Safeguarding Your Vessel: Zinc vs. Aluminum Anodes in Saltwater
Protecting marine assets from galvanic corrosion in saltwater is crucial. This guide offers a professional, authoritative comparison of zinc and aluminum anodes. It empowers you to make informed decisions for your vessel's longevity and operational efficiency. Understanding the right choice ensures maximum protection.

The Science Behind Corrosion Protection: How Sacrificial Anodes Work
Galvanic corrosion poses a constant threat to submerged metals. Sacrificial anodes counteract this process. This section explains the fundamental principles of marine corrosion and anode function. It details how these critical components safeguard your vessel.
What is Galvanic Corrosion in Saltwater?
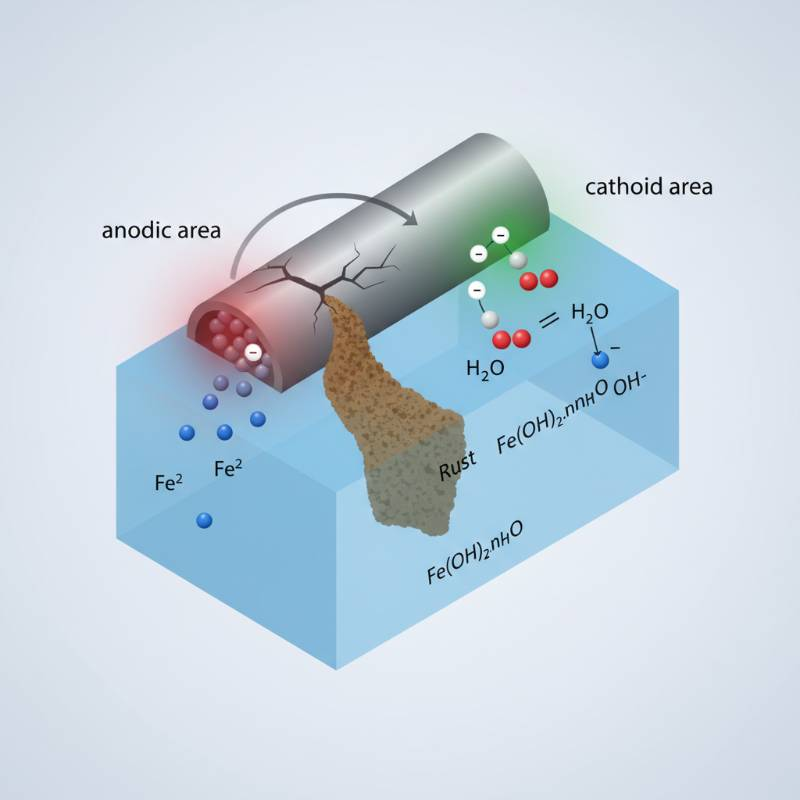
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are electrically connected and immersed in an electrolyte (like saltwater). The less noble (more active) metal corrodes preferentially, acting as an anode, while the more noble metal becomes a cathode and is protected. This electrochemical reaction can severely damage marine components.
Saltwater acts as a highly conductive electrolyte. It accelerates the corrosive process between metals. Understanding this mechanism is vital for effective prevention strategies. Learn more about comprehensive corrosion solutions from industry leaders.
The Essential Role of Sacrificial Anodes
Sacrificial anodes are purposely made of a more active metal. They are designed to corrode instead of your vessel's vital components. These anodes effectively divert the corrosive current. This ensures the integrity and operational efficiency of your marine equipment. They are a frontline defense against costly damage.
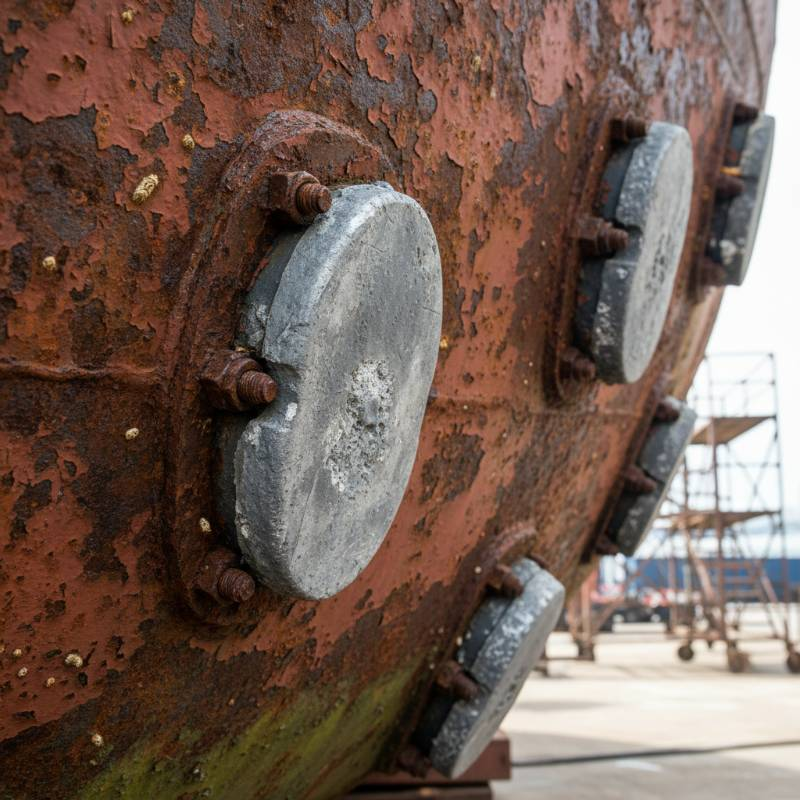
The anode "sacrifices" itself, protecting propellers, shafts, rudders, and hulls. Proper anode selection is a cornerstone of marine maintenance. For technical insights into material science, consider resources like NACE International.

Zinc Anodes: The Traditional Standard for Saltwater Environments
Zinc anodes have been the preferred choice for saltwater corrosion protection for decades. Their robust properties make them a reliable solution. This section provides an authoritative overview of their characteristics and applications. It highlights why they remain a staple in marine protection.
Key Advantages of Zinc Anodes
Zinc offers consistent, powerful protection in highly saline conditions. It maintains a stable voltage output, ensuring effective galvanic protection. Its long-standing reputation in marine applications speaks to its reliability. Zinc anodes perform exceptionally well in pure saltwater environments.
High driving voltage against most marine metals.
Consistent performance in high-salinity water.
Proven track record over many years.
Considerations and Disadvantages of Zinc
Despite their effectiveness, zinc anodes have certain drawbacks. They are denser than aluminum, adding more weight to a vessel. Zinc's efficiency significantly decreases in brackish or freshwater. This can lead to passivation, where a protective oxide layer forms, stopping its function.
Environmental concerns also exist regarding zinc's release into marine ecosystems. Regulations are increasingly stringent. Responsible marine practices consider these factors. For specific titanium products, including specialized anodes, explore our offerings.
When to Opt for Zinc Anodes
Zinc anodes are ideal for vessels operating exclusively in saltwater. This includes offshore boats, large ships, and structures in constant high-salinity exposure. Their robust performance in these conditions makes them the most effective choice. They are a reliable solution for dedicated saltwater use.
Aluminum Anodes: Advanced Protection for Diverse Marine Conditions
Aluminum anodes have emerged as a versatile and environmentally conscious alternative. They offer advanced protection for a broader range of marine environments. This section details their unique properties and suitability. It explains why they are gaining prominence in the marine industry.

Advantages of Aluminum Anodes
Aluminum anodes, specifically alloys like MIL-SPEC A-24779 (aluminum-indium), offer superior efficiency. They perform effectively across varying water types: salt, brackish, and fresh. They are significantly lighter than zinc, reducing vessel weight. This contributes to better fuel efficiency and performance.
Their reduced environmental footprint is another major advantage. They release fewer toxic byproducts into the water. This aligns with growing ecological concerns and regulations. Our titanium anodes and other specialized products leverage similar material science for optimal performance.
Effective in saltwater, brackish water, and freshwater.
Lighter weight, improving vessel performance.
Lower environmental impact compared to zinc.
Higher current capacity per pound than zinc.
Potential Drawbacks of Aluminum Anodes
Aluminum anodes can be more susceptible to passivation in certain conditions. This is particularly true if the alloy composition is incorrect. High-quality aluminum anodes contain indium or other elements. These prevent passivation. Ensuring the correct alloy is crucial for consistent protection.
Initial cost might be slightly higher than zinc. However, their longer lifespan and versatility often provide better long-term value. Always verify the anode's alloy composition. This ensures it meets industry standards for marine use.
When to Choose Aluminum Anodes
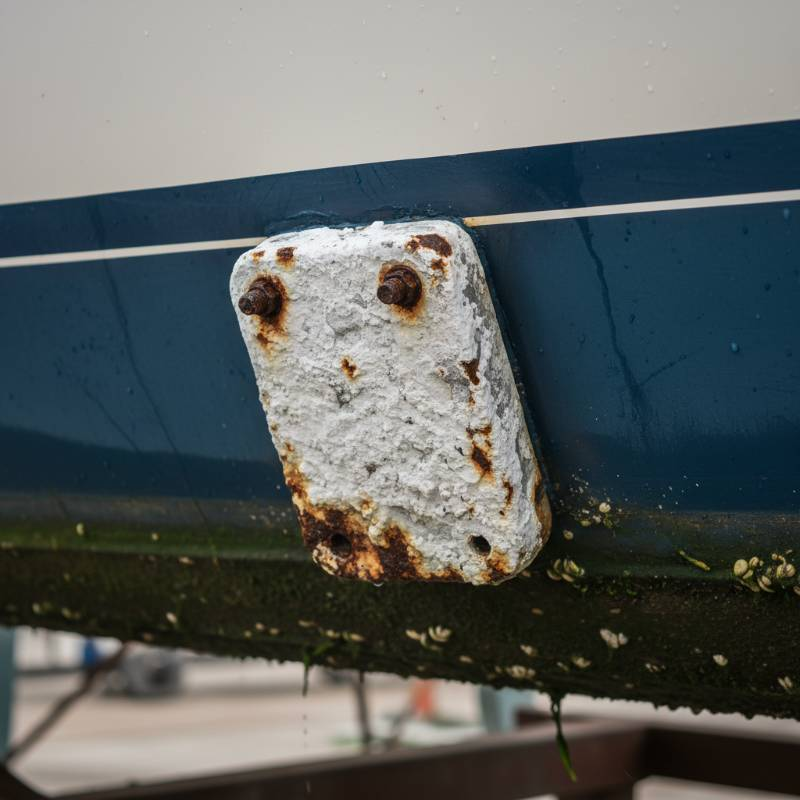
Aluminum anodes are optimal for vessels that frequently move between different water types. This includes boats navigating coastal areas, rivers, and lakes. Their multi-water effectiveness simplifies anode management. They are also ideal for vessels where weight reduction is a priority. This makes them a smart choice for many modern marine applications.
Zinc vs. Aluminum Anodes: A Detailed Performance Showdown
Choosing between zinc and aluminum anodes requires a detailed understanding of their performance. This section provides a direct, side-by-side analysis. It evaluates critical metrics to guide your selection process with precision. This comparison will help you make the best decision.
Protective Efficacy and Current Output
Both anode types provide galvanic protection, but their electrochemical potential differs. Zinc has a lower (more negative) potential, making it very active in saltwater. Aluminum alloys are slightly less negative but maintain consistent output across varying salinities. This translates to effective corrosion prevention in their respective optimal environments.
Lifespan and Consumption Rates
Aluminum anodes generally offer a longer lifespan than zinc anodes. This is due to their higher current capacity per pound. They corrode more slowly for the same level of protection. This means less frequent replacements. However, actual consumption rates depend on water conditions and the protected metal's surface area. Regular inspection remains crucial.
Environmental Impact and Regulations
Zinc is a heavy metal, and its dissolution can impact marine life. Aluminum, particularly high-purity alloys, is considered more environmentally benign. Many regions are adopting stricter regulations on marine discharges. This makes aluminum a more compliant and ecologically responsible choice. Consult local environmental agencies for specific guidance, such as the EPA's Vessel General Permit.

Cost-Benefit Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Value
While zinc anodes often have a lower upfront cost, aluminum can offer superior long-term value. Their extended lifespan reduces replacement frequency and labor costs. Aluminum's versatility avoids the need for different anode types when changing water environments. Consider the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price.
| Feature | Zinc Anodes | Aluminum Anodes |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Environment | Pure Saltwater | Saltwater, Brackish, Freshwater |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Current Output Consistency | Excellent in Saltwater; Poor in Fresh/Brackish | Good across all water types (with proper alloy) |
| Lifespan | Shorter (higher consumption rate) | Longer (lower consumption rate) |
| Environmental Impact | Higher (heavy metal) | Lower (more benign) |
| Cost (Initial) | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Passivation Risk | Low in saltwater; High in fresh/brackish | Low with proper alloy (e.g., indium-doped) |
Selecting the Optimal Anode for Your Vessel
Empower yourself with a systematic approach to anode selection. This section outlines critical factors influencing the best choice. It ensures maximum protection for your specific marine application. A careful assessment prevents costly mistakes.
Understanding Your Vessel's Environment: Water Type and Temperature
The primary determinant for anode choice is the water type. Saltwater, brackish water, or freshwater each demand different anode properties. Water temperature also affects galvanic activity. Colder water generally reduces corrosion rates. Matching the anode to the environment is paramount for effectiveness.
Vessel Construction and Other Metals Present
Consider the material composition of your hull, propulsion system, and other submerged components. Stainless steel, bronze, aluminum, and even paint systems interact galvanically. Anodes must be compatible with all protected metals. This ensures comprehensive protection without adverse reactions. Seek expert advice for complex systems, or refer to resources like BoatUS guides on corrosion.
Usage Patterns and Maintenance Regimen
How frequently your vessel is in water directly impacts anode consumption. Vessels stored on trailers need less frequent anode checks. Those continuously in water require diligent monitoring. Aligning anode selection with your maintenance capabilities is important. This ensures timely inspection and replacement. For custom fabrication of marine components, consult our technical experts.
Ensuring Peak Performance: Anode Installation, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
Proper installation and diligent maintenance are as crucial as anode selection. This section provides expert guidance. It helps maximize the effectiveness and longevity of your sacrificial anodes. Following these practices prevents premature failure and costly damage.

Best Practices for Anode Installation
Anodes must have excellent electrical contact with the metal they protect. Clean the mounting surface thoroughly before installation. Ensure fasteners are tight and corrosion-free. Paint or marine growth can insulate an anode, rendering it useless. Follow manufacturer guidelines precisely. This ensures optimal electrical conductivity and protective efficiency.
Routine Anode Inspection and Replacement
Establish a proactive maintenance schedule for inspecting anode wear. Check anodes at least annually, or more frequently for active vessels. Replace anodes when they are approximately 50% consumed. Waiting longer risks exposing your vessel's crucial components to corrosion. This preventative marine maintenance saves significant repair costs.
Common Anode Issues and Practical Solutions
Premature anode consumption indicates excessive galvanic activity. This might be due to stray current or insufficient anode coverage. Anodes not corroding suggest poor electrical contact or passivation. Clean connections, check wiring, and ensure correct anode material. Consulting with a marine electrician or a specialist in corrosion solutions is recommended for persistent issues. China Titanium Factory offers global leadership in metal fabrication and technical expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions About Marine Anodes
Get quick, authoritative answers to common queries regarding zinc and aluminum anodes. This section covers their application and maintenance in saltwater environments. It provides essential information for boat owners and marine professionals.
Q1: Can I mix zinc and aluminum anodes on my boat?
A1: No, mixing zinc and aluminum anodes is generally not recommended. They have different electrochemical potentials. This can lead to the faster consumption of one anode type while the other remains inactive. It is best to use a single type of anode consistent with your primary operating environment.
Q2: How often should I replace my sacrificial anodes?
A2: Anodes should be inspected at least once a year, preferably during haul-out. Replace them when they are approximately 50% consumed. Vessels in highly corrosive environments or with heavy usage may require more frequent checks and replacements.
Q3: What happens if I don't replace my anodes?
A3: Failing to replace depleted anodes leaves your vessel's submerged metal components unprotected. This can lead to severe galvanic corrosion, damaging propellers, shafts, rudders, and other vital parts. Such damage is costly to repair and can compromise vessel safety.
Q4: Are "no-maintenance" anodes a viable option?
A4: While some systems claim "no maintenance," all cathodic protection systems require monitoring. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) systems use an external power source. They reduce the need for sacrificial anodes but still need regular checks and maintenance. Sacrificial anodes are consumable and always require replacement.
Ensure Unwavering Protection for Your Marine Assets
Ready to optimize your vessel's corrosion defense with expert-grade materials and solutions? China Titanium Factory provides advanced material engineering and custom anode manufacturing. Partner with a global leader for unmatched reliability and efficiency.
Contact Our Experts Today