forces without bending or breaking, which is why it's a favorite in aerospace and cars. This titanium strength isn't just about resisting force; it's also about staying strong under pressure, which is vital in high-stakes areas like space travel and aviation. Its titanium durability also means it can last a long time in harsh conditions, like saltwater or acidic environments, without rusting. This ability to resist tough environments makes titanium parts last longer, cutting down on how often they need to be replaced or fixed.
Let's look at some of the main titanium advantages that make it stand out:
Lightweight Yet Strong: Titanium's high titanium strength-to-weight ratio makes it a go-to material for industries needing to cut weight without losing strength. This is super important in aerospace, where every gram helps save fuel and boost performance. Lighter vehicles also mean better fuel economy and less pollution, which is good for the environment. Cars also get a big boost, becoming more efficient and faster with less energy.
Rust-Proof Power (Corrosion Resistance): Titanium's ability to resist rust is another huge titanium advantage. Unlike other metals that rust or break down in wet or salty places, titanium forms a protective layer on its surface that stops more rust. This makes it perfect for ocean uses and chemical factories. Even if scratched, this protective layer fixes itself, keeping the metal safe and reliable for a long time. This feature is especially valuable where maintenance is hard, like deep-sea exploration.
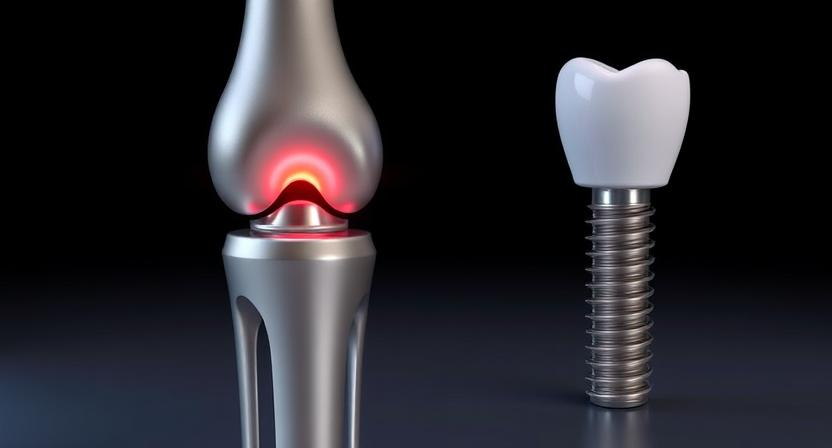
Body-Friendly (Biocompatibility): In medicine, titanium's biocompatibility is priceless. It's widely used in joint replacements and dental implants because it blends well with human bones and tissues. This blending process helps create strong, long-lasting implants. Patients with titanium implants often have fewer problems and recover faster. This reduces hospital stays and makes surgeries more successful, making titanium a top pick for doctors worldwide.
Stable in Heat (Low Thermal Expansion): Titanium's low thermal expansion means it stays the same size even when temperatures change. This is really useful in precise engineering and manufacturing. Parts made from titanium keep their shape and size even with big temperature swings, ensuring consistent performance. This is crucial in fields like electronics and aerospace, where exact measurements are key to success.
While pure titanium metal is impressive, mixing it with other elements like aluminum and vanadium creates alloys that have even better titanium properties. These alloys can be made harder, more heat-resistant, and even stronger, opening up more uses for titanium. Developing new alloys is an exciting area of research, with scientists always looking for ways to unlock more potential from this versatile metal.
Pure titanium metal and its alloys are used in many places:
In the aerospace world, titanium alloys are used for airplane frames, jet engines, and landing gear. Their mix of lightness, titanium strength, and heat resistance makes them perfect for the tough demands of flying. They can handle high temperatures and stress, making aircraft parts safe and dependable. The lighter weight also helps save fuel, which is good for the environment.

Cars benefit from titanium's lightness and titanium durability. For example, titanium exhaust systems make cars lighter, improving fuel efficiency and performance. Titanium's titanium strength also lets designers create thinner, yet tough, parts, leading to cooler car designs. Its resistance to high temperatures also makes it great for engine parts, ensuring they last a long time.

Titanium alloys are also big in medicine. Besides implants, they're used for surgical tools because they're strong and can handle sterilization. Titanium doesn't react with body fluids, making it safe for medical devices and ensuring they last. Its versatility allows for custom-fit devices and tools, improving surgeries and patient care.
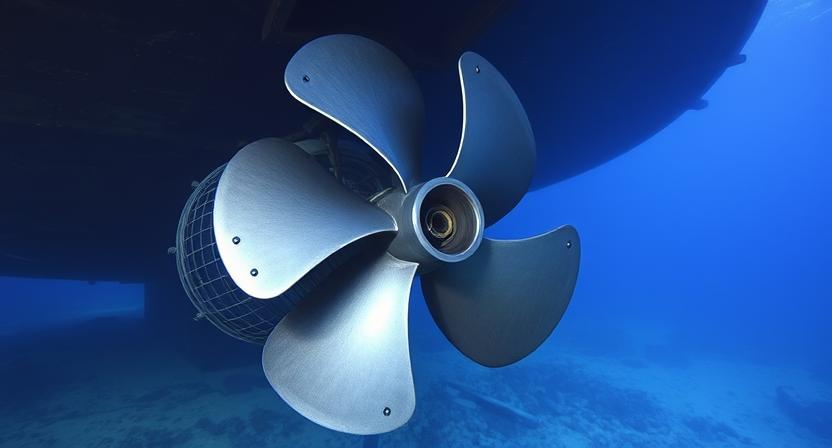
Titanium's rust resistance is highly valued in the marine industry. It's used for propeller shafts, underwater pipes, and heat exchangers. Its ability to stand up to seawater means long-lasting performance and lower maintenance costs. This titanium durability is super important in ocean environments, where equipment failure can be costly. So, titanium parts are increasingly chosen for new marine projects.

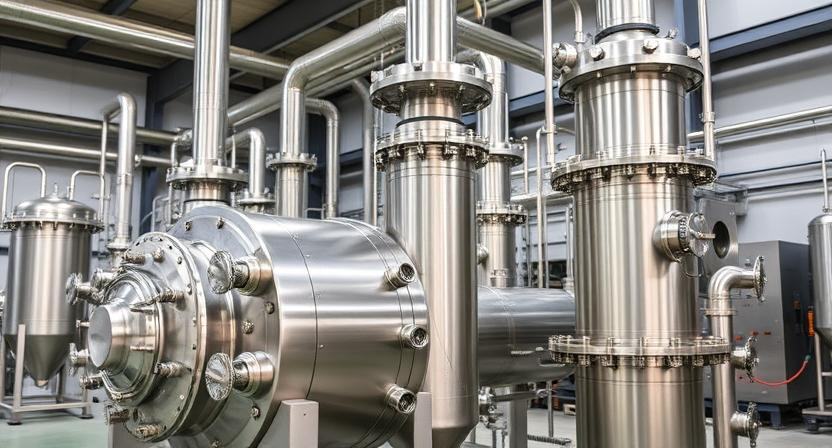
In chemical processing, titanium's resistance to harsh chemicals makes it ideal for making reactors, heat exchangers, and pressure vessels. Its long life and reliability save money by reducing downtime and repairs. The chemical industry loves titanium because it can handle strong chemicals without breaking down, keeping processes safe and sound. This reliability is key for steady production and meeting safety rules.

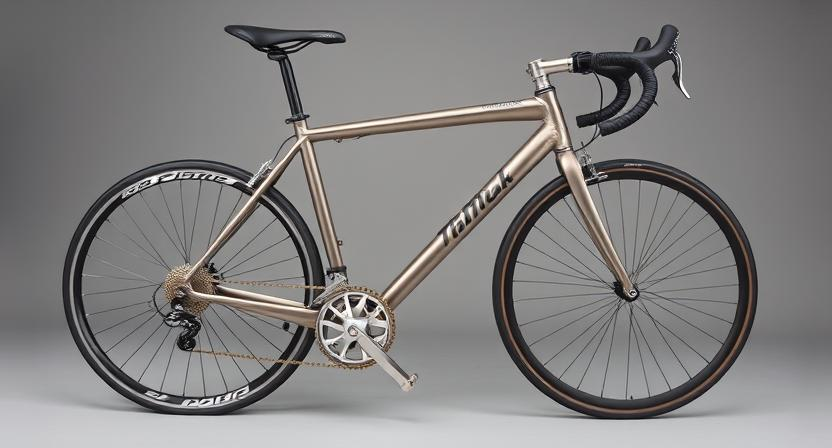
The sports industry uses titanium's lightness and titanium strength for high-performance equipment. Bikes, golf clubs, and tennis rackets made from titanium give athletes an edge in performance and endurance. The lighter weight means more speed and agility, while the titanium strength ensures durability and precision. These titanium advantages make it a favorite for athletes wanting to win with advanced gear.

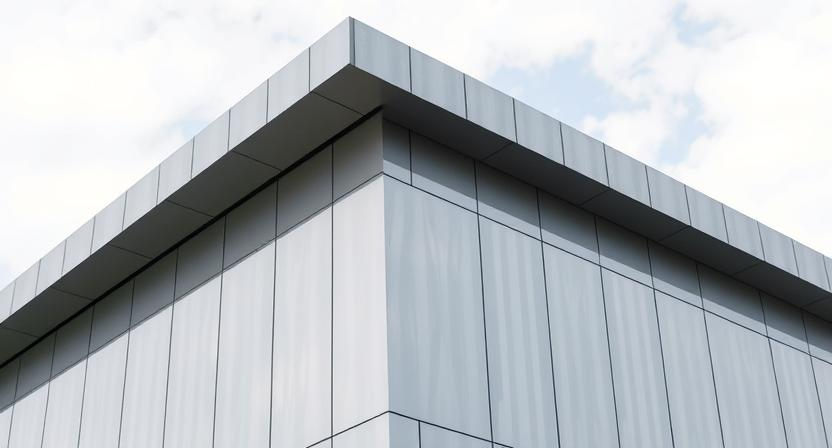
In architecture, titanium is used for its good looks and titanium durability. It's used for building exteriors and roofs, giving structures a modern look while protecting them from the weather for a long time. Titanium's unique finish can make buildings look sleek and modern, often seen in famous projects. Its ability to resist wear and tear without losing its shine makes it a smart choice for eco-friendly building.

As technology moves forward and industries keep looking for better materials, the demand for titanium is set to grow. Ongoing research aims to create new titanium alloys with even better titanium properties, opening doors for more cool uses. New manufacturing methods, like 3D printing, are also expanding what's possible with titanium, allowing for more complex and custom designs. As industries push for more efficiency and performance, titanium will likely become even more important.
Pure titanium metal and its alloys offer a ton of titanium benefits, from unmatched titanium strength and titanium durability to amazing rust resistance and biocompatibility. Its uses span across many industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and more. As we keep exploring its potential, titanium will surely play a huge role in shaping the future of materials science and engineering. In short, the unique titanium properties of pure titanium metal make it a must-have material in today's tech world. Whether in the sky, on the road, or inside our bodies, titanium's titanium advantages are clear, promising a bright future for this incredible metal. With more research, we can expect even more groundbreaking uses for titanium, making it a cornerstone of modern industry.