Understanding ICCP Systems and Anode Installation Fundamentals
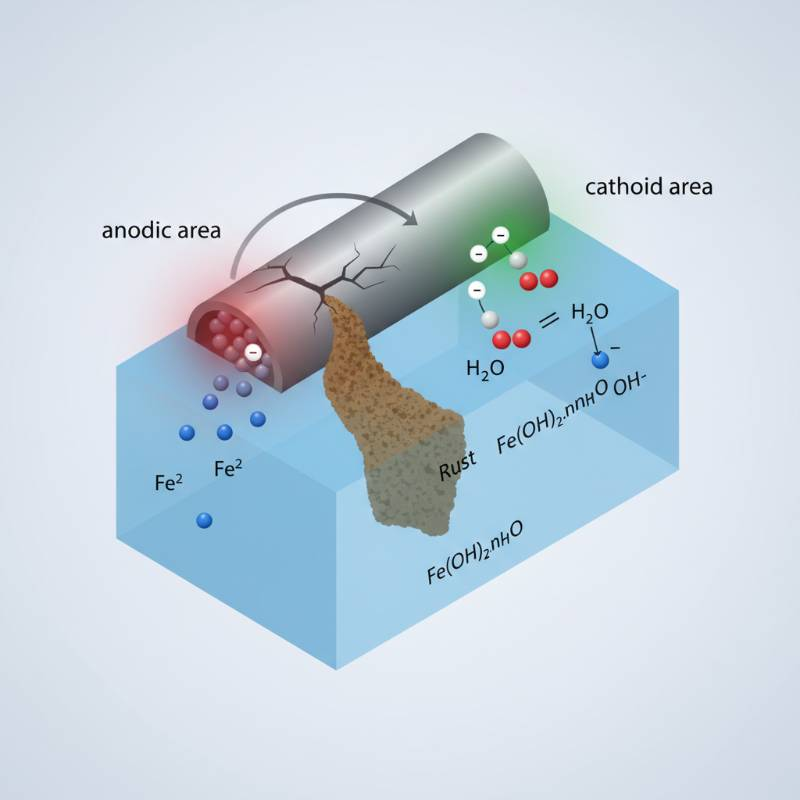
Industrial assets face constant threats from corrosion. This electrochemical process degrades materials over time. It compromises structural integrity and operational safety.
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) systems offer a robust defense. They actively prevent corrosion in various environments. These systems are critical for infrastructure longevity.
Definition: An Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) system utilizes an external DC power source to drive current through an inert anode. This current flows to the protected structure, effectively stopping the corrosion process by making the structure the cathode of an electrochemical cell.
The fundamental role of ICCP systems is to safeguard metallic structures. This includes pipelines, storage tanks, and marine facilities. Anodes are central to this protection.
Precise anode installation is paramount for system efficacy. Incorrect placement or connection can lead to protection gaps. This negates the system's purpose. Therefore, adherence to strict installation protocols is essential.

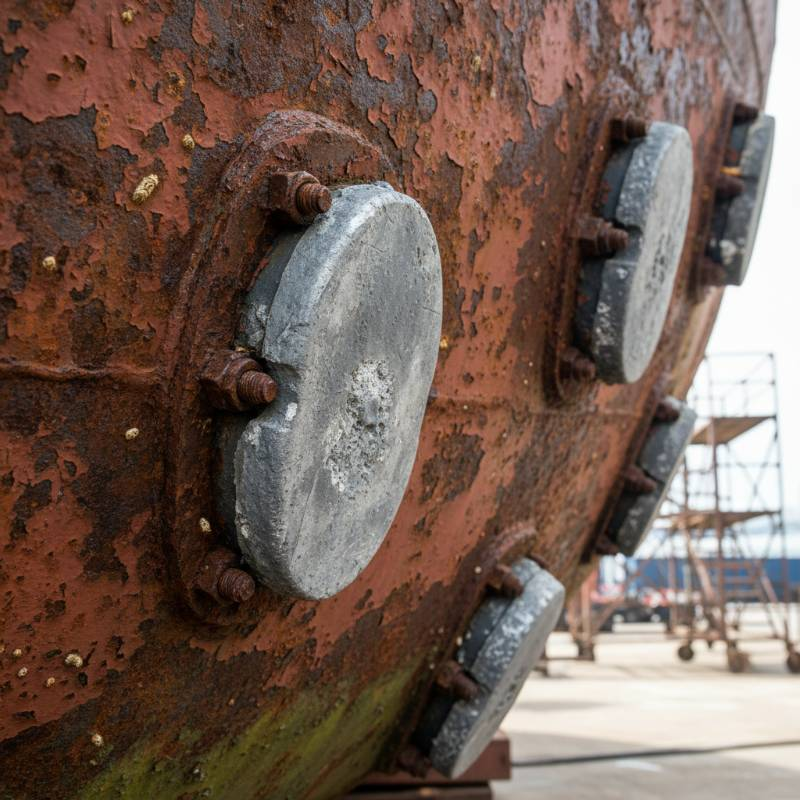
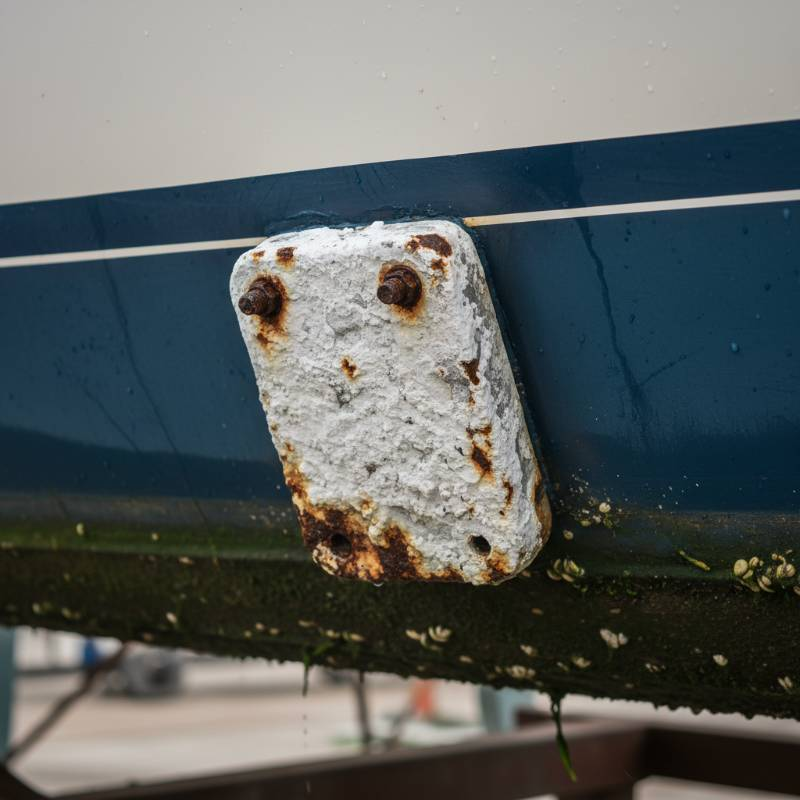
Manufacturers like China Titanium Factory specialize in high-quality anode materials. Their products form the backbone of reliable ICCP installations. Understanding these fundamentals ensures successful corrosion prevention strategies.
Why Proper ICCP Anode Installation is Critical for Asset Longevity
Correct anode installation directly influences the lifespan of industrial assets. It ensures optimal corrosion control. This extends operational efficiency and reduces replacement costs.
Conversely, improper installation carries significant risks. It can lead to premature system failure. This results in costly repairs and increased maintenance expenses.
Compromised structural integrity is another severe consequence. This poses safety hazards. It can also lead to environmental damage, particularly with pipelines and storage tanks.
Adherence to best practices yields long-term benefits. It guarantees continuous protection. This preserves asset value and ensures regulatory compliance. High-quality anodes, like those from China Titanium Factory's services, require expert installation to deliver their full potential.
Selecting the Right Anode: Types and Applications in ICCP Systems
Anode material selection is a critical design phase. Different materials suit various environmental conditions. Each type offers unique advantages and limitations.
Understanding these characteristics is key to informed material specification. This ensures the ICCP system performs effectively and lasts its intended design life.
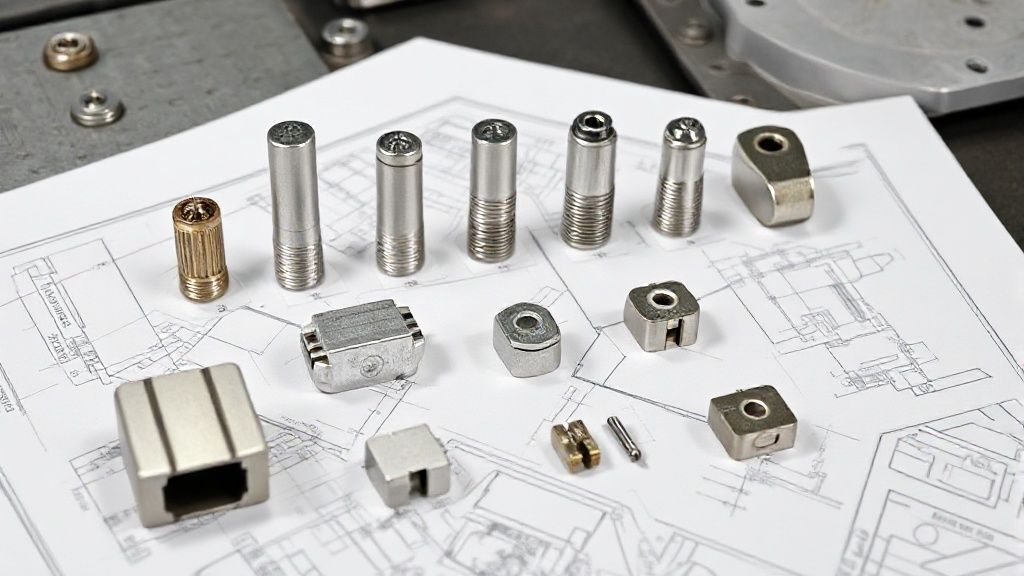

Common Anode Materials
Several anode types are prevalent in ICCP systems. Each is engineered for specific performance requirements.
Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) Anodes: These are highly versatile. They feature a titanium substrate coated with noble metal oxides. MMO anodes offer high current output and long service life. They are suitable for soil, freshwater, and seawater applications.
Graphite Anodes: These are cost-effective. They are often used in groundbeds with carbonaceous backfill. Graphite anodes have good chemical resistance. However, they can consume over time.
Platinized Titanium Anodes: These anodes provide excellent performance in aggressive environments. They are common in seawater and high-salinity applications. Their platinum coating ensures stability and low consumption rates. China Titanium Factory offers various platinized titanium products.
High Silicon Cast Iron (HSSCI) Anodes: These are robust and heavy. They are typically used in deep well groundbeds and freshwater. HSSCI anodes offer good current output but can be brittle.
Anode Material Comparison
The following table provides a concise comparison of common anode types. This aids in selecting the best material for specific project needs.
| Anode Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) | Titanium substrate with noble oxide coating. | Soil, freshwater, seawater, concrete. | High current output, low consumption, versatile. | Higher initial cost than graphite. |
| Graphite | Carbon-based material. | Groundbeds with carbonaceous backfill. | Cost-effective, good chemical resistance. | Consumes over time, lower efficiency in some media. |
| Platinized Titanium | Titanium substrate with a thin platinum coating. | Seawater, high-salinity environments. | Excellent stability, very low consumption, high performance. | High initial cost. |
| High Silicon Cast Iron (HSSCI) | Iron alloy with high silicon content. | Deep well groundbeds, freshwater. | Robust, good current output. | Brittle, heavy, prone to hydrogen embrittlement in certain conditions. |
The environment, current requirements, and budget dictate the final choice. Consulting with material experts ensures optimal selection.
Comprehensive Pre-Installation Planning: Site Assessment and System Design
Successful ICCP anode installation begins long before any physical work. Meticulous pre-installation planning is non-negotiable. It minimizes risks and optimizes system performance.
Site Surveys and Environmental Assessment
A thorough site survey identifies potential challenges. It includes mapping existing infrastructure. Environmental impact assessments evaluate soil conditions and water bodies. This helps select appropriate anode materials and installation methods.
Soil resistivity testing is particularly vital. It determines the electrical resistance of the soil. This data directly influences anode spacing and current requirements. Accurate measurements ensure effective current distribution.
System Design and Material Specification
System design involves calculating protective current needs. It also determines the number and placement of anodes. Rectifier sizing and cable specifications are integral. Design principles must adhere to industry standards, such as those from NACE International (now AMPP).
Material specification details every component. This includes anodes, backfill, cables, and splice kits. High-quality materials, like those sourced from reputable suppliers, ensure durability. China Titanium Factory provides various anode and component options.
Cost Analysis and Regulatory Compliance
Robust cost analysis and budgeting prevent financial overruns. It accounts for materials, labor, and potential contingencies. Regulatory compliance involves obtaining necessary permits and approvals. Local, state, and national regulations must be followed explicitly.
Step-by-Step Guide to ICCP Anode Installation Procedures
The physical installation of ICCP anodes requires meticulous attention to detail. Each step must be executed precisely. This ensures the system functions as designed and provides optimal protection.
1. Site Preparation and Safety Protocols
Clear the installation area of debris and obstructions. Mark all underground utilities accurately. Implement a comprehensive safety plan. This includes personal protective equipment (PPE) and emergency procedures. Adhere to all local safety regulations.
2. Excavation and Trenching
Excavate trenches to the specified depth and width. This accommodates the anodes and backfill. Ensure trench stability to prevent collapses. The dimensions must match design specifications exactly.
3. Precise Anode Placement and Spacing
Position anodes according to the detailed system design drawings. Maintain precise spacing between anodes. This ensures uniform current distribution. Correct placement prevents hot spots or under-protected areas.
4. Secure Cable Connections and Insulation
Connect anode lead wires to the main header cable. Use exothermic welds or crimped connectors. These must be gas-tight and waterproof. Apply high-quality insulation and sealants. This protects connections from moisture and damage.
5. Proper Backfill Procedures
Apply carbonaceous backfill (e.g., coke breeze) around anodes. This improves electrical contact with the soil. It also extends anode life. Ensure thorough compaction to eliminate voids. The backfill layer must be consistent.
6. Rectifier Connection and Initial Testing
Connect the header cable to the rectifier. Ensure all electrical connections are secure and correct. Perform initial system testing. This includes measuring current output and structure-to-soil potentials. Verify all readings meet design specifications.
For specialized installation support and high-performance anodes, consider contacting China Titanium Factory experts.
Ensuring Long-Term Performance: Monitoring and Maintenance of ICCP Anodes
Installation is just the first step. Sustaining ICCP system integrity requires ongoing vigilance. Regular monitoring and proactive maintenance are essential for long-term performance.
Routine Inspection Schedules
Establish a strict inspection schedule. This includes visual checks of rectifiers and connections. It also involves periodic electrical measurements. Regular inspections identify potential issues early.
Advanced Performance Monitoring Techniques
Utilize advanced techniques for comprehensive assessment. Potential measurements determine the level of cathodic protection. Current output analysis checks rectifier efficiency. Data interpretation helps identify trends and predict failures.
Remote monitoring systems offer continuous oversight. They provide real-time data. This allows for immediate response to system anomalies. Such systems are crucial for extensive infrastructure.
Maintaining accurate records of all measurements and observations is vital. This historical data supports diagnostics. It also guides future maintenance strategies. For best practices, refer to guidelines from organizations like ASTM International.
Proactive Maintenance Practices
Address minor issues before they escalate. This includes cleaning rectifier components. It also involves tightening loose connections. Replacing worn cables prevents system disruption. Proactive maintenance maximizes system longevity and efficiency.
Anode replacement may be necessary over time. This depends on the anode type and consumption rate. Proper planning for anode replacement minimizes downtime. It ensures continuous protection for assets.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in ICCP Anode Systems
Even well-installed ICCP systems can develop issues. Systematic diagnostic steps are crucial for effective problem resolution. Timely troubleshooting restores operational continuity and protection.
Low Current Output
Low current output indicates insufficient protection. This can stem from rectifier malfunction. It may also be due to high circuit resistance. Check rectifier settings first. Inspect all cable connections for corrosion or damage.
High Circuit Resistance
High resistance often points to faulty connections. It can also indicate degraded backfill. Perform continuity tests on all cables. Measure resistance between anodes and the protected structure. Re-excavation might be necessary to inspect buried connections or backfill material.
Premature Anode Failure
Anodes can fail prematurely due to several reasons. These include improper material selection. Excessive current density or damage during installation are also factors. Regular potential surveys help detect areas of insufficient protection. This indicates potential anode issues.
Rectifier Malfunctions
Rectifiers are the power source. They can experience component failures. Check fuses, circuit breakers, and internal wiring. Ensure stable power input. Professional electrical diagnostics may be required for complex rectifier issues.
A systematic approach to diagnostics saves time and resources. It ensures the ICCP system returns to optimal operation quickly.
Safety and Environmental Best Practices for ICCP Anode Projects
Safety and environmental stewardship are paramount. They must be integrated into every phase of an ICCP anode project. This ensures the well-being of personnel and the surrounding ecosystem.
Material Handling Safety
Anodes and backfill materials can be heavy or hazardous. Use appropriate lifting equipment for heavy anodes. Follow manufacturer guidelines for handling carbonaceous backfill. Ensure proper ventilation when working with dusty materials.
Electrical Safety
Working with DC power requires strict electrical safety protocols. De-energize all circuits before making connections. Use insulated tools and wear appropriate PPE. Adhere to Lockout/Tagout procedures. Refer to OSHA guidelines for electrical safety.
Risk Assessment and Site Safety
Conduct a thorough risk assessment for each project. Identify potential hazards, such as excavation collapses or confined spaces. Implement control measures. Establish clear communication channels and emergency response plans. All personnel must be trained in site-specific safety procedures.
Environmental Impact Mitigation
Minimize environmental disturbance during excavation. Properly manage and dispose of excavated soil. Prevent contamination of soil and water bodies. Use erosion control measures. Restore the site to its original condition after completion. Sustainable practices protect both the environment and project reputation.
ICCP Anode Installation in Action: Real-World Case Studies
Examining real-world examples highlights the practical application of these principles. Case studies showcase challenges, solutions, and tangible benefits. They provide valuable insights for future projects.
Case Study 1: Pipeline Protection in Aggressive Soil
A major oil pipeline traversed highly corrosive, high-resistivity soil. Traditional sacrificial anodes proved insufficient. Engineers designed an ICCP system using deep well MMO anodes. Specialized backfill was used to lower groundbed resistance. The meticulous installation ensured uniform current distribution. This extended the pipeline's life by decades, preventing costly ruptures.
Case Study 2: Storage Tank Bottom Protection
An aging above-ground storage tank faced severe corrosion on its bottom plate. Installing external anodes was impractical. An internal ICCP system with platinized titanium anodes was chosen. These anodes were strategically placed within the tank's sand pad. This innovative approach provided effective protection. It avoided extensive structural modifications. It maintained the tank's operational integrity.
Case Study 3: Marine Structure Corrosion Control
A critical offshore platform required enhanced corrosion protection. The harsh marine environment demanded robust solutions. An ICCP system utilizing platinized titanium mesh anodes was installed. These anodes were attached directly to the submerged structure. The system effectively mitigated corrosion. It reduced maintenance diving requirements significantly. This improved safety and operational costs.
These examples illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of ICCP systems. They also highlight the importance of expert design and installation. Each project requires tailored solutions. Suppliers like China Titanium Factory contribute vital components to such demanding applications.
Essential ICCP Terminology and Frequently Asked Questions
A clear understanding of key terminology is fundamental for ICCP professionals. This section provides a glossary of common terms. It also addresses frequently asked questions. This clarifies complex concepts and common queries.
ICCP Glossary
Anode:
The electrode where oxidation (corrosion) preferentially occurs in an electrochemical cell. In ICCP, anodes are designed to corrode sacrificially or to provide current without significant consumption, protecting the main structure.
Cathode:
The electrode where reduction occurs. In cathodic protection, the protected structure becomes the cathode, thereby preventing its corrosion.
Rectifier:
An electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In ICCP systems, it provides the necessary DC power to drive the protective current.
Backfill:
Material, often carbonaceous (e.g., coke breeze), used to surround anodes in groundbeds. It improves electrical contact with the soil and helps dissipate current more effectively.
Potential Measurement:
The measurement of the electrical potential difference between the protected structure and a reference electrode. This indicates the level of cathodic protection achieved.
For additional definitions and technical resources, consult industry standards organizations.
Mastering ICCP Anode Installation for Superior Corrosion Protection
Effective corrosion control is paramount for industrial asset management. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection systems offer a powerful solution. Their success hinges on meticulous anode installation and ongoing maintenance.
This guide has outlined the critical steps. It covered planning, material selection, and precise installation procedures. It also addressed monitoring, troubleshooting, and safety. Adhering to these best practices ensures system efficacy and asset longevity.
Professionals are encouraged to apply this detailed knowledge. It enhances project execution and delivers superior corrosion protection. Investing in proper installation yields substantial long-term benefits. These include reduced maintenance, extended asset life, and improved safety.
Partnering with experienced suppliers and installers is crucial. China Titanium Factory stands ready to provide high-quality anodes and expert guidance. Their commitment to excellence supports robust ICCP solutions globally.
Frequently Asked Questions About ICCP Anode Installation
What is the primary purpose of an ICCP anode?
The primary purpose of an ICCP anode is to provide a point of current discharge into the electrolyte (e.g., soil or water) to protect the target metallic structure. It acts as the positive terminal, driving electrons to the structure to prevent corrosion.
How does soil resistivity affect anode installation?
Soil resistivity is a critical factor. High resistivity soil requires more anodes or a deeper groundbed to achieve adequate current distribution. It significantly influences anode spacing, backfill selection, and the overall system design to ensure effective protection.
What are the common types of backfill used with ICCP anodes?
Carbonaceous backfills are most common. These include coke breeze, calcined petroleum coke, and natural graphite. They reduce anode-to-earth resistance, provide a uniform environment for the anode, and consume sacrificially to extend anode life.
How often should an ICCP system be monitored after installation?
Monitoring frequency varies based on industry standards and asset criticality. Typically, monthly or quarterly checks of rectifier output and annual or semi-annual potential surveys are recommended. More aggressive environments may require more frequent checks.
Can existing structures be retrofitted with ICCP systems?
Yes, many existing structures can be successfully retrofitted with ICCP systems. This often requires a detailed assessment of the structure's condition, existing corrosion levels, and specific site constraints. Proper design and installation can significantly extend the life of aging assets.
Ensure Unwavering Asset Protection with Expert ICCP Solutions
Do not compromise on the integrity and longevity of your critical infrastructure. Partner with industry leaders for superior ICCP anode materials and expert guidance. Secure your assets against corrosion with confidence.
Consult Our Experts Today →