Introduction to Titanium Alloy Grades: Properties, Classification, and Importance
Engineers consistently seek materials that offer superior performance under challenging conditions. Titanium alloys represent a critical solution in this pursuit. These remarkable materials combine an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio with outstanding corrosion resistance.
This unique combination makes them indispensable across a wide range of industries. These include aerospace, medical, marine, and high-performance industrial applications. Understanding the different titanium alloy grades is crucial for optimal material selection.
Choosing the correct grade ensures maximum efficiency, safety, and longevity for any given project. This guide provides an authoritative overview of titanium's properties and classifications. It also explains the importance of selecting the right grade.

Titanium is a transition metal. It exhibits excellent biocompatibility and high melting points. Its unique properties stem from its atomic structure and crystal phases. These phases can be manipulated through alloying and heat treatment.
"Titanium alloys are metallic materials composed primarily of titanium and other chemical elements. These elements enhance specific mechanical and physical properties. They typically improve strength, ductility, and temperature resistance."
The classification of titanium alloys broadly falls into three categories. These are alpha (α), alpha-beta (α+β), and beta (β) alloys. Each category possesses distinct microstructures and property sets. These differences dictate their suitability for various demanding environments.
For complex projects, sourcing reliable materials is paramount. Chinatitaniumfactory.com offers a comprehensive range of high-quality titanium products. The company provides materials tailored for specific industrial needs.
Commercially Pure (CP) Titanium Grades: Unpacking the Fundamentals
Commercially Pure (CP) titanium defines a series of unalloyed titanium grades. These grades are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and formability. They are classified based on their oxygen content. Higher oxygen content generally correlates with increased strength and reduced ductility.
CP titanium is highly sought after in industries where material purity is critical. These include chemical processing and marine applications. It is also essential for certain medical devices.
Grade 1 Titanium: Properties and Uses
Grade 1 represents the softest and most ductile of the CP titanium grades. It offers superior formability. This makes it ideal for applications requiring extensive cold forming. Its excellent corrosion resistance is also a key feature. Grade 1 typically contains the lowest oxygen and iron content.
Common uses include explosive cladding, medical device components, and architectural applications. It is also used in desalination plants. The material's high ductility allows for intricate designs.
Grade 2 Titanium: The Most Common CP Grade
Grade 2 titanium is the most widely used CP grade. It offers a good balance of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Its properties make it versatile for many industrial applications. These include heat exchangers, chemical processing equipment, and power generation components.
The material is easily weldable and fabricable. This contributes to its popularity. It provides reliable performance in corrosive environments.
Grade 3 and Grade 4 Titanium: Increased Strength
Grade 3 titanium offers higher strength than Grade 2. It maintains good ductility and corrosion resistance. It finds uses in pressure vessels and aerospace structures. Grade 4 is the strongest of the CP grades. It provides excellent strength with moderate formability.
Grade 4 is often chosen for airframe components and surgical fixtures. Its robust nature suits demanding structural applications. Selecting the right CP grade depends on specific mechanical and environmental requirements.
The Workhorse Alloy: Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) and its Versatility
Ti-6Al-4V, commonly known as Grade 5 titanium, is the most widely used titanium alloy. It accounts for over 50% of all titanium applications. This alpha-beta alloy offers an outstanding combination of properties. These include high strength, light weight, and excellent corrosion resistance.
Its versatility makes it indispensable across numerous demanding sectors. It is a cornerstone material for aerospace, automotive, and high-performance industrial applications. The alloy's composition of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium contributes to its superior mechanical characteristics.

Key Properties and Advantages of Grade 5
Grade 5 titanium boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio. This is significantly higher than many steels and aluminum alloys. It also exhibits superior fatigue resistance. This characteristic is vital for components subjected to cyclic loading.
The alloy maintains its strength at elevated temperatures. It resists cracking and propagation effectively. These properties make it ideal for critical structural components. These components are found in aircraft, rockets, and racing cars.
Furthermore, Ti-6Al-4V offers good weldability and excellent fabrication characteristics. This allows for complex part geometries. Its resistance to general and pitting corrosion is also noteworthy.
Multi-Standard Comparison: Ti-6Al-4V
Ti-6Al-4V is recognized globally under various standards. This ensures consistent quality and performance worldwide. The table below compares common designations and their typical properties.
| Standard/Designation | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM B348 Grade 5 | 895 min | 828 min | 10 min | Aerospace, Industrial |
| AMS 4911 | 895 min | 828 min | 10 min | Aerospace Sheet/Plate |
| MIL-T-9047G | 895 min | 828 min | 10 min | Military Aerospace |
| ISO 5832-3 (Biomedical) | 895 min | 828 min | 10 min | Surgical Implants (ELI) |
Note: Values are typical minimums and can vary based on specific processing and heat treatment. For precise specifications, refer to the respective standard documents. AZoM provides detailed material properties for various alloys.
Medical and Biomedical Applications: Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23)
Ti-6Al-4V ELI, also known as Grade 23, is a specialized variant of Grade 5. The "ELI" stands for "Extra Low Interstitial." This designation indicates reduced levels of interstitial elements. These include oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and iron. Lower interstitial content significantly enhances ductility and fracture toughness.
These improved properties are critical for medical and biomedical applications. Grade 23 is the preferred material for permanent implantable devices. Its enhanced biocompatibility and mechanical integrity are paramount.
Enhanced Biocompatibility and Fracture Toughness
Biocompatibility is the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific application. Ti-6Al-4V ELI exhibits excellent biocompatibility. It does not provoke adverse reactions within the human body. This makes it safe for long-term implantation.
Its superior fracture toughness is equally important. It ensures the integrity of implants under physiological stresses. This reduces the risk of failure in critical applications. These applications include orthopedic and dental implants.
Critical Role in Medical Device Manufacturing
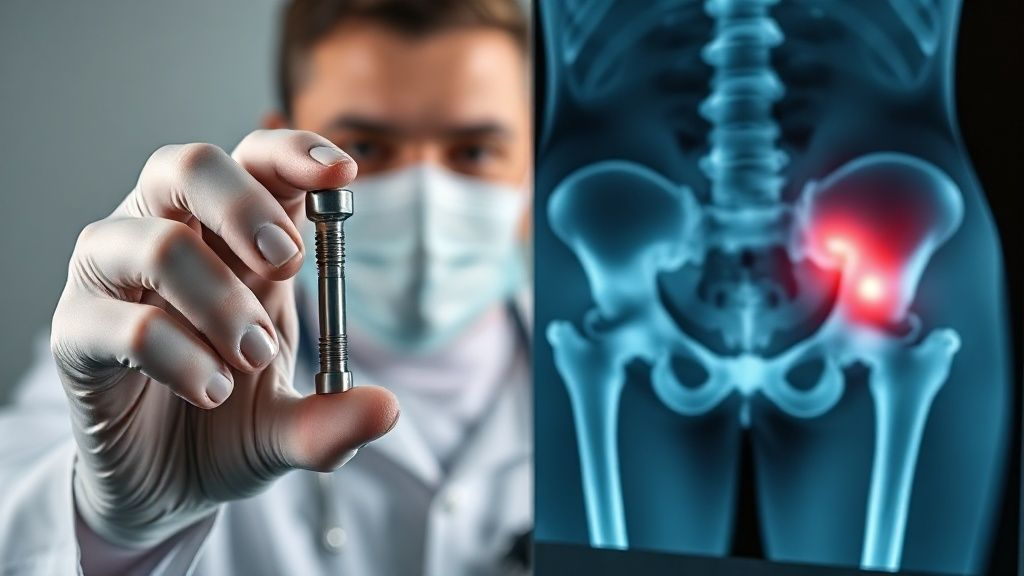
Grade 23 titanium plays a critical role in manufacturing various medical devices. It is used in surgical implants like hip and knee replacements. Spinal fusion devices also rely on this material. Dental implants and surgical instruments benefit from its properties.
Its resistance to body fluids and sterilizing agents ensures long-term functionality. The material's strength allows for smaller, less invasive implant designs. This improves patient outcomes. For specialized medical-grade titanium, manufacturers often turn to experts like Chinatitaniumfactory.com.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Other Key Titanium Alloys
While CP titanium and Ti-6Al-4V dominate the market, many other titanium alloys exist. These specialized alloys are engineered for specific, often extreme, applications. They offer unique metallurgical characteristics. These characteristics include enhanced high-temperature strength, creep resistance, or specific strength-to-weight profiles.
Understanding these alloys expands an engineer's toolkit. It allows for more precise material selection in advanced engineering projects.
Ti-5Al-2.5Sn: High-Temperature Stability
Ti-5Al-2.5Sn is an alpha alloy known for its good weldability and excellent stability at elevated temperatures. It maintains its mechanical properties up to 480°C (900°F). This makes it suitable for aerospace engine components and airframe structures. It also finds use in cryogenic applications. Its lack of heat treatability simplifies processing.
Ti-3Al-2.5V: Seamless Tubing Specialist
Ti-3Al-2.5V, or Grade 9, is an alpha-beta alloy. It offers medium strength and good cold formability. It is often called "half-6-4" due to its lower alloy content compared to Grade 5. This alloy is particularly favored for seamless tubing applications. These include hydraulic lines in aircraft and sporting goods like bicycle frames.
Its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and ductility make it a top choice for these uses.

Beta Titanium Alloys: For Ultra-High Strength
Beta titanium alloys, such as Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al and Ti-15V-3Cr-3Al-3Sn, are heat-treatable. They can achieve very high strengths. These alloys possess excellent hardenability. They are often used for fasteners, landing gear, and springs. Their superior strength and fatigue properties are highly valued.
However, beta alloys typically have lower ductility and require more complex processing. Their use is reserved for applications where maximum strength is paramount. MatWeb offers a vast database of material properties, including various titanium alloys.
Comparative Analysis: Selecting the Right Titanium Grade for Your Project
Choosing the optimal titanium grade is a critical engineering decision. It significantly impacts a project's performance, cost, and manufacturability. This selection process requires a thorough understanding of each grade's unique properties. It also demands consideration of the application's specific requirements.
Factors such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, operating temperature, and processing characteristics all play a role. Cost considerations and availability are also important practical aspects.
Key Factors in Material Selection
Mechanical Properties: Evaluate tensile strength, yield strength, ductility, and fracture toughness.
Corrosion Resistance: Consider the operating environment and potential exposure to aggressive chemicals.
Temperature Range: Assess both cryogenic and high-temperature performance requirements.
Formability and Weldability: Determine ease of fabrication for complex parts.
Cost and Availability: Balance performance with budget and supply chain logistics.
Titanium Grade Comparison Chart
The following table provides a quick reference for comparing popular titanium grades. It highlights their primary characteristics and typical applications. This helps guide initial material selection decisions.
| Grade | Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Relative Cost (1-5, 5 being highest) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP Grade 1 | Alpha | Highest ductility, excellent corrosion resistance | Chemical processing, desalination, medical devices | 1 |
| CP Grade 2 | Alpha | Good balance of strength, ductility, corrosion | Heat exchangers, general industrial, marine | 2 |
| Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | Alpha-Beta | High strength, lightweight, fatigue resistance | Aerospace, automotive, high-performance industrial | 3 |
| Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) | Alpha-Beta | Enhanced biocompatibility, superior fracture toughness | Medical implants, surgical devices | 4 |
| Grade 9 (Ti-3Al-2.5V) | Alpha-Beta | Medium strength, good formability, excellent for tubing | Hydraulic lines, sporting goods | 3 |
| Beta Alloys (e.g., Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al) | Beta | Ultra-high strength, heat-treatable, good hardenability | Fasteners, landing gear, springs | 5 |
For detailed technical specifications and to discuss specific project requirements, customers can contact the experts at Chinatitaniumfactory.com. Their team offers tailored solutions for complex engineering challenges.
Interactive Material Selection: Tools and Resources for Engineers
Modern engineering demands efficient and precise material selection. Digital tools and resources streamline this complex process. They provide engineers with immediate access to vast material databases and comparison functionalities. These tools help in making informed decisions quickly.
Interactive calculators and property comparison matrices are invaluable. They aid in evaluating different titanium grades against specific design parameters. This reduces design cycles and minimizes potential errors.
Leveraging Digital Platforms for Alloy Selection
Many online platforms offer comprehensive material property databases. These resources allow engineers to search, filter, and compare various titanium alloys. They can evaluate mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties side-by-side. This capability is essential for optimizing material choices.
Some tools also include cost estimation features. This helps in budgeting for materials. They provide insights into the economic implications of different grade selections. Utilizing these resources can significantly enhance project efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits of Interactive Tools
Accelerated Design: Quickly identify suitable materials, shortening development timelines.
Reduced Risk: Minimize the chance of material failure by selecting the most appropriate grade.
Cost Optimization: Compare material costs and processing requirements effectively.
Knowledge Enhancement: Access detailed technical data and industry standards.
For example, the ASM International materials database offers extensive information. It covers a vast array of metals, including titanium alloys. These resources empower engineers to make data-driven decisions. They ensure the selection of the best material for every application.
Real-World Impact: Case Studies in Titanium Alloy Applications
The versatility and high performance of titanium alloys are best illustrated through real-world applications. These case studies demonstrate how specific grades address complex engineering challenges. They highlight titanium's practical value across diverse industries.
From the depths of the ocean to the vastness of space, titanium delivers unparalleled reliability. Its unique properties enable advancements not possible with other materials. The examples below showcase its critical role.
Aerospace: Structural Components (Ti-6Al-4V)
Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) is extensively used in commercial aircraft and military jets. Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio reduces overall aircraft mass. This leads to improved fuel efficiency and increased payload capacity. Components include landing gear, engine parts, and airframe structures. The alloy's fatigue resistance ensures long operational life under extreme conditions.
Medical: Implants (Ti-6Al-4V ELI)
Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23) is the gold standard for medical implants. Its biocompatibility and resistance to body fluids are crucial. It is used in orthopedic prostheses, dental implants, and surgical instruments. The material's fracture toughness provides durability. This ensures patient safety and long-term functional success.
Marine and Offshore: Components (CP Titanium)
Commercially Pure titanium grades, especially Grade 2, excel in marine environments. Their exceptional resistance to seawater corrosion is unparalleled. They are used in heat exchangers, submersible components, and offshore platforms. This prevents costly maintenance and extends equipment life. Chinatitaniumfactory.com provides various titanium products and services suitable for these harsh conditions.
Global Sourcing and Supply Chain: Navigating Titanium Procurement
Procuring high-quality titanium alloys requires navigating a complex global supply chain. Identifying reputable suppliers is paramount. It ensures the integrity and performance of the final product. Factors like material certification, stock availability, and lead times are critical considerations.
Engineers and procurement specialists must understand the nuances of the titanium market. This includes regional specialties and regulatory compliance. Establishing strong relationships with trusted suppliers is a key strategy.
Identifying Reputable Suppliers
A reputable supplier provides certified materials that meet international standards. They offer comprehensive documentation, including mill test reports. Experience in handling various titanium grades is also important. Suppliers should demonstrate a commitment to quality control and customer service.
Companies like Chinatitaniumfactory.com are known for their expertise in titanium manufacturing and distribution. They ensure clients receive materials that meet exact specifications for critical applications.
Stock Availability and Lead Times
Titanium alloys, especially specialized grades, can have varying availability. Strategic planning is crucial for procurement. Understanding typical lead times for custom orders is also important. Maintaining a strong communication channel with suppliers helps manage expectations. It also mitigates potential project delays.
Global events can impact supply chains. Therefore, having diversified sourcing options is a wise approach. This ensures continuity of supply for critical projects. The U.S. Geological Survey provides statistics on titanium production and consumption, offering insights into market trends.
The Future of Titanium: Emerging Alloys and Sustainable Practices
The field of titanium metallurgy continues to evolve. Researchers are constantly developing new alloys. These alloys offer enhanced properties for future applications. Advancements in manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing, are also transforming the industry. This opens new possibilities for complex part geometries and optimized material use.
Sustainability is also a growing focus. Efforts to improve titanium recycling and reduce environmental impact are gaining traction. The future of titanium promises even greater innovation and responsible production.
Advancements in Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing (AM), or 3D printing, is revolutionizing titanium fabrication. It allows for the creation of intricate, near-net-shape components. This reduces material waste and lead times. AM is particularly beneficial for complex aerospace and medical parts. New titanium powders and printing techniques are continuously emerging. These expand the capabilities of this technology.

Sustainable Practices and Recycling
Titanium production is energy-intensive. Therefore, recycling plays a vital role in reducing its environmental footprint. Efforts focus on improving scrap collection and processing technologies. This ensures that valuable titanium can be reused. The goal is to create a more circular economy for this critical material. Sustainable sourcing and manufacturing are becoming increasingly important for industry leaders.
The development of new, more efficient extraction methods is also underway. These aim to lower the energy consumption of primary titanium production. The International Titanium Association (ITA) actively promotes advancements in titanium technology and sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Alloy Grades
What is the primary difference between Commercially Pure (CP) titanium and titanium alloys?
CP titanium contains varying levels of interstitial elements, primarily oxygen, which determine its grade (Grade 1-4). It is known for excellent corrosion resistance and ductility. Titanium alloys, like Ti-6Al-4V, incorporate other metallic elements (e.g., aluminum, vanadium) to significantly enhance mechanical properties such as strength, fatigue resistance, and high-temperature performance, often at the expense of some ductility or ease of formability.
Why is Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) so widely used in aerospace?
Ti-6Al-4V is favored in aerospace due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior fatigue resistance, and good corrosion resistance. These properties allow for the design of lighter, more durable aircraft components, leading to improved fuel efficiency and operational safety. It performs reliably under the extreme stresses and temperatures encountered in flight.
What does "ELI" mean in Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23)?
"ELI" stands for "Extra Low Interstitial." This indicates that the alloy has significantly reduced levels of interstitial elements like oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and iron. This reduction enhances the material's ductility and fracture toughness, making it highly suitable for critical medical and biomedical implants where superior resistance to fracture and long-term reliability within the human body are essential.
Are there titanium grades suitable for high-temperature environments?
Yes, several titanium alloys are designed for high-temperature applications. For instance, Ti-5Al-2.5Sn (an alpha alloy) offers good stability and strength up to approximately 480°C (900°F). Other specialized high-temperature alloys, often with additions of silicon or zirconium, are developed for even more extreme conditions in advanced aerospace engines and industrial processes.
How do I ensure I select the correct titanium grade for my project?
Selecting the correct grade involves a comprehensive evaluation of your project's specific requirements. Consider factors such as required mechanical properties (strength, ductility), operating environment (corrosion, temperature), fabrication needs (weldability, formability), and cost. Consulting with material experts and utilizing material selection tools or databases can provide invaluable guidance. Chinatitaniumfactory.com's specialists can assist with detailed material recommendations.
Ready to Optimize Your Material Selection?
Precision in material choice drives success in demanding industries. Leverage expert knowledge and a diverse inventory of high-quality titanium alloys for your next project.
Consult Our Titanium Experts