Corrosion poses a significant threat to industrial infrastructure and valuable assets. This pervasive issue can lead to costly repairs, operational failures, and safety hazards. Protecting metal structures from degradation is paramount across many sectors.
Sacrificial anodes offer a proven, cost-effective solution. They provide essential electrochemical protection. Understanding their purpose is key to ensuring the longevity and reliability of your critical equipment.
What is a Sacrificial Anode and Why is it Essential?

A sacrificial anode is a critical component in corrosion prevention. It safeguards metals through cathodic protection. This method is vital for preserving valuable assets.
Corrosion is a natural process. Metals degrade due to reactions with their environment. This can compromise structural integrity and operational safety.
Sacrificial anodes are designed to corrode instead of the protected metal. They serve as an active defense mechanism. This extends the lifespan of equipment significantly.
A sacrificial anode is a metal, typically zinc, magnesium, or aluminum, used to protect another metal from corrosion by undergoing oxidation itself.
Their essential role lies in preventing premature asset degradation. They ensure the reliability of critical infrastructure. This includes pipelines, marine vessels, and storage tanks. China Titanium Factory specializes in high-quality materials for such demanding applications.
Without anodes, corrosion can lead to expensive repairs. It can also cause dangerous structural failures. Their use is a fundamental aspect of effective asset protection.
The Science Behind the Shield: How Sacrificial Anodes Prevent Corrosion
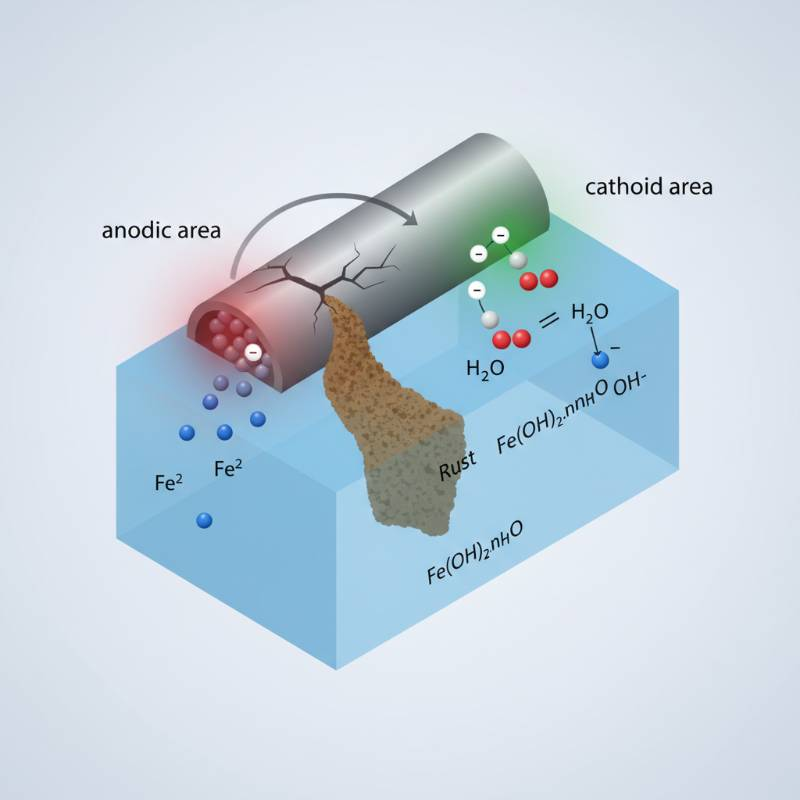
The protection offered by sacrificial anodes relies on electrochemical principles. Specifically, it addresses galvanic corrosion. This occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact.
An electrolyte, like water or soil, must also be present. This creates an electrical circuit. One metal becomes the anode; the other becomes the cathode.
The more "active" metal acts as the sacrificial anode. It gives up its electrons. These electrons flow to the "less active" metal, which is the cathode. This process protects the cathode from corroding.
Galvanic corrosion is an electrochemical process. It occurs when two dissimilar metals are electrically coupled in the presence of an electrolyte.
The anode metal corrodes preferentially. It effectively "sacrifices" itself. This prevents the primary structure from degrading. The electron flow stops the corrosion reaction on the protected metal. This is the core of cathodic protection. For robust solutions, consider consulting experts in materials science, such as those at China Titanium Factory's services division.
This mechanism is highly effective. It is a cornerstone of modern corrosion control strategies. The material selection for anodes is critical for optimal performance. NACE International provides further insights into galvanic corrosion.
Unpacking the 'Purpose': Key Benefits of Sacrificial Anodes
The primary purpose of sacrificial anodes is clear: asset preservation. They deliver significant advantages across numerous applications. These benefits translate into substantial long-term value.
One major benefit is extending equipment life. Anodes protect critical components from rust and decay. This means fewer replacements and longer operational periods.
They also provide cost-effective corrosion control. Preventing corrosion is far cheaper than repairing damage. This proactive approach saves substantial capital expenditure.
Enhanced operational safety is another crucial aspect. Structural integrity remains intact. This reduces the risk of failures and accidents. High-quality anode products contribute directly to safer operations.
Reduced maintenance requirements are a practical advantage. Less corrosion means less frequent inspections and repairs. This frees up resources and reduces downtime.
Ultimately, anodes protect your investment. They ensure assets perform reliably for years. This makes them indispensable in demanding industrial environments.
Choosing Your Protector: Types of Sacrificial Anode Materials

Selecting the right anode material is crucial. It depends on the environment and the metal being protected. Zinc, magnesium, and aluminum are the most common types.
Zinc Anodes
Zinc anodes are highly effective in saltwater. They have a stable electrochemical potential. This makes them ideal for marine applications. Boats, docks, and offshore structures commonly use zinc. They are less effective in freshwater or soil. This is due to a passive film that can form on their surface.
Magnesium Anodes
Magnesium anodes are the most active of the three. They are primarily used in freshwater and soil. Their high driving voltage provides robust protection. This is vital for underground pipelines and water heaters. However, their high activity means they deplete faster. They are unsuitable for saltwater use.
Aluminum Anodes
Aluminum anodes offer a versatile option. They perform well in saltwater and brackish water. They also have a higher capacity than zinc. This means they last longer for the same weight. Aluminum anodes are often alloyed with indium or zinc. This prevents passivation. They are a good choice for larger vessels and offshore platforms.
Anode Material Comparison
Understanding the differences is key to optimal protection. Here is a brief comparison:
| Material | Primary Application | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc | Saltwater | Stable potential, reliable in marine environments. |
| Magnesium | Freshwater, Soil | Highest driving voltage, fast depletion. |
| Aluminum | Saltwater, Brackish Water | High capacity, good balance of performance and longevity. |
Environmental impact is also a consideration. All materials are generally safe. However, proper disposal is always recommended. Consult with a specialist for specific environmental concerns.
Where Sacrificial Anodes Stand Guard: Common Applications
Sacrificial anodes are indispensable across a wide array of industries. Their utility spans from marine environments to residential systems. They ensure critical infrastructure remains protected.
Safeguarding Marine Vessels: Boats, Docks, and Offshore Structures
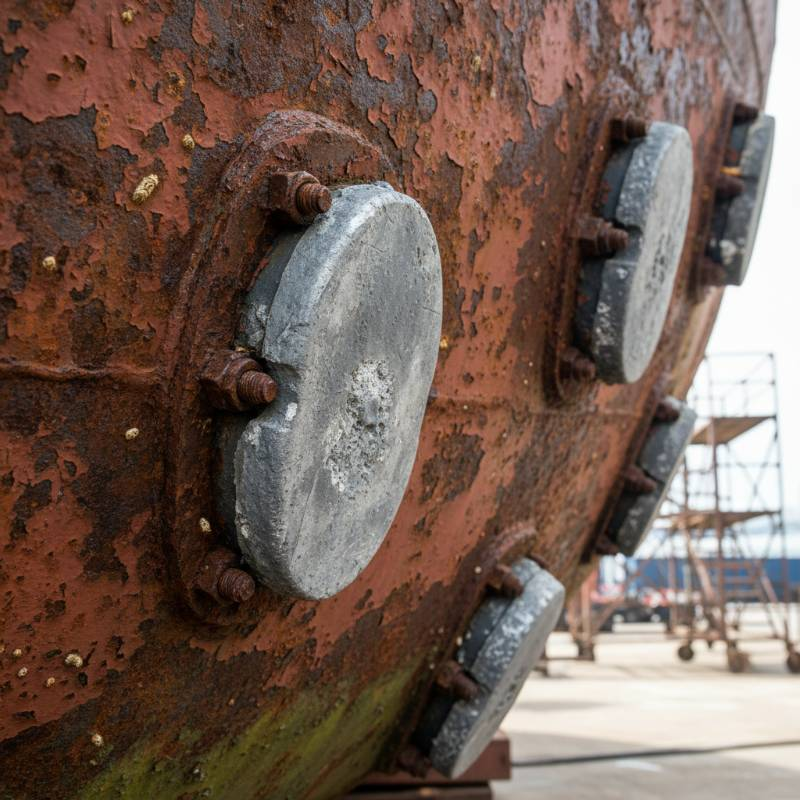
Marine environments are notoriously corrosive. Saltwater accelerates metal degradation. Sacrificial anodes are vital here. They protect hulls, propellers, rudders, and other underwater metals.
Boats and yachts rely on zinc or aluminum anodes. These prevent galvanic corrosion from eating away at metal components. Docks and piers also benefit from anode protection. Large offshore platforms, like oil rigs, use extensive anode systems. These systems safeguard massive steel structures from the harsh ocean environment. China Titanium Factory offers robust solutions for marine applications.
Protecting Home Essentials: Water Heaters and HVAC Systems
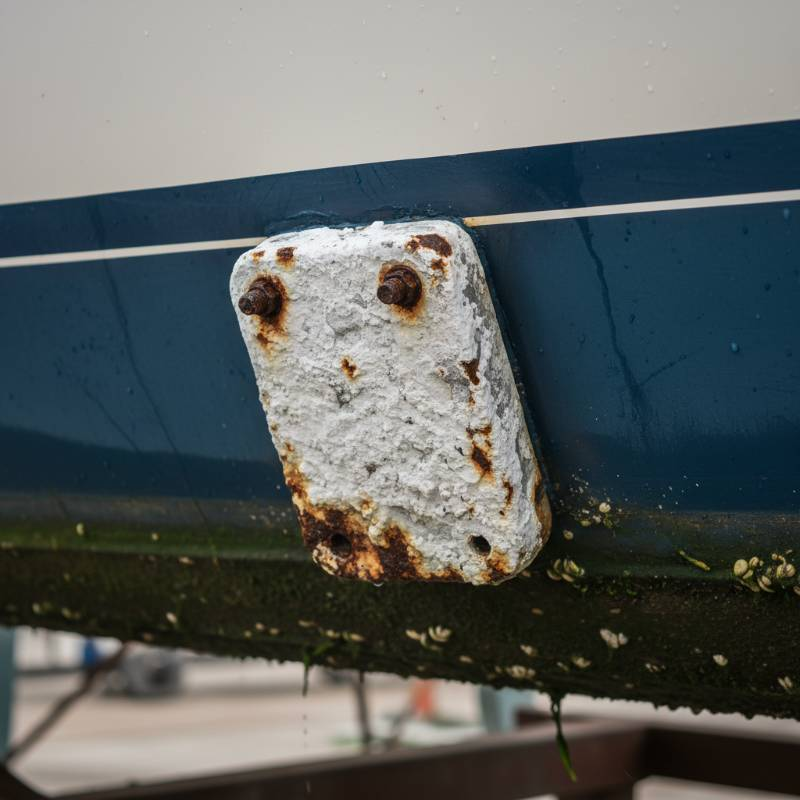
Corrosion isn't limited to industrial settings. It affects everyday household items. Water heater tanks are a prime example. An anode rod prevents internal tank corrosion.
These rods are typically made of magnesium or aluminum. They sacrifice themselves to protect the steel tank. This extends the water heater's life significantly. Without an anode rod, tanks would quickly rust through. HVAC systems with water-based components also benefit from this protection. This ensures efficiency and longevity for homeowners.
Underground Guardians: Pipelines and Storage Tanks
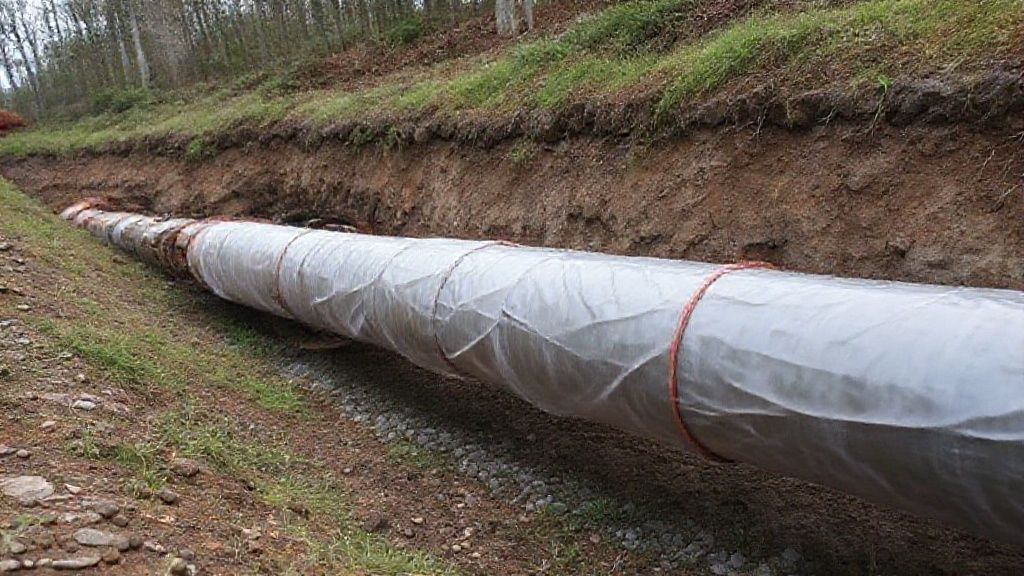

Buried metal structures face unique corrosion challenges. Soil conditions, moisture, and varying pH levels can cause rapid degradation. Oil and gas pipelines are critical assets.
Sacrificial anodes, often magnesium, protect these pipelines. They are strategically buried along the pipeline route. This prevents external corrosion. Underground storage tanks (USTs) also require this protection. Anodes safeguard tanks holding fuel or chemicals. This prevents leaks and environmental contamination. Cathodic protection is a regulatory requirement for many buried structures. The EPA provides guidelines for UST protection.
Beyond Sacrificial: Comparing Corrosion Protection Methods
While sacrificial anodes are highly effective, other methods exist. Understanding these options is vital. It allows for comprehensive corrosion control strategies.
Sacrificial vs. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP)
Sacrificial cathodic protection is passive. It uses the natural potential difference between metals. Impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) is active. It uses an external power source.
ICCP employs inert anodes and a DC power supply. This forces current to flow to the protected structure. ICCP is suitable for large structures. It can provide higher levels of protection. However, it requires more maintenance and monitoring. Sacrificial anodes are simpler and require no external power. They are ideal for remote or smaller applications.
Other Corrosion Control Methods
Corrosion inhibitors are chemicals. They are added to environments to slow corrosion. Coatings and linings provide a physical barrier. They separate the metal from corrosive elements. Material selection is also critical. Using corrosion-resistant alloys can prevent issues. Titanium, for example, offers exceptional corrosion resistance. Titanium bars and other forms are excellent for highly corrosive settings.
The best method depends on the specific scenario. A combination of strategies often yields optimal results. Experts at China Titanium Factory can guide you.
Ensuring Continuous Protection: Maintenance and Replacement of Sacrificial Anodes
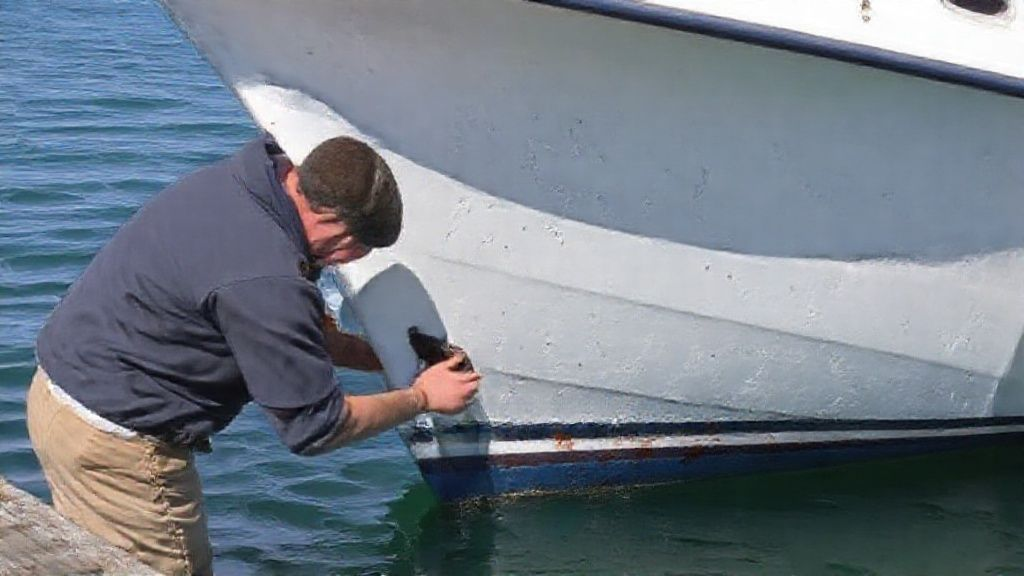

Sacrificial anodes are designed to deplete over time. Their effectiveness diminishes as they corrode. Regular inspection and timely replacement are critical.
Visual inspection is the primary method. Check anodes for signs of significant depletion. They should show signs of active corrosion. If an anode looks brand new, it might not be working. This indicates a potential problem with the electrical connection.
The typical lifespan of an anode varies. Factors include environment, size, and material. Marine anodes typically last one to three years. Water heater anode rods can last five to ten years. However, high water hardness can shorten this. It is important to adhere to manufacturer recommendations.
Replacing depleted anodes maintains continuous protection. Failing to replace them leaves your assets vulnerable. This can lead to costly corrosion damage. Keep records of inspection and replacement dates. This ensures a proactive maintenance schedule. Stay informed with industry best practices for anode maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sacrificial Anodes
What happens if a sacrificial anode isn't replaced?
If a sacrificial anode is not replaced, it will eventually deplete completely. Once depleted, the protected metal will no longer receive cathodic protection. This leaves it vulnerable to corrosion, leading to damage and reduced lifespan. For example, a water heater tank could rust through much faster.
How do I know which type of anode to use?
The correct anode type depends on the environment. Use zinc or aluminum anodes for saltwater. Magnesium anodes are best for freshwater and soil. Always consider the specific metal you are protecting. Consulting with a corrosion expert is recommended for complex applications.
Can I install a sacrificial anode myself?
For simple applications, like a boat propeller anode, DIY installation is possible. Water heater anode rods can also be replaced by a homeowner. However, for critical infrastructure like pipelines, professional installation is essential. Proper electrical contact is crucial for effectiveness. Incorrect installation can render the anode useless.
Are sacrificial anodes environmentally friendly?
Generally, sacrificial anodes are considered environmentally safe. The corrosion products are typically non-toxic. Zinc, magnesium, and aluminum are common elements. However, proper disposal of depleted anodes is important. This prevents any potential environmental impact. Always check local regulations for disposal.
Ensure Unwavering Asset Protection
Don't let corrosion compromise your valuable investments. Partner with a global leader in high-performance materials. Contact China Titanium Factory today for expert solutions and superior sacrificial anodes that guarantee reliability and efficiency.
Get a Quote