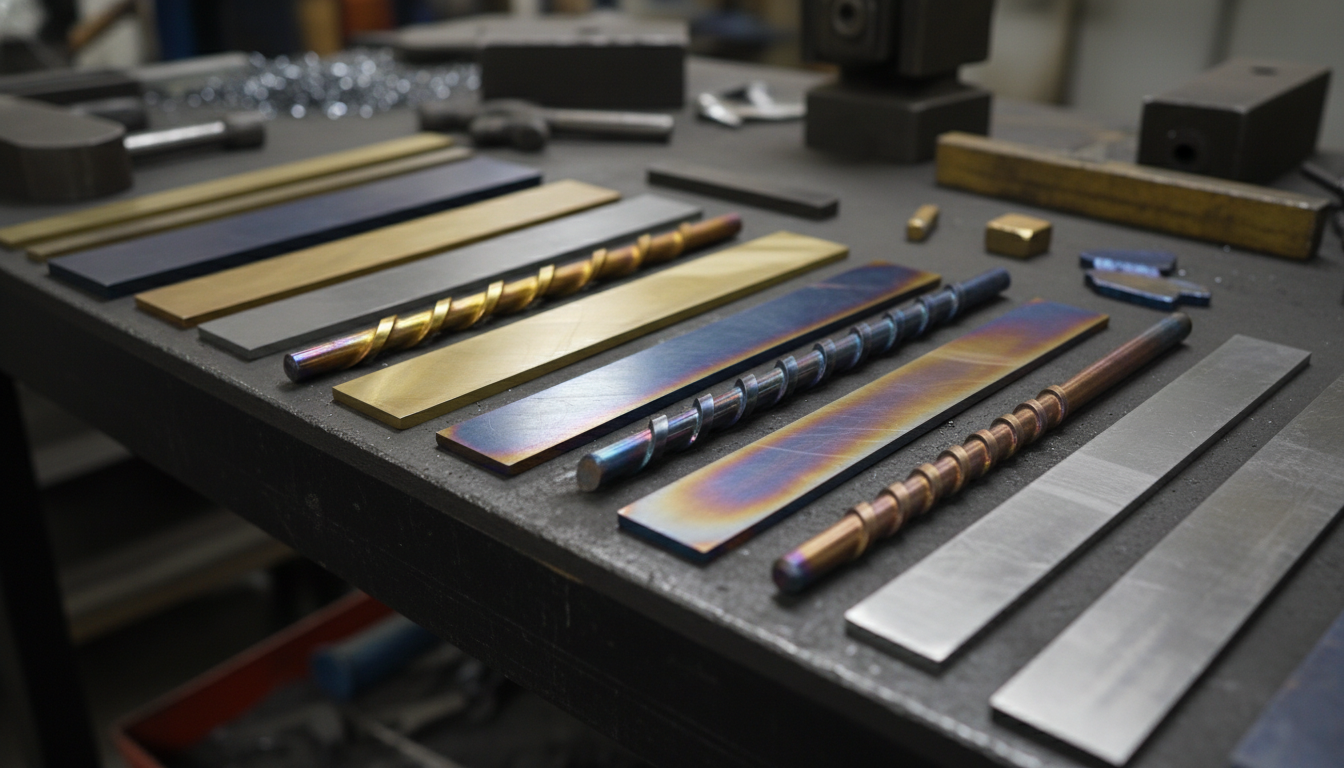
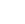What is Gold Anodized Titanium?
Seeking the luxurious appeal of gold but needing the robust performance of titanium? Standard gold plating often falls short. It's prone to chipping, fading, and can introduce issues for sensitive skin. This is where gold anodized titanium steps in as a superior alternative.
Gold anodized titanium isn't a surface coating in the traditional sense. Instead, it’s a process that creates a vibrant, gold-like finish directly from the titanium itself. This electrochemical treatment forms a transparent oxide layer on the metal's surface.
The magic isn't in adding a pigment. The color comes from light interference, similar to how oil slicks show rainbows. This unique method delivers an aesthetic appeal that's both striking and inherently part of the material. It's a game-changer for applications demanding both beauty and resilience.
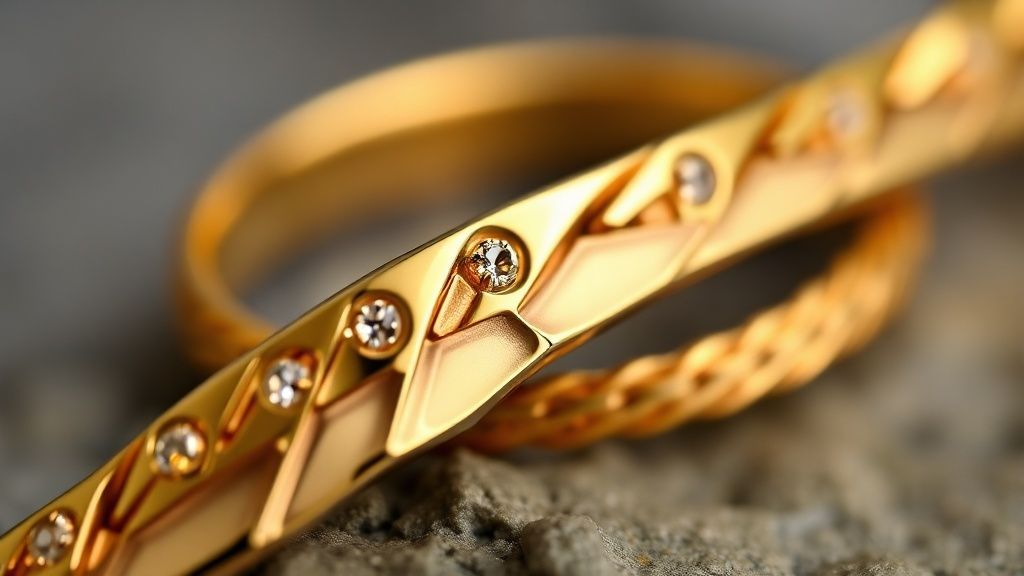

The Science Behind Gold Anodized Titanium: Anodization Explained
The ability to transform plain titanium into a dazzling gold hue isn't magic; it's precise science. This transformation occurs through an electrochemical process called anodization. Unlike painting or plating, anodization integrates the color directly into the metal's surface structure.
The goal is to grow a controlled, thin, transparent oxide layer on the titanium. The thickness of this layer determines the final color. It’s a remarkable feat of material engineering, turning a dull grey metal into a spectrum of vibrant colors, including gold.
How Titanium Anodization Works
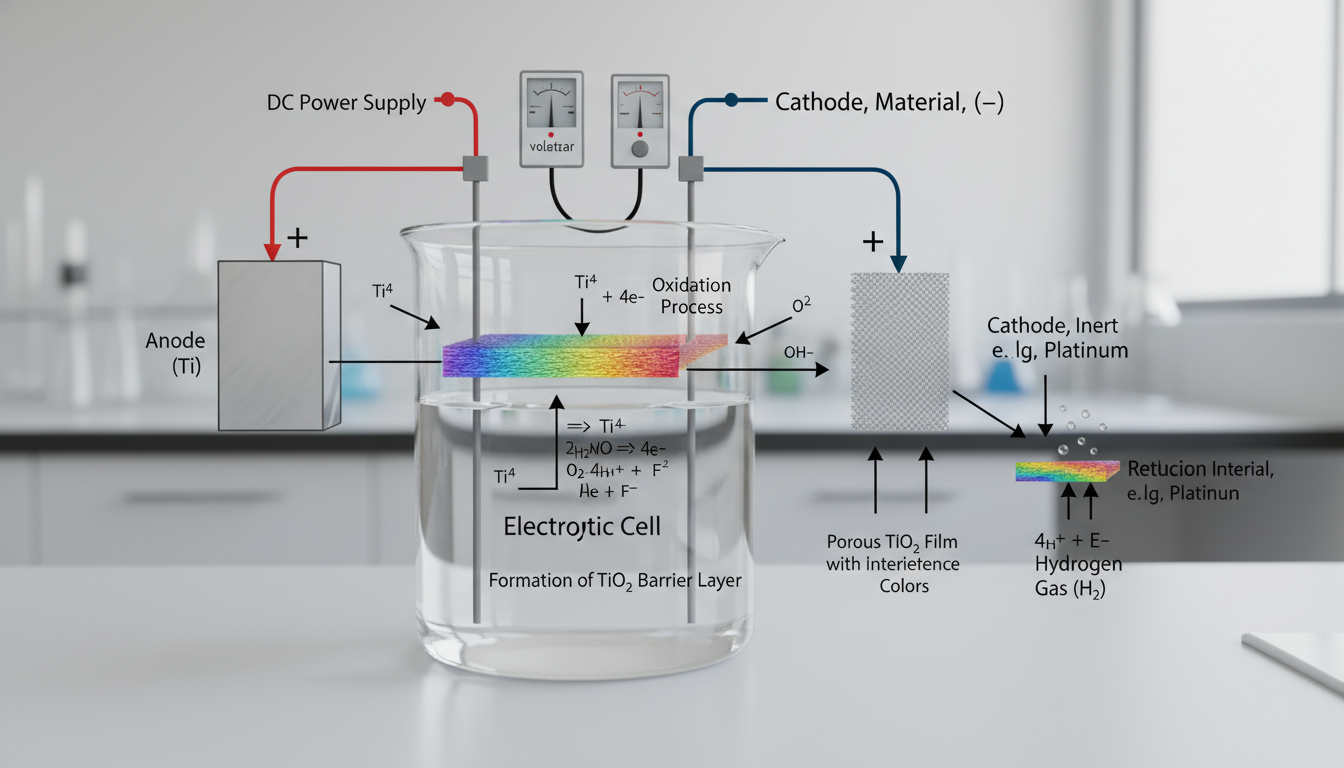
Titanium anodization is an electrolytic passivation process. A titanium workpiece acts as the anode in an electrolytic cell. It’s immersed in an electrolyte solution, often a mild acid like sulfuric acid or trisodium phosphate, and then connected to a positive DC power source. A cathode (typically stainless steel) completes the circuit.
When current flows, titanium reacts with oxygen from the electrolyte. This forms a titanium dioxide (TiO₂) layer on the surface. This oxide layer isn't merely a coating; it's an integral part of the titanium itself. Its uniform thickness is critical for consistent color.
Anodization: An electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. For titanium, this process is unique in that it creates a transparent oxide layer that produces color through light interference.
Achieving the Gold Hue: Voltage and Oxide Thickness
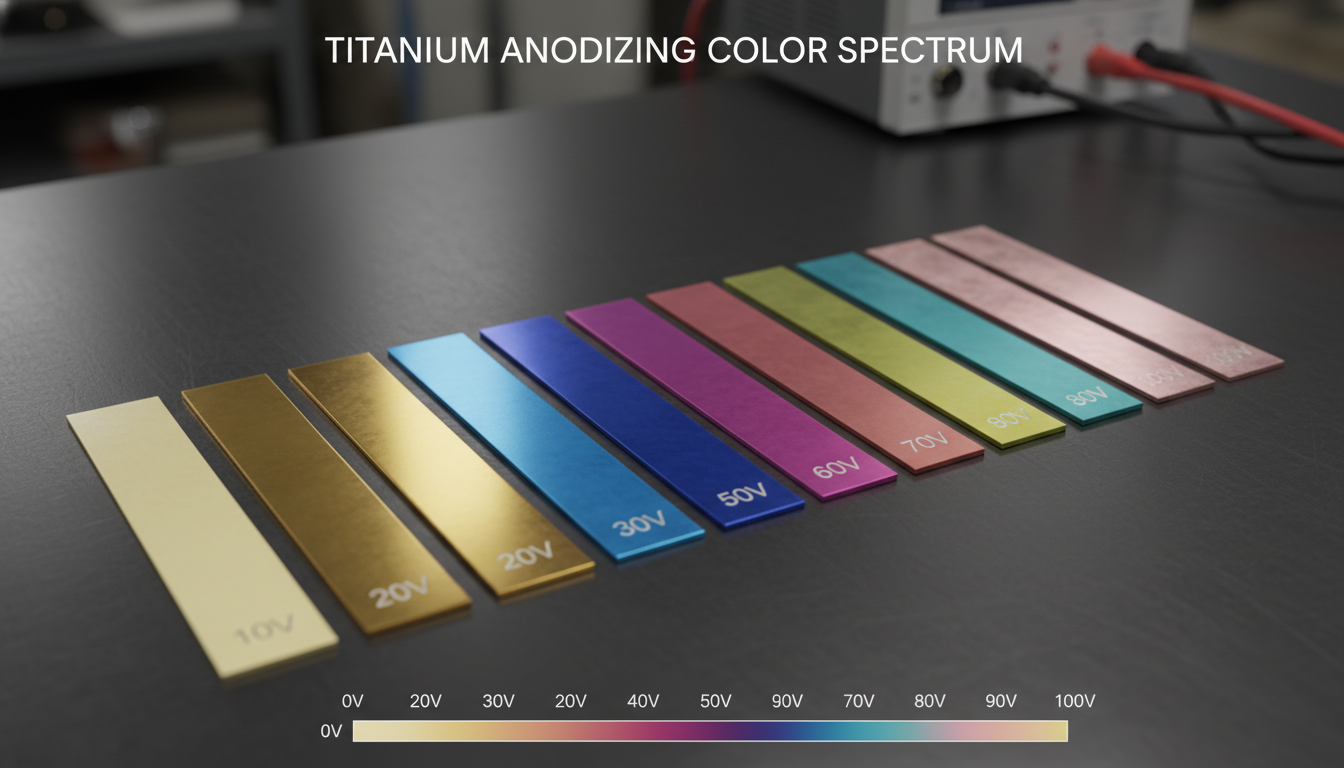
The specific gold color on anodized titanium is directly tied to the applied voltage during the process. Adjusting the voltage precisely controls the thickness of the oxide layer. This thin film then interacts with light.
Light interference is the principle at play. As white light hits the oxide layer, some light reflects off the top surface, while other light penetrates the layer and reflects off the underlying titanium. These two sets of light waves interfere with each other. Depending on the oxide layer's thickness, certain wavelengths of light are amplified or canceled out, resulting in a perceived color. For gold, this typically requires a specific voltage range, often around 60-80 volts, to achieve the correct oxide thickness (around 100-150 nanometers).

For more detailed insights into specific voltage charts for various titanium colors, resources like Finishing.com provide valuable technical data.
Key Factors Influencing the Gold Finish Quality
Achieving a consistent, high-quality gold finish on titanium demands meticulous control over several factors. Slight variations can lead to uneven coloring or undesirable hues.
Surface Preparation: This is paramount. The titanium surface must be impeccably clean and free of oils, dirt, or previous oxide layers. Mechanical polishing or sandblasting prior to cleaning can influence the final texture and reflective quality.
Electrolyte Composition: The type and concentration of the electrolyte solution affect the oxide growth rate and quality. Different electrolytes can yield slightly different color variations even at the same voltage.
Current Density and Temperature: Maintaining a stable current density and controlling the electrolyte temperature are crucial. Fluctuations can lead to inconsistent oxide thickness and, consequently, uneven coloration.
Titanium Grade: While most titanium alloys can be anodized, pure titanium (Grade 1-4) generally produces the most vibrant and consistent colors. Alloys like Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) can also be anodized, but results may vary slightly. Understanding different titanium alloys is key to predicting anodization outcomes.
Mastering these variables is what separates a mediocre finish from a truly stunning, uniform gold. Expert providers like China Titanium Factory understand these nuances, ensuring top-tier results for custom titanium fabrication and finishing.
Unveiling the Unique Properties of Gold Anodized Titanium
The allure of gold anodized titanium extends far beyond its captivating color. The anodization process itself enhances several critical material properties, making it an engineering marvel. It's not just about looking good; it's about performing better.
This process transforms the surface of titanium, imbuing it with characteristics essential for demanding applications. From medical devices to high-performance components, these enhanced properties are what truly set it apart.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
The anodic oxide layer formed on titanium is remarkably hard. This integral layer significantly increases the surface hardness of the material. Consequently, gold anodized titanium exhibits superior scratch and wear resistance compared to uncoated titanium or many other metallic finishes. It stands up to daily abuse.
Because the color isn't a separate coating, it won't chip, peel, or flake off. This inherent durability means the gold finish maintains its integrity and appearance much longer, even in high-contact applications.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
Titanium is already renowned for its natural corrosion resistance. The anodization process takes this a step further. The stable, passive titanium dioxide layer created during anodization provides an even more robust barrier against corrosive environments.
This enhanced protection makes gold anodized titanium an excellent choice for applications exposed to harsh chemicals, saltwater, or biological fluids. Its resistance to degradation ensures longevity and reliability in critical components.
Biocompatibility and Hypoallergenic Nature
Perhaps one of the most significant advantages of titanium, amplified by anodization, is its biocompatibility. The titanium dioxide layer is inert and non-toxic. It causes virtually no adverse reactions when in contact with human tissue or bodily fluids.
This makes gold anodized titanium ideal for medical implants, surgical tools, and body jewelry. For individuals with metal sensitivities, it's a hypoallergenic dream. Unlike gold plating, which might contain allergenic metals, anodized titanium offers peace of mind. Research from institutions like the National Institutes of Health consistently validates titanium's excellent biocompatibility.
Diverse Applications of Gold Anodized Titanium
The unique blend of aesthetic appeal and superior material properties makes gold anodized titanium incredibly versatile. It's found its way into industries where performance and presentation are equally non-negotiable. From a jeweler's workbench to an operating room, its utility is broad.
Jewelry Making: Aesthetic Appeal and Longevity
In the world of high-end jewelry, body jewelry, and luxury watches, gold anodized titanium shines. Its lightweight nature is a major draw. Think large, statement pieces that won't weigh you down. The vibrant, lasting gold color, coupled with its hypoallergenic properties, makes it a premium choice for direct skin contact.
It offers designers an alternative to traditional gold, providing a similar visual impact with enhanced durability and a fraction of the weight. No more green skin or tarnishing worries.
Medical and Dental Implants
This is where gold anodized titanium truly proves its mettle. Its exceptional biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are paramount in medical and dental fields. Surgical instruments, prosthetics, and dental implants often benefit from this finish.
The gold color can sometimes serve a functional purpose too, aiding in identification of different component sizes or types during surgery. More importantly, the inert oxide layer minimizes tissue reaction, promoting better integration with the body. China Titanium Factory produces precision titanium components for these critical applications.
Industrial and Architectural Design
Beyond personal adornment and medical use, gold anodized titanium plays a role in demanding industrial and architectural contexts. Its high strength-to-weight ratio combined with aesthetic durability makes it suitable for aerospace components where weight savings are critical, and specific visual identification might be useful.
In automotive applications, custom parts can benefit from both the resilience and distinctive look. For architectural design, decorative elements can leverage titanium's longevity and vibrant, non-fading gold finish to create striking, durable structures.
Gold Anodized Titanium vs. Other Gold-Colored Materials
When you want a gold aesthetic, you have options. But not all gold-colored finishes are created equal. Gold anodized titanium often stands head and shoulders above its counterparts, especially concerning durability, biocompatibility, and overall performance. Let's stack it against common alternatives.
Anodizing vs. Gold Plating: A Detailed Comparison
Gold plating is a common method for applying a thin layer of real gold onto a base metal. It's often used for decorative purposes. However, it comes with significant drawbacks when compared to anodization.
Anodization creates an integral oxide layer. Gold plating deposits a separate metallic layer. This difference is fundamental to their performance. Gold plating can wear off, scratch, and expose the underlying metal, which may tarnish or cause allergic reactions. Anodized titanium, conversely, is far more durable, colorfast, and inherently hypoallergenic since no foreign metals are applied.
PVD Coating vs. Anodizing for Titanium
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is another popular method for creating gold-like finishes, notably Titanium Nitride (TiN). TiN coatings are hard, wear-resistant, and have a distinct gold appearance. They are often used for tools and industrial components.
While PVD coatings offer excellent hardness and abrasion resistance, they are still a deposited layer. They can sometimes chip or delaminate under extreme stress. Anodization, as an integral oxide layer, avoids these issues. The aesthetic of anodized gold is also often described as richer and more iridescent, compared to the more opaque, metallic look of TiN.
Other Titanium Coloring Techniques
Besides anodization, other methods can color titanium, though they often have limitations compared to the electrochemical process:
Heat Coloring: Applying heat to titanium in the presence of oxygen can also create an oxide layer, producing various colors, including yellows and bronzes. However, precise color control is difficult, and the results are often less uniform and durable than anodization.
Chemical Coloring: Certain chemical baths can produce oxide films. Similar to heat coloring, achieving precise, consistent colors across a batch can be challenging.
These methods are generally less controlled and less robust than anodization, making them less suitable for high-precision or high-durability applications where consistent gold coloring is essential.
| Feature | Gold Anodized Titanium | Gold Plating (on Titanium) | PVD (TiN) Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Source | Light interference from TiO₂ layer | Thin layer of actual gold metal | Deposited Titanium Nitride compound |
| Durability | Excellent; integral, hard oxide layer | Fair; prone to wear, chipping, scratching | Very Good; hard, wear-resistant coating |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent; inert TiO₂ layer | Variable; depends on base metal and plating purity | Good; generally bio-inert |
| Appearance | Iridescent, rich gold, vibrant | Metallic gold, can be very bright | Opaque, metallic gold/brass tone |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Moderate; good value for durability | High; due to actual gold content | Moderate to High; specialized equipment |
Caring for Your Gold Anodized Titanium Products
While gold anodized titanium boasts impressive durability, proper care ensures its stunning finish lasts a lifetime. Think of it like a fine instrument; a little attention goes a long way. Protecting that vibrant gold means understanding how to clean and what to avoid.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Keeping your gold anodized titanium pristine is straightforward. Gentle is the key. For routine cleaning, a soft cloth and mild soap (like dish soap) with warm water are usually sufficient.
Simply wipe the surface, rinse thoroughly with clean water, and then pat dry with a lint-free cloth. Avoid abrasive sponges or harsh scrubbing, as these can dull the finish over time. For more stubborn grime, a soft-bristled brush can be used carefully.

Avoiding Damage and Prolonging Life
To keep that brilliant gold hue, steer clear of harsh chemicals. Ammonia-based cleaners, bleach, or abrasive polishes can degrade the anodized layer or cause discoloration. Likewise, avoid ultrasonic cleaners for anodized pieces, as the vibrations and harsh solutions can sometimes weaken the oxide film.
While the finish is scratch-resistant, it's not invincible. Store items separately to prevent them from rubbing against harder metals or sharp objects. With a little common sense, your gold anodized titanium will maintain its luster for years.
The Sustainable Choice: Environmental Benefits of Gold Anodized Titanium
Beyond its aesthetic and functional advantages, gold anodized titanium offers compelling environmental benefits. In an era focused on sustainability, the manufacturing choices matter. Anodization stands out as a more eco-conscious process compared to many traditional coloring or coating methods.
The process generates minimal waste and avoids the use of heavy metals often associated with plating. The primary byproduct is the electrolyte solution, which, when properly managed, poses fewer environmental risks than hazardous plating chemicals. This makes gold anodized titanium a smart choice for companies and consumers committed to greener practices.
For more on sustainable manufacturing practices in metal finishing, consult resources from organizations like the Products Finishing magazine, which often covers industry standards and advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gold Anodized Titanium
Is gold anodized titanium actual gold?
No, gold anodized titanium is not actual gold. The gold color is created by an electrochemical process called anodization, which forms a transparent oxide layer on the surface of the titanium. This layer interacts with light to produce the perception of gold, similar to how a prism creates colors, without any actual gold metal being present.
How durable is the gold color?
The gold color on anodized titanium is highly durable. Since it's an integral part of the titanium's surface (an oxide layer), it won't chip, peel, or fade like plated finishes. It offers excellent scratch and wear resistance, making it suitable for long-lasting applications. However, extreme abrasion or harsh chemicals can still damage the finish over time.
Is gold anodized titanium hypoallergenic?
Yes, gold anodized titanium is considered hypoallergenic. Titanium itself is renowned for its biocompatibility. The anodization process simply enhances the naturally occurring, inert titanium dioxide layer. This means it's safe for direct contact with skin and body tissue, making it an excellent choice for jewelry and medical implants, especially for those with sensitivities to other metals.
Can any titanium product be gold anodized?
Generally, most pure titanium grades (like Grade 1-4) and some alloys (like Ti-6Al-4V) can be gold anodized. However, the quality and consistency of the finish depend heavily on the titanium's surface condition, alloy composition, and the precision of the anodization process. Complex geometries might require specialized techniques. It's best to consult with experts like China Titanium Factory for specific product capabilities.
What are the main advantages of gold anodized titanium over gold plating?
Gold anodized titanium offers several advantages: superior durability as the color is integral to the surface, not a separate layer; enhanced biocompatibility because no foreign metals are applied; lighter weight; and a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process. Gold plating, while using real gold, is prone to wear, chipping, and can be less suitable for sensitive skin or harsh environments.
Need Custom Gold Anodized Titanium Solutions?
From medical-grade components to striking architectural elements, our expertise in titanium fabrication and advanced anodizing techniques ensures exceptional quality and precision. Let us bring your vision to life with durable, beautiful gold anodized titanium.
Get a Quote Today