MMO Anodes: Offer exceptional versatility and cost-efficiency for large-scale applications such as chlor-alkali production and water treatment, characterized by their low overpotential and robust design.
Platinized Titanium Anodes: Are favored for high-purity applications like specialized electroplating and medical devices due to their superior chemical inertness and precise electrochemical control, despite higher material costs.
Selection Criteria: Decision-making hinges on the specific electrochemical reaction, required current density, electrolyte composition, budget constraints, and desired lifespan.
Durability & Maintenance: Both anode types require specific operational protocols and maintenance strategies to maximize service life and maintain performance.
Introduction: The Critical Role of Anodes in Electrochemical Systems
Platinized Titanium Anodes: Engineering, Performance, and Applications
Manufacturing and Structural Integrity of Platinized Titanium Anodes
Electrochemical Properties and Operational Parameters of Platinized Titanium
Primary Applications and Industry Adoption of Platinized Titanium Anodes
Advantages and Inherent Limitations of Platinized Titanium Anodes
Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) Anodes: Design, Efficiency, and Versatility
Direct Technical Comparison: MMO vs. Platinized Titanium Anodes
MMO Anodes in Large-Scale Chlor-Alkali Production: A Case Study
Platinized Titanium Anodes in Specialized Electroplating: A Case Study
Ensuring Anode Longevity: Troubleshooting and Maintenance Protocols
Future Outlook: Innovations and Sustainable Developments in Anode Technology
How do temperature and pH affect anode performance and lifespan?
Can these anodes be repaired or recoated to extend their service life?
Which anode is more suitable for highly corrosive environments?
Conclusion: Strategic Anode Selection for Optimal Electrochemical Performance
Anodes serve as fundamental components across a vast array of electrochemical systems, driving essential industrial processes from metal refining to water purification.
Their function is pivotal in enabling desired electrolysis reactions by providing a surface for oxidation, thereby influencing efficiency, product quality, and system longevity.
The judicious material selection for these electrodes is paramount, directly impacting the performance and economic viability of diverse industrial applications.
This technical guide provides a comprehensive comparison of two prominent anode technologies: Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) anodes and Platinized Titanium anodes, detailing their engineering, performance, and application specifics.
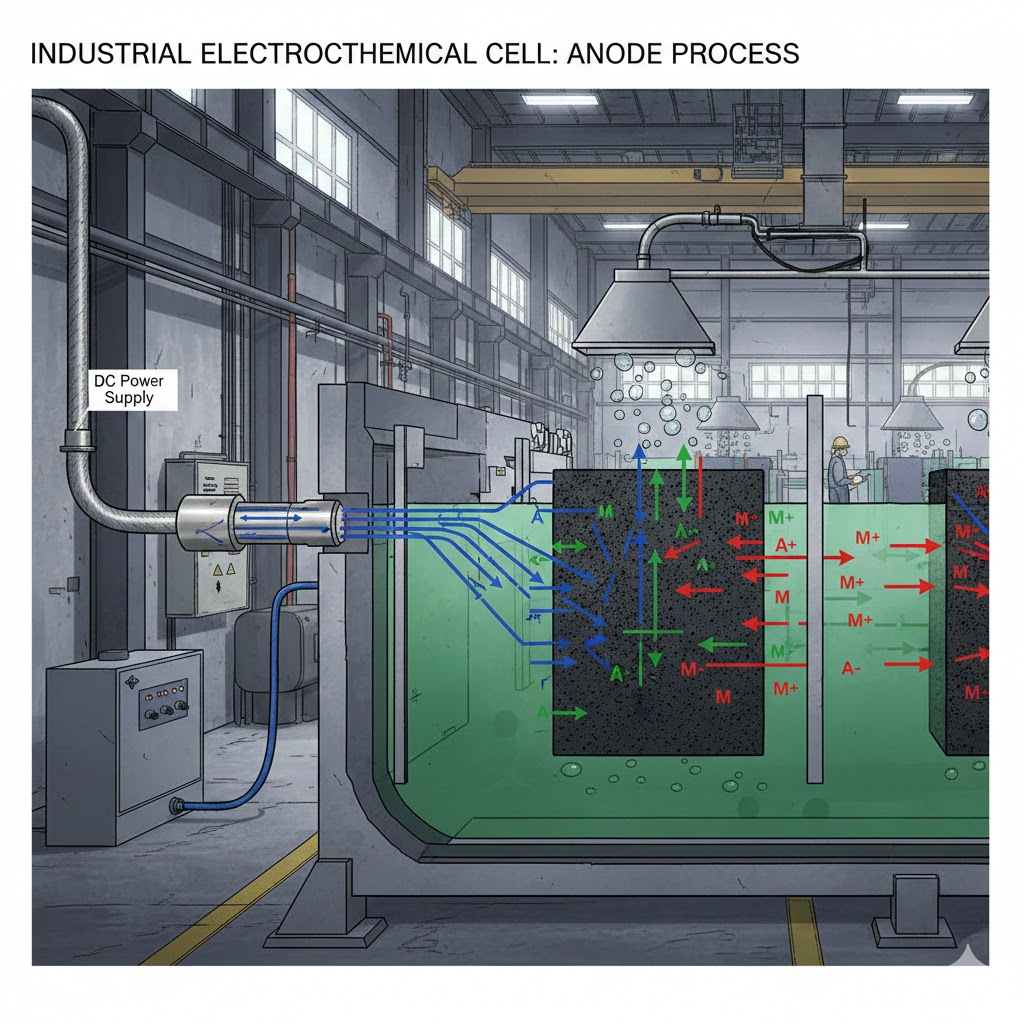
Anodes are electrodes where oxidation reactions occur, releasing electrons into the external circuit. This fundamental process is central to all electrochemical reactions.
The classification of anodes often depends on their composition and intended use, ranging from sacrificial anodes in cathodic protection to dimensionally stable anodes in industrial electrolysis.
Key material properties such as corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and catalytic activity are critical for optimal performance.
Anode Definition: An anode is an electrode through which the conventional electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. It is the site where oxidation (loss of electrons) occurs in an electrochemical cell.
A crucial performance criterion is overpotential, which represents the additional voltage required to drive a reaction beyond its thermodynamic equilibrium potential.
Lower overpotential translates directly to higher energy efficiency and reduced operational costs in electrochemical processes.
Platinized Titanium anodes represent a specialized class of dimensionally stable anodes, leveraging the excellent corrosion resistance of titanium with the superior catalytic properties of platinum.
These anodes are engineered for demanding environments where high purity and precise electrochemical control are essential. Their operational characteristics make them suitable for a variety of niche applications.
The manufacturing precision and inherent material properties contribute to their reliability in critical processes, as detailed by leading manufacturers like China Titanium Factory.
The fabrication of platinized titanium anodes involves the meticulous application of a thin platinum coating onto a titanium substrate.
The primary manufacturing techniques include electroplating, where platinum is deposited from a solution, or thermal decomposition, which offers a more robust coating.
Critical aspects include rigorous titanium substrate preparation to ensure optimal adhesion strength and uniform coating thickness, typically ranging from 1 to 5 microns.
Quality control measures are crucial to prevent pinholes and ensure the integrity of the platinum layer, which directly impacts the anode's lifespan and performance.
Platinized titanium anodes exhibit excellent electrolytic stability and low overpotential for several key reactions, particularly oxygen evolution.
They are capable of sustaining high current density operations, often up to several kA/m², making them suitable for processes requiring intense electrochemical activity.
Their performance is stable in a broad range of acid solutions, including sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, where many other materials would rapidly corrode.
The electrode kinetics are highly favorable for precise control of plating and synthesis reactions, contributing to high reaction efficiency.
Platinized titanium anodes find extensive use in applications demanding high purity and minimal contamination.
Electroplating: Especially for precious metals (gold, rhodium) and high-quality decorative or functional coatings.
Water Treatment: In advanced oxidation processes for purifying drinking water and wastewater, particularly for disinfection through electrochlorination.
Electrosynthesis: For the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals where selectivity and absence of side reactions are critical.
Marine Cathodic Protection: Though less common than MMOs, they are used in specific high-performance or small-scale marine applications.
Medical Devices: For certain electrolytic processes in medical and laboratory settings due to their biocompatibility and inertness.
The inherent inertness of platinum ensures that Platinized Titanium anodes introduce minimal impurities into the electrolyte. This characteristic is indispensable for sensitive processes such as high-purity electroplating and specialized chemical synthesis, where even trace contamination can compromise product quality or reaction specificity.
The primary advantages of platinized titanium anodes include their exceptional corrosion resistance in acidic media and high conductivity, facilitating stable and efficient electrochemical reactions.
Their precision and reliability are highly valued in critical applications where performance cannot be compromised. The durability challenges often relate to the thinness of the platinum layer.
However, the significant platinum cost is a major limitation, making them economically prohibitive for large-scale, high-current applications.
They are also susceptible to anode poisoning by certain impurities in the electrolyte, which can reduce catalytic activity and shorten service life. For more information on anode solutions, consider consulting China Titanium Factory's experts.
Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) anodes, often referred to as Dimensionally Stable Anodes (DSAs), represent a revolutionary advancement in electrochemical technology.
These anodes are characterized by a layered structure where a thin, electrocatalytically active coating of noble metal oxides (e.g., ruthenium oxide, iridium oxide) is applied to a titanium substrate.
MMO anodes offer excellent electrocatalytic activity, low overpotential, and stability across a wide range of diverse electrolytes, making them highly versatile for numerous industrial processes.
The creation of an MMO coating typically involves applying a solution of metal salts (e.g., chlorides of ruthenium, iridium, titanium) onto a titanium substrate.
This is followed by repeated cycles of drying and high-temperature calcination, a process known as thermal decomposition. This method forms a robust, crystalline oxide layer.
The precise oxide composition is critical, as it dictates the anode's activity and selectivity for specific electrochemical reactions.
Factors such as coating thickness, porosity, and the ratio of active to inactive oxides significantly impact coating adhesion and overall anode performance.
MMO anodes are renowned for their superior electrocatalysis, particularly for chlorine and oxygen evolution reactions.
Their design minimizes energy losses, leading to high current efficiency and significantly lower low energy consumption compared to traditional graphite or lead dioxide anodes.
The reaction selectivity can be tailored by adjusting the oxide composition, optimizing them for specific processes like chlor-alkali production.
These anodes demonstrate excellent long-term stability and operational robustness under a wide range of current densities and electrolyte conditions.
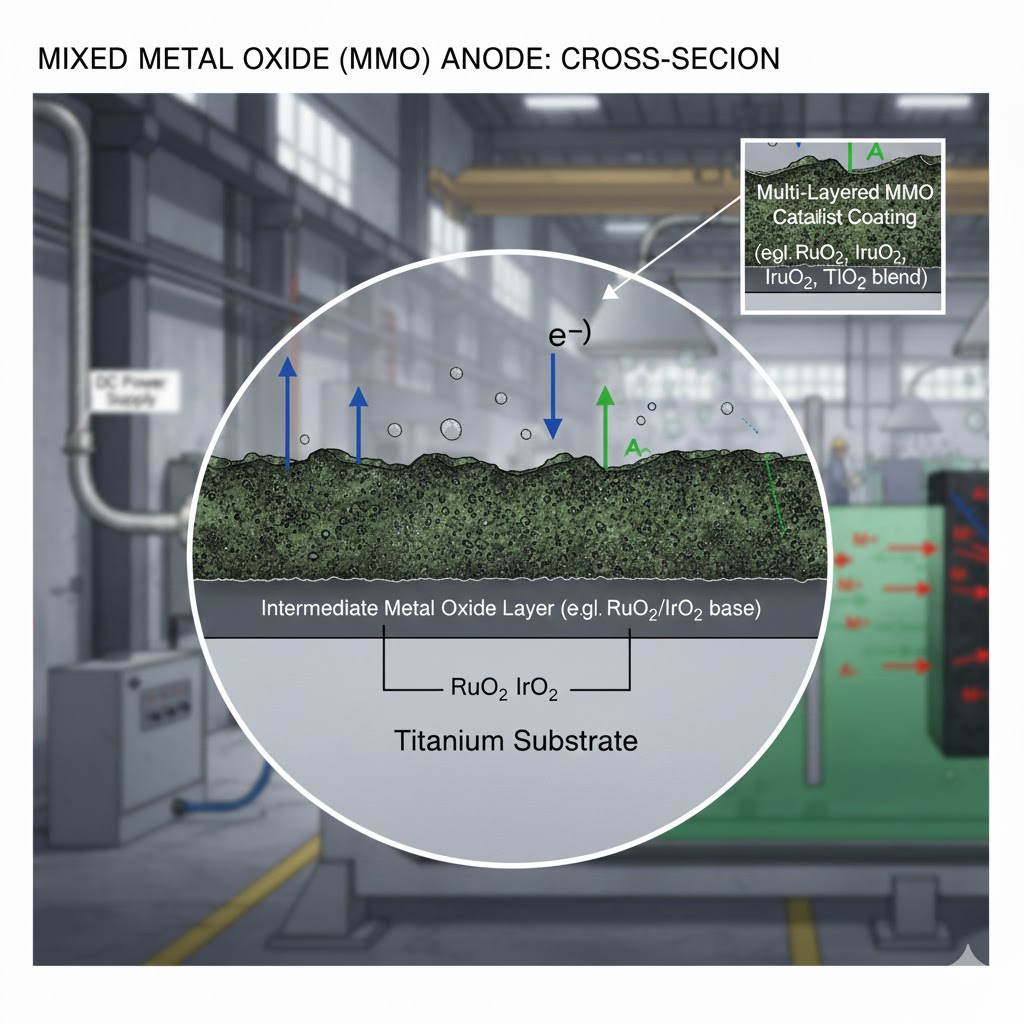
MMO anodes have fundamentally transformed several industries due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Chlor-Alkali Industry: They are the standard for chlorine and sodium hydroxide production, replacing mercury and diaphragm cells.
Water Treatment: Widely used in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment for disinfection and removal of organic pollutants.
Electrowinning: For the recovery of non-ferrous metals like copper, nickel, and cobalt from leach solutions.
Electrogalvanizing: In the steel industry for applying zinc coatings, offering better current distribution and coating quality.
Cathodic Protection: For protecting pipelines, storage tanks, and marine structures from corrosion.
The performance of MMO anodes can be highly optimized through customization of the oxide blend. Tailoring the ratio of ruthenium, iridium, and other metal oxides allows for fine-tuning the anode's electrocatalytic activity for specific reactions, maximizing efficiency and selectivity for a given application.
MMO anodes offer significant advantages, including their superior cost-effectiveness due to lower raw material costs compared to pure platinum, and their high efficiency in various electrochemical processes.
They are characterized by their robustness and long operational lifespan, making them a reliable choice for continuous industrial operations.
Practical considerations include careful selection of the oxide composition to match the electrolyte and reaction, as improper selection can lead to faster coating wear.
While highly versatile, there are application specific limitations, particularly in extremely aggressive environments or where ultra-high purity is paramount, which might favor platinized titanium.
The selection between MMO and Platinized Titanium anodes requires a rigorous, side-by-side analysis across critical engineering, electrochemical, and economic parameters.
Each anode type presents distinct strengths and weaknesses that must be weighed against specific project requirements and operational contexts.
Understanding these differences is crucial for optimal anode comparison and informed decision-making in electrochemical system design.
MMO anodes generally exhibit lower overvoltage comparison for chlorine evolution, making them highly efficient for chlor-alkali and hypochlorite generation.
Platinized titanium anodes, conversely, demonstrate excellent performance for oxygen evolution and in systems requiring minimal side reactions, such as certain electroplating baths.
The reaction kinetics and current distribution can vary significantly, influencing the suitability for different processes.
MMOs are often chosen for bulk chemical production, while Pt-Ti is preferred for precision applications. For detailed specifications, refer to technical data sheets available from reputable suppliers like China Titanium Factory.
Both anode types leverage titanium's inherent corrosion resistance as a substrate, but their active coatings behave differently.
Platinized titanium offers exceptional stability in highly acidic environments where many other materials would rapidly degrade, showing minimal anode degradation.
MMO anodes are robust across a broader range of pH values, including neutral and alkaline solutions, with specific formulations optimized for different aggressive conditions. Further insights on anode durability can be found in a detailed study on electrode materials by ScienceDirect.
The lifespan comparison often shows MMOs having a longer life in their optimized environments due to the robust nature of the oxide layer, while Pt-Ti's lifespan is highly dependent on coating thickness and prevention of mechanical abrasion or poisoning.
The capital expenditure for platinized titanium anodes is typically higher due to the significant platinum price.
MMO anodes, utilizing less expensive rare earth metals like ruthenium and iridium in thin layers, generally have a lower initial cost.
However, operating costs are influenced by energy efficiency. MMOs often boast lower energy consumption due to their superior electrocatalytic activity for specific reactions, leading to a better return on investment over time for large-scale operations.
A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis must consider both initial outlay and projected energy and maintenance costs over the anode's expected service life.
The environmental impact of anode production and use is an increasingly important consideration.
The material sourcing for both platinum and rare earth metals involves complex supply chains and environmental considerations during mining and refining.
MMO anodes, by enabling more energy-efficient processes and replacing less sustainable electrode materials, contribute to green electrochemistry.
Both types offer some recycling potential for their noble metal components, extending their sustainability profile.
The selection of the most appropriate anode type is a critical engineering decision that requires careful consideration of various factors.
This decision matrix provides a structured approach for anode selection guide, aligning anode characteristics with specific application suitability and operational goals.
| Characteristic | MMO Anodes | Platinized Titanium Anodes |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effectiveness, high efficiency for chlorine/oxygen evolution, versatility. | High purity, chemical inertness, precise control, excellent in acidic media. |
| Key Limitation | Coating wear, potential for poisoning by certain ions. | High initial cost, susceptibility to mechanical damage, poisoning. |
| Typical Applications | Chlor-alkali, water treatment, cathodic protection, electrowinning. | Precious metal electroplating, electrosynthesis, medical devices, high-purity water treatment. |
| Optimal Environment | Broad pH range (acidic to alkaline), high current density. | Highly acidic solutions, low current density precision processes. |
| Cost Profile | Lower initial cost, excellent long-term operational economics. | Higher initial cost, justified by specific performance requirements. |
Examining industrial applications through case studies provides concrete evidence of anode performance and suitability.
These examples highlight how different anode technologies are deployed to achieve specific electrochemical objectives, demonstrating their practical impact and operational benefits.
The insights derived from real-world scenarios are invaluable for engineers and decision-makers in optimizing their own electrochemical systems.
A prominent example of MMO anode success is their widespread adoption in the chlor-alkali industry, a cornerstone of chemical manufacturing.
In a large-scale plant, the transition from graphite electrodes to MMO anodes resulted in a significant reduction in cell voltage, leading to substantial energy savings of up to 20-30%.
This chlor-alkali case study demonstrated enhanced current efficiency for chlorine gas production and sodium hydroxide production, coupled with a dramatic decrease in electrode consumption.
The robust MMO anode performance translated into higher purity products and a more environmentally friendly process, validating their economic and operational superiority for this application.
Consider a specialized electroplating case study for high-end jewelry, where rhodium plating is critical for finish and durability.
Traditional lead anodes caused undesirable lead contamination in the rhodium bath and exhibited poor longevity. The implementation of platinized titanium anodes provided a stable, inert electrode surface.
This led to a consistent, high-quality surface finishing, eliminating bath contamination and significantly extending the bath's lifespan.
The Pt-Ti anode advantages in this context, despite higher initial cost, were justified by superior product quality, reduced waste, and long-term operational stability in precious metal plating.
Maximizing the lifespan extension and sustained performance of both MMO and Platinized Titanium anodes requires adherence to comprehensive anode maintenance and troubleshooting protocols.
Common operational issues such as electrode passivation, coating degradation, or mechanical damage can lead to performance degradation.
Regular inspection, monitoring of cell voltage, and electrolyte analysis are crucial for early detection of problems. Preventative measures include maintaining optimal operating parameters and preventing contact with corrosive agents not suited for the anode type. Further guidance on corrosion protection and maintenance can be found through resources like AMPP (formerly NACE International).
In some cases, recoating services can extend the anode's service life, offering a cost-effective alternative to full replacement.
The field of anode technology is continuously evolving, driven by the demand for increased energy efficiency and greater environmental responsibility.
Anode innovation focuses on developing novel materials and advanced coatings that offer superior electrocatalytic activity, enhanced durability, and reduced reliance on critical raw materials.
Emerging trends include the development of non-noble metal oxide anodes and composite materials designed for specific, challenging electrochemical environments.
These green technologies aim to further reduce the carbon footprint of industrial electrochemical processes, aligning with broader sustainable electrochemistry goals.

This section addresses common inquiries to assist engineers, researchers, and procurement managers in making informed decisions regarding anode selection and application. These anode FAQs cover critical aspects from cost to operational parameters.
For platinized titanium anodes, the predominant anode cost driver is the market platinum price, which is a high-value noble metal. The manufacturing cost associated with precision electroplating also contributes significantly.
For MMO anodes, while the active metals (e.g., ruthenium, iridium) are precious, they are used in much smaller quantities. Therefore, the manufacturing cost (thermal decomposition, quality control) and the volume of titanium substrate typically drive the overall cost, alongside ongoing energy cost from operation.
Temperature effects and pH stability are critical operating conditions. Elevated temperatures generally increase reaction rates but can also accelerate anode degradation and coating wear for both types.
Platinized titanium anodes are highly stable in strongly acidic conditions but can be vulnerable in highly alkaline environments at elevated temperatures. MMO anodes are designed with specific oxide formulations to optimize performance and corrosion rate across a broader pH range, with formulations tailored for acidic, neutral, or alkaline electrolytes. Selecting the correct MMO formulation for the specific pH is crucial for long lifespan.
Yes, both MMO and Platinized Titanium anodes can often undergo recoating services, which is a common practice to extend their service life extension.
This process typically involves cleaning the depleted anode substrate, stripping any remaining active coating, and then re-applying a new layer of the active material. The economic feasibility of recoating versus purchasing new anodes depends on the size, complexity, and initial condition of the anode, as well as the cost of the precious metals.
Reputable manufacturers, such as China Titanium Factory, often offer recoating programs.
For extremely corrosive environments, particularly those with strong acids and high temperatures, both anode types offer significant anode durability due to their titanium substrate.
Platinized Titanium anodes excel in highly concentrated acid resistance, especially sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, where the platinum layer provides exceptional chemical inertness.
MMO anodes, with their varied oxide compositions, can be specifically engineered for resistance to a wider array of aggressive chemicals and pH ranges, including strong alkaline resistance. The optimal choice depends on the specific chemical composition and operational conditions of the highly corrosive environment.
The strategic anode selection guide presented herein underscores the nuanced decision-making process required for optimal electrochemical optimization.
Both Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) and Platinized Titanium anodes offer distinct advantages tailored to specific industrial requirements. MMO anodes excel in large-scale, cost-efficient applications where versatility and robust performance across varied electrolytes are paramount.
Conversely, Platinized Titanium anodes are the preferred choice for high-purity, precision processes where chemical inertness and minimal contamination are critical, despite their higher initial investment.
Ultimately, a successful engineering decision hinges on a thorough evaluation of the specific electrochemical reaction, operational conditions, desired performance goals, and long-term cost efficiency. Engaging with expert suppliers, such as China Titanium Factory, can provide invaluable support in navigating these complex choices.