In the world of advanced materials, finding a finish that is both visually striking and exceptionally durable can be a challenge. Black anodized titanium rises to this occasion, offering a unique combination of aesthetic appeal and robust performance. This comprehensive guide explores the science, benefits, and diverse applications of this remarkable material, providing a deep dive into why it has become a premier choice across high-tech industries.

At its core, anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the naturally occurring oxide layer on a metal's surface. For titanium, this process can be precisely controlled to produce a range of colors, including a deep, true black. Unlike paints or platings, this anodized titanium black finish is not an additive layer but an integral part of the titanium itself.
The process involves immersing a titanium part in a specialized electrolyte bath, such as one containing manganese sulfate, and passing an electrical current through it. This oxidizes the surface, creating a thicker, more robust layer of titanium dioxide. By carefully manipulating the voltage and the electrolyte composition, the thickness and structure of this oxide layer can be controlled to absorb light, resulting in a durable, non-reflective black anodizing finish. This is distinct from Type II anodizing, which often uses dyes to achieve coloration.
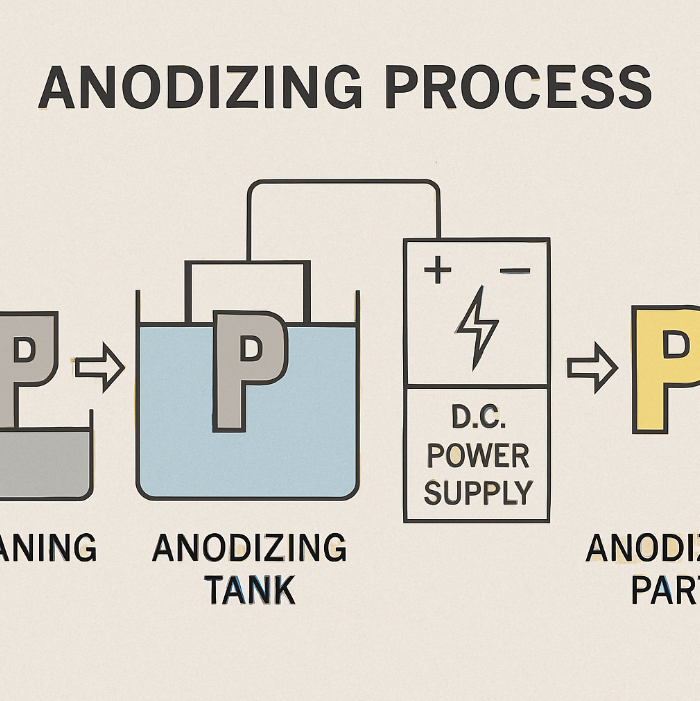
The final appearance and properties of anodized black titanium can also depend on the specific alloy being used. Different grades of titanium will react differently to the anodizing process.
| Titanium Grade | Anodizing Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grade 2 (Commercially Pure) | Tends to produce a dark gray or muted black finish with very strong adhesion. |
| Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | Can achieve a deep, matte black finish, making it popular for aesthetic applications. |
| Grade 6 (Ti-5Al-2.5Sn) | Often considered optimal, producing a consistent and durable black finish. |
The term 2g black anodized titanium often refers to a specific proprietary process or a finish achieved on a particular grade, emphasizing its quality and suitability for applications like high-end body jewelry where precision and biocompatibility are paramount.
The popularity of black anodized titanium stems from a powerful set of benefits that make it superior to many other materials and coatings.
The anodizing process creates a hardened surface that is highly resistant to scratches, scuffs, and general wear and tear. This makes it an ideal titanium coating for high-contact parts and products that need to withstand demanding conditions while maintaining their appearance.
Titanium is naturally resistant to corrosion, and the anodizing process enhances this property even further. The thickened oxide layer provides an inert barrier against a wide range of chemicals, salts, and environmental factors, preventing rust and degradation. This is crucial for components used in marine, chemical, or medical environments.
One of titanium's most celebrated properties is its incredible strength-to-weight ratio. It is as strong as steel but around 45% lighter. The anodizing process adds negligible weight, ensuring that components remain light and strong, a critical factor in industries like aerospace and high-performance automotive.
The deep, non-reflective black finish of anodized black titanium is highly sought after for its sleek, modern aesthetic. Beyond looks, the non-glare surface is a functional benefit in applications like military hardware, surgical instruments, and cockpit instrumentation where reducing reflections is essential.
The unique properties of black anodized titanium have led to its adoption in a wide array of demanding fields.
Aerospace and Defense: Used for fasteners, structural components, engine parts, and missile casings where weight, strength, and stealth are critical. The non-reflective surface is a key advantage for military applications.
Medical and Dental: Its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion from bodily fluids make it perfect for surgical instruments, orthopedic implants (like bone screws), and dental hardware. The black color can also provide contrast against tissue during surgery.
Automotive and Motorsport: Found in high-performance exhaust systems, suspension components, valves, and decorative trim. Its durability and heat resistance are key benefits in this environment.
Consumer Electronics: The premium look and feel, combined with its durability, make it a popular choice for the casings of smartphones, laptops, and high-end watches.
Jewelry and Fashion: As a hypoallergenic and durable material, black titanium is increasingly used for rings, bracelets, and other accessories, offering a modern and sophisticated alternative to traditional metals.
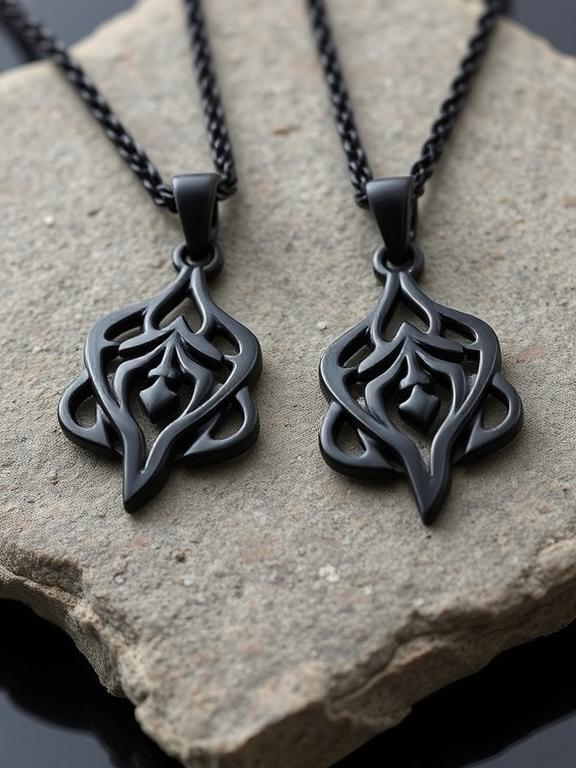

How does black anodizing stack up against other common black finishes like PVD and Cerakote?
| Feature | Black Anodized Titanium | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | Cerakote |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Electrochemical conversion of the surface | Thin film deposited onto the surface | Polymer-ceramic coating (sprayed on) |
| Adhesion | Integral part of the metal; won't chip or peel | Excellent, but can chip under extreme stress | Very good, but can scratch or wear off |
| Thickness | Microns | Microns | Thicker than PVD/Anodizing |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent | Varies by material | Generally not biocompatible |
Q: Is black anodized titanium expensive?
A: While the initial cost of titanium and the anodizing process can be higher than for other materials like aluminum or steel, the long-term durability and lack of need for replacement often make it a more cost-effective solution over the product's lifespan.
Q: How do you care for black anodized titanium?
A: It is very low maintenance. Cleaning with a soft cloth and mild soap is usually all that is needed. Avoid abrasive cleaners that could potentially scratch the surface.
Q: Will the black color fade over time?
A: The color is exceptionally stable and UV resistant. Unlike some dyed finishes, the black from this type of anodizing will not fade from exposure to sunlight.
Black anodized titanium is more than just a color; it's a high-performance surface treatment that enhances the already impressive properties of titanium. Offering a rare blend of strength, lightness, corrosion resistance, and visual appeal, it provides a competitive edge in product design and engineering. As industries continue to push the boundaries of performance and longevity, the demand for advanced materials like anodized black titanium is set to grow, solidifying its place as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Finishing.com. (n.d.). Anodizing titanium black in color. Retrieved from https://www.finishing.com/239/21.shtml
Valence Surface Technologies. (2023). Understanding The Benefits Of Titanium Anodize For Your Next Project. Retrieved from https://www.valencesurfacetech.com/the-news/anodized-titanium/
Xometry. (2022). Everything You Need To Know About Black Anodizing. Retrieved from https://www.xometry.com/resources/machining/black-anodizing/