What is Titanium Anode Lifespan? Defining Electrochemical Durability
In industrial electrochemistry, "lifespan" is not a measure of physical disintegration. It is a measure of functional efficiency. A titanium anode reaches the end of its service life when the catalytic coating is depleted, leading to a phenomenon known as "anode passivation."
"Titanium anode service life is technically defined as the operational duration until the cell voltage increases by 5V to 10V over the initial operating baseline, indicating the loss of electrocatalytic activity."
At China Titanium Factory, we observe that many operators mistake a functioning current for a healthy anode. If your voltage is climbing, your energy costs are skyrocketing. The coating—whether Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) or Platinum—is the engine. Once it thins, the underlying titanium substrate forms a non-conductive oxide layer. This is terminal.

Primary Factors Influencing Titanium Anode Service Life
Longevity is not a static number. It is a variable of stress. According to research published by The Electrochemical Society, several environmental stressors dictate the rate of coating erosion.
Current Density: The Primary Accelerator
Current density (measured in A/m² or A/dm²) has an inverse relationship with lifespan. Doubling the current density does not just halve the life; it often accelerates degradation exponentially. High current loads generate more heat and aggressive intermediate radicals at the anode surface.
Electrolyte Chemistry and pH
Anodes operating in extreme pH ranges (highly acidic or highly alkaline) face tougher conditions. Fluoride ions are particularly "poisonous" to titanium substrates, as they can bypass the protective oxide layer and cause pitting. Maintaining chemical equilibrium is vital for MMO titanium anode stability.
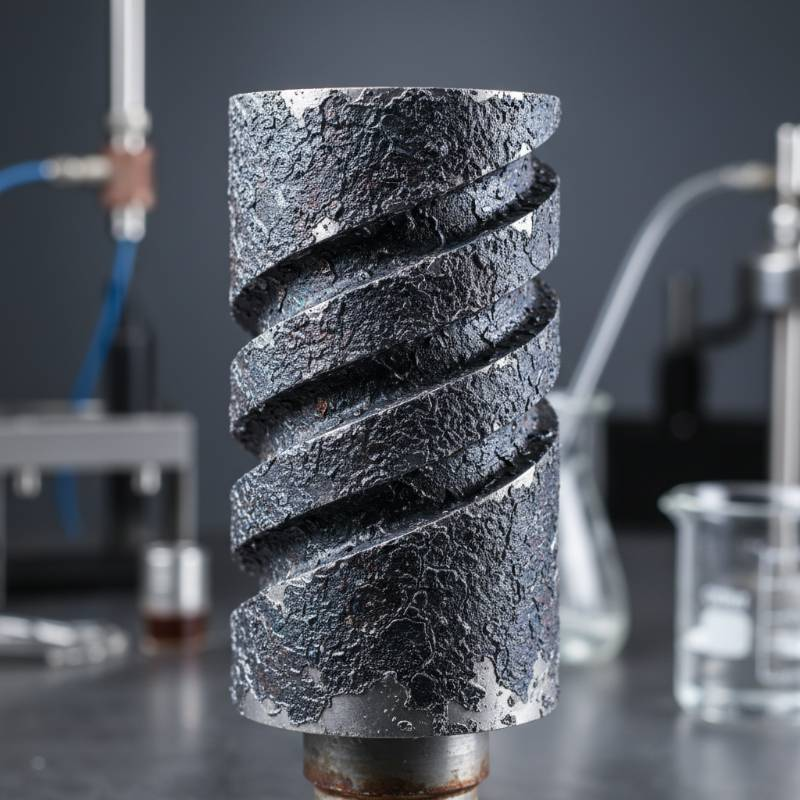
Comparative Analysis: Lifespan of MMO vs. Platinum vs. Lead Dioxide
Selecting the right coating is the most significant decision in the procurement phase. Each chemistry serves a specific electrochemical niche.
| Coating Type | Typical Lifespan | Primary Environment |
|---|---|---|
| MMO (Iridium/Ruthenium) | 5 - 20 Years | Seawater, Chlor-alkali |
| Platinum-Plated | 3 - 7 Years | Electroplating, Ionized Water |
| Lead Dioxide (PbO2) | 1 - 3 Years | Electrowinning, Organic Waste |

The "Anode-Life 360™" Optimization Framework
At China Titanium Factory, we utilize the Anode-Life 360™ Framework to ensure our clients maximize their ROI. We define [titanium anode lifespan] as a manageable variable rather than an unpredictable expiration date.
Precision Coating Selection: Matching the noble metal loading (grams per square meter) to the specific current density of the application.
Dynamic Current Regulation: Implementing "soft-start" protocols to prevent thermal shock to the coating interface.
Chemical Equilibrium Management: Monitoring trace impurities like manganese or iron that can foul the anode surface.
Proactive Maintenance Cycles: Scheduled cleaning to prevent scale-induced hot spots.
Our Golden Rule: "Stability over Intensity." Operating an anode at 80% of its rated current capacity can often increase its lifespan by 150%.
Maintenance Protocols to Maximize Anode Longevity
Neglect is the fastest way to kill a titanium electrode. Scale buildup acts as an insulator, forcing the remaining active areas to carry a higher current load, leading to localized burnout.
Acid Washing Procedures
Periodic immersion in a 5-10% citric acid or hydrochloric acid solution can remove calcium carbonates. Never use mechanical scrapers or abrasive brushes. You will strip the precious metal coating instantly. Chemical cleaning is the only acceptable method.
The Risks of Polarity Reversal
While some systems use polarity reversal to self-clean, this is brutal on the coating. Unless the anode is specifically designed for reversal, this practice will cause the coating to flake off due to hydrogen evolution beneath the active layer.
Application-Specific Durability: From Pools to Industrial Wastewater
The environment is the judge. In saltwater pool chlorinators, an MMO anode might last 5-7 years because the current density is relatively low and the water is clean. Contrast this with industrial wastewater treatment.
In wastewater, the presence of organic "trash" and complex ions creates a high-fouling environment. Here, a platinum titanium anode might only last 2 years if not properly maintained. Our analysis shows that cathodic protection systems represent the longest lifespan application, often exceeding 20 years due to the extremely low current demands.

Troubleshooting and Visual Signs of Anode Failure
Early detection saves money. Once an anode fails completely, it can damage the rectifier or contaminate the electrolyte. Keep a technical log of the following indicators:
Voltage Creep: A steady 10-15% increase in voltage over three months without a change in production volume.
Visual Pitting: Small "craters" on the surface indicating the titanium base is being attacked.
Color Shift: MMO coatings often turn from a dark grey/black to a lighter, brownish hue as they deplete.
Current Drop: In constant voltage systems, a sudden drop in Amperage indicates increased resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Titanium Anode Lifespan
How long do titanium anodes last in a saltwater pool?
Typically, a high-quality MMO titanium anode in a residential saltwater pool lasts between 3 to 7 years. Lifespan depends heavily on salt concentration and cell cleaning frequency.
Can you recoat a titanium anode?
Yes. If the titanium substrate is structurally sound and not severely pitted, it can be stripped and recoated. This is a cost-effective alternative to purchasing new assemblies, often saving 30-50% in material costs.
What is the main cause of premature failure?
The "Silent Killer" is usually over-current. Running an anode beyond its design specifications causes the coating to overheat and lose adhesion, leading to rapid passivation.
Optimize Your Electrochemical Performance
Don't guess your service life. Get precision-engineered anodes designed for your specific current density and chemistry.
Consult Our Technical Team